Deidre Seeto - Profile on Academia.edu (original) (raw)
Papers by Deidre Seeto
Online interactive learning tutorials: Addressing plagiarism, referencing and graphical presentation
... O'Donnell, VL, Tobbell, J., Lawthom, R., Zammit, M. (2009). Transition to postgraduate s... more ... O'Donnell, VL, Tobbell, J., Lawthom, R., Zammit, M. (2009). Transition to postgraduate study: Practice, participation and the widening participation agenda. Active Learning in Higher Education, 10, 26-40. Peterson, A., Neil, D. & Warren, C. (2009). ...
Interactive online learning
The emergence of mobile learning technologies and flexible delivery of information was the basis ... more The emergence of mobile learning technologies and flexible delivery of information was the basis for developing three online tutorials. The Academic Integrity tutorial addresses key aspects of why referencing is important, the meaning of collusion and the consequences of academic misconduct. The Referencing tutorial demonstrates the specifics of referencing using the Harvard and Chicago styles and the Graphic Presentation tutorial incorporates information on the nature of graphics and how they should be used in academic writing. The seamless design of the tutorials incorporates linear navigation, meaningful contexts, learning by doing and a thorough testing of concepts. The tutorials have improved students’ understanding of academic integrity, how to reference correctly, and present graphical information effectively
Ezine and iRadio as Knowledge Creation Metaphors for Scaffolding Learning in Physical and Virtual Learning Spaces
IGI Global eBooks, Jan 26, 2012
eZine and iRadio represent knowledge creation metaphors for scaffolding learning in a blended lea... more eZine and iRadio represent knowledge creation metaphors for scaffolding learning in a blended learning environment. Through independent and collaborative work online participating students experience a simulated virtual publishing space in their classrooms. This chapter is presented as an auto-ethnographic account highlighting the voices of the learning designer and the teacher. Using an iterative research design, evidence is provided for three iterations of each course. A collaborative approach to the development, planning, implementation, and evaluation of two tertiary music elective courses between lecturers, tutors, learning and technological designers is narrated. The student voice is embedded in the methodology, which involved an innovative approach that blends software development and pedagogy in iterations of software and experience design. The chapter describes how the teachers and learning designers translate these data into action and design. A blended learning space was incorporated within each of these elective music courses and the movement between these learning spaces is described and problematized. The research suggests that learning design, which provides real world examples and resources integrating authentic task design, can provide meaningful and engaging experiences for students. The dialogue between learning designers and teachers and iterative review of the learning process and student outcomes has engaged students meaningfully to achieve transferable learning outcomes.
With increasing emphasis from universities on workplace learning programs in which students under... more With increasing emphasis from universities on workplace learning programs in which students undertake industry placements as part of their degrees, there is a need for disciplines without a tradition of workplace learning to engage with potential industry partners. A key way to address this need is for universities to design web-based portals through which industry partners can engage with these programs. To build industry-university partnerships successfully, industry portals must: be easy for industry partners to find online, and facilitate efficient communication between industry partners and university workplace learning staff and students. Integration with university web systems and governance frameworks can lead to delays in the launch of a web-based industry partner portal. This paper focuses on the early stages of the design and implementation of Queensland University of Technology's Creative Industries Industry Portal as a case study of a new development in web-based university-industry engagement.
The role of the learning designer has expanded from the commonly known activities of an instructi... more The role of the learning designer has expanded from the commonly known activities of an instructional designer to incorporate a range of new roles, largely prompted by new technologies. In this paper, we articulate an approach that further extends the role of the learning designer to encompass evaluation and design-based research, in collaboration with the subject matter expert. Such collaboration is professionally enhancing for both parties, and adds to the sum of knowledge on the effective design of learning environments, by documenting and disseminating the learning design process.
Programs: Implementation and Design Issues Abstract: With increasing emphasis from universities o... more Programs: Implementation and Design Issues Abstract: With increasing emphasis from universities on workplace learning programs in which students undertake industry placements as part of their degrees, there is a need for disciplines without a tradition of workplace learning to engage with potential industry partners. A key way to address this need is for universities to design web-based portals through which industry partners can engage with these programs. To build industry-university partnerships successfully, industry portals must: be easy for industry partners to find online, and facilitate efficient communication between industry partners and university workplace learning staff and students. Integration with university web systems and governance frameworks can lead to delays in the launch of a web-based industry partner portal. This paper focuses on the early stages of the design and implementation of Queensland University of Technology’s Creative Industries Industry Portal as ...
Teaching and Learning Support Services
The role of the learning designer has expanded from the commonly known activities of an instructi... more The role of the learning designer has expanded from the commonly known activities of an instructional designer to incorporate a range of new roles, largely prompted by new technologies. In this paper, we articulate an approach that further extends the role of the learning designer to encompass evaluation and design-based research, in collaboration with the subject matter expert. Such collaboration is professionally enhancing for both parties, and adds to the sum of knowledge on the effective design of learning environments, by documenting and disseminating the learning design process.
Faculty Partnership Program Report S1 2015 Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences Establishing the Bachelor of Clinical Science iLearn Pattern
In complex organisations like universities, the ways in which faculties and disciplines integrate... more In complex organisations like universities, the ways in which faculties and disciplines integrate technology into their curricula is far from consistent, with the quality of the outcomes varying considerably. The reasons for this include the diverse learning and teaching needs in faculties, the variety of pedagogical traditions in disciplines, and also the lack of accessible learning design processes for academic and professional staff. This raises significant challenges but also offers opportunities to review existing practices to inform future developments using design patterns for learning with technology as a lever. The aim of this paper is to introduce a learning design process, namely the Design, Develop, Implement (DDI), which Macquarie University piloted to support curriculum development underpinned by design thinking principles. This paper openly addresses the challenges and successes of the DDI process for different disciplines using data gathered directly from the partici...
Concepts for the Modern Learning Environment
eZine and iRadio represent knowledge creation metaphors for scaffolding learning in a blended lea... more eZine and iRadio represent knowledge creation metaphors for scaffolding learning in a blended learning environment. Through independent and collaborative work online participating students experience a simulated virtual publishing space in their classrooms. This chapter is presented as an auto-ethnographic account highlighting the voices of the learning designer and the teacher. Using an iterative research design, evidence is provided for three iterations of each course. A collaborative approach to the development, planning, implementation, and evaluation of two tertiary music elective courses between lecturers, tutors, learning and technological designers is narrated. The student voice is embedded in the methodology, which involved an innovative approach that blends software development and pedagogy in iterations of software and experience design. The chapter describes how the teachers and learning designers translate these data into action and design. A blended learning space was ...
Online interactive learning tutorials: addressing plagiarism, referencing and graphical presentation
fyhe.com.au
... O'Donnell, VL, Tobbell, J., Lawthom, R., Zammit, M. (2009). Transition to postgraduate s... more ... O'Donnell, VL, Tobbell, J., Lawthom, R., Zammit, M. (2009). Transition to postgraduate study: Practice, participation and the widening participation agenda. Active Learning in Higher Education, 10, 26-40. Peterson, A., Neil, D. & Warren, C. (2009). ...
Who's learning, 2006
The role of the learning designer has expanded from the commonly known activities of an instructi... more The role of the learning designer has expanded from the commonly known activities of an instructional designer to incorporate a range of new roles, largely prompted by new technologies. In this paper, we articulate an approach that further extends the role of the ...
Are students really that different from their lecturers? A case study in perceptions of emerging learning technologies in higher education
With increasing emphasis from universities on workplace learning programs in which students under... more With increasing emphasis from universities on workplace learning programs in which students undertake industry placements as part of their degrees, there is a need for disciplines without a tradition of workplace learning to engage with potential industry partners. A key way to address this need is for universities to design web-based portals through which industry partners can engage with these programs. To build industry-university partnerships successfully, industry portals must: be easy for industry partners to find online, and facilitate efficient communication between industry partners and university workplace learning staff and students. Integration with university web systems and governance frameworks can lead to delays in the launch of a web-based industry partner portal. This paper focuses on the early stages of the design and implementation of Queensland University of Technology's Creative Industries Industry Portal as a case study of a new development in web-based university-industry engagement.
Online interactive learning tutorials: Addressing plagiarism, referencing and graphical presentation
... O'Donnell, VL, Tobbell, J., Lawthom, R., Zammit, M. (2009). Transition to postgraduate s... more ... O'Donnell, VL, Tobbell, J., Lawthom, R., Zammit, M. (2009). Transition to postgraduate study: Practice, participation and the widening participation agenda. Active Learning in Higher Education, 10, 26-40. Peterson, A., Neil, D. & Warren, C. (2009). ...
Interactive online learning
The emergence of mobile learning technologies and flexible delivery of information was the basis ... more The emergence of mobile learning technologies and flexible delivery of information was the basis for developing three online tutorials. The Academic Integrity tutorial addresses key aspects of why referencing is important, the meaning of collusion and the consequences of academic misconduct. The Referencing tutorial demonstrates the specifics of referencing using the Harvard and Chicago styles and the Graphic Presentation tutorial incorporates information on the nature of graphics and how they should be used in academic writing. The seamless design of the tutorials incorporates linear navigation, meaningful contexts, learning by doing and a thorough testing of concepts. The tutorials have improved students’ understanding of academic integrity, how to reference correctly, and present graphical information effectively
Ezine and iRadio as Knowledge Creation Metaphors for Scaffolding Learning in Physical and Virtual Learning Spaces
IGI Global eBooks, Jan 26, 2012
eZine and iRadio represent knowledge creation metaphors for scaffolding learning in a blended lea... more eZine and iRadio represent knowledge creation metaphors for scaffolding learning in a blended learning environment. Through independent and collaborative work online participating students experience a simulated virtual publishing space in their classrooms. This chapter is presented as an auto-ethnographic account highlighting the voices of the learning designer and the teacher. Using an iterative research design, evidence is provided for three iterations of each course. A collaborative approach to the development, planning, implementation, and evaluation of two tertiary music elective courses between lecturers, tutors, learning and technological designers is narrated. The student voice is embedded in the methodology, which involved an innovative approach that blends software development and pedagogy in iterations of software and experience design. The chapter describes how the teachers and learning designers translate these data into action and design. A blended learning space was incorporated within each of these elective music courses and the movement between these learning spaces is described and problematized. The research suggests that learning design, which provides real world examples and resources integrating authentic task design, can provide meaningful and engaging experiences for students. The dialogue between learning designers and teachers and iterative review of the learning process and student outcomes has engaged students meaningfully to achieve transferable learning outcomes.
With increasing emphasis from universities on workplace learning programs in which students under... more With increasing emphasis from universities on workplace learning programs in which students undertake industry placements as part of their degrees, there is a need for disciplines without a tradition of workplace learning to engage with potential industry partners. A key way to address this need is for universities to design web-based portals through which industry partners can engage with these programs. To build industry-university partnerships successfully, industry portals must: be easy for industry partners to find online, and facilitate efficient communication between industry partners and university workplace learning staff and students. Integration with university web systems and governance frameworks can lead to delays in the launch of a web-based industry partner portal. This paper focuses on the early stages of the design and implementation of Queensland University of Technology's Creative Industries Industry Portal as a case study of a new development in web-based university-industry engagement.
The role of the learning designer has expanded from the commonly known activities of an instructi... more The role of the learning designer has expanded from the commonly known activities of an instructional designer to incorporate a range of new roles, largely prompted by new technologies. In this paper, we articulate an approach that further extends the role of the learning designer to encompass evaluation and design-based research, in collaboration with the subject matter expert. Such collaboration is professionally enhancing for both parties, and adds to the sum of knowledge on the effective design of learning environments, by documenting and disseminating the learning design process.
Programs: Implementation and Design Issues Abstract: With increasing emphasis from universities o... more Programs: Implementation and Design Issues Abstract: With increasing emphasis from universities on workplace learning programs in which students undertake industry placements as part of their degrees, there is a need for disciplines without a tradition of workplace learning to engage with potential industry partners. A key way to address this need is for universities to design web-based portals through which industry partners can engage with these programs. To build industry-university partnerships successfully, industry portals must: be easy for industry partners to find online, and facilitate efficient communication between industry partners and university workplace learning staff and students. Integration with university web systems and governance frameworks can lead to delays in the launch of a web-based industry partner portal. This paper focuses on the early stages of the design and implementation of Queensland University of Technology’s Creative Industries Industry Portal as ...
Teaching and Learning Support Services
The role of the learning designer has expanded from the commonly known activities of an instructi... more The role of the learning designer has expanded from the commonly known activities of an instructional designer to incorporate a range of new roles, largely prompted by new technologies. In this paper, we articulate an approach that further extends the role of the learning designer to encompass evaluation and design-based research, in collaboration with the subject matter expert. Such collaboration is professionally enhancing for both parties, and adds to the sum of knowledge on the effective design of learning environments, by documenting and disseminating the learning design process.
Faculty Partnership Program Report S1 2015 Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences Establishing the Bachelor of Clinical Science iLearn Pattern
In complex organisations like universities, the ways in which faculties and disciplines integrate... more In complex organisations like universities, the ways in which faculties and disciplines integrate technology into their curricula is far from consistent, with the quality of the outcomes varying considerably. The reasons for this include the diverse learning and teaching needs in faculties, the variety of pedagogical traditions in disciplines, and also the lack of accessible learning design processes for academic and professional staff. This raises significant challenges but also offers opportunities to review existing practices to inform future developments using design patterns for learning with technology as a lever. The aim of this paper is to introduce a learning design process, namely the Design, Develop, Implement (DDI), which Macquarie University piloted to support curriculum development underpinned by design thinking principles. This paper openly addresses the challenges and successes of the DDI process for different disciplines using data gathered directly from the partici...
Concepts for the Modern Learning Environment
eZine and iRadio represent knowledge creation metaphors for scaffolding learning in a blended lea... more eZine and iRadio represent knowledge creation metaphors for scaffolding learning in a blended learning environment. Through independent and collaborative work online participating students experience a simulated virtual publishing space in their classrooms. This chapter is presented as an auto-ethnographic account highlighting the voices of the learning designer and the teacher. Using an iterative research design, evidence is provided for three iterations of each course. A collaborative approach to the development, planning, implementation, and evaluation of two tertiary music elective courses between lecturers, tutors, learning and technological designers is narrated. The student voice is embedded in the methodology, which involved an innovative approach that blends software development and pedagogy in iterations of software and experience design. The chapter describes how the teachers and learning designers translate these data into action and design. A blended learning space was ...
Online interactive learning tutorials: addressing plagiarism, referencing and graphical presentation
fyhe.com.au
... O'Donnell, VL, Tobbell, J., Lawthom, R., Zammit, M. (2009). Transition to postgraduate s... more ... O'Donnell, VL, Tobbell, J., Lawthom, R., Zammit, M. (2009). Transition to postgraduate study: Practice, participation and the widening participation agenda. Active Learning in Higher Education, 10, 26-40. Peterson, A., Neil, D. & Warren, C. (2009). ...
Who's learning, 2006
The role of the learning designer has expanded from the commonly known activities of an instructi... more The role of the learning designer has expanded from the commonly known activities of an instructional designer to incorporate a range of new roles, largely prompted by new technologies. In this paper, we articulate an approach that further extends the role of the ...
Are students really that different from their lecturers? A case study in perceptions of emerging learning technologies in higher education
With increasing emphasis from universities on workplace learning programs in which students under... more With increasing emphasis from universities on workplace learning programs in which students undertake industry placements as part of their degrees, there is a need for disciplines without a tradition of workplace learning to engage with potential industry partners. A key way to address this need is for universities to design web-based portals through which industry partners can engage with these programs. To build industry-university partnerships successfully, industry portals must: be easy for industry partners to find online, and facilitate efficient communication between industry partners and university workplace learning staff and students. Integration with university web systems and governance frameworks can lead to delays in the launch of a web-based industry partner portal. This paper focuses on the early stages of the design and implementation of Queensland University of Technology's Creative Industries Industry Portal as a case study of a new development in web-based university-industry engagement.




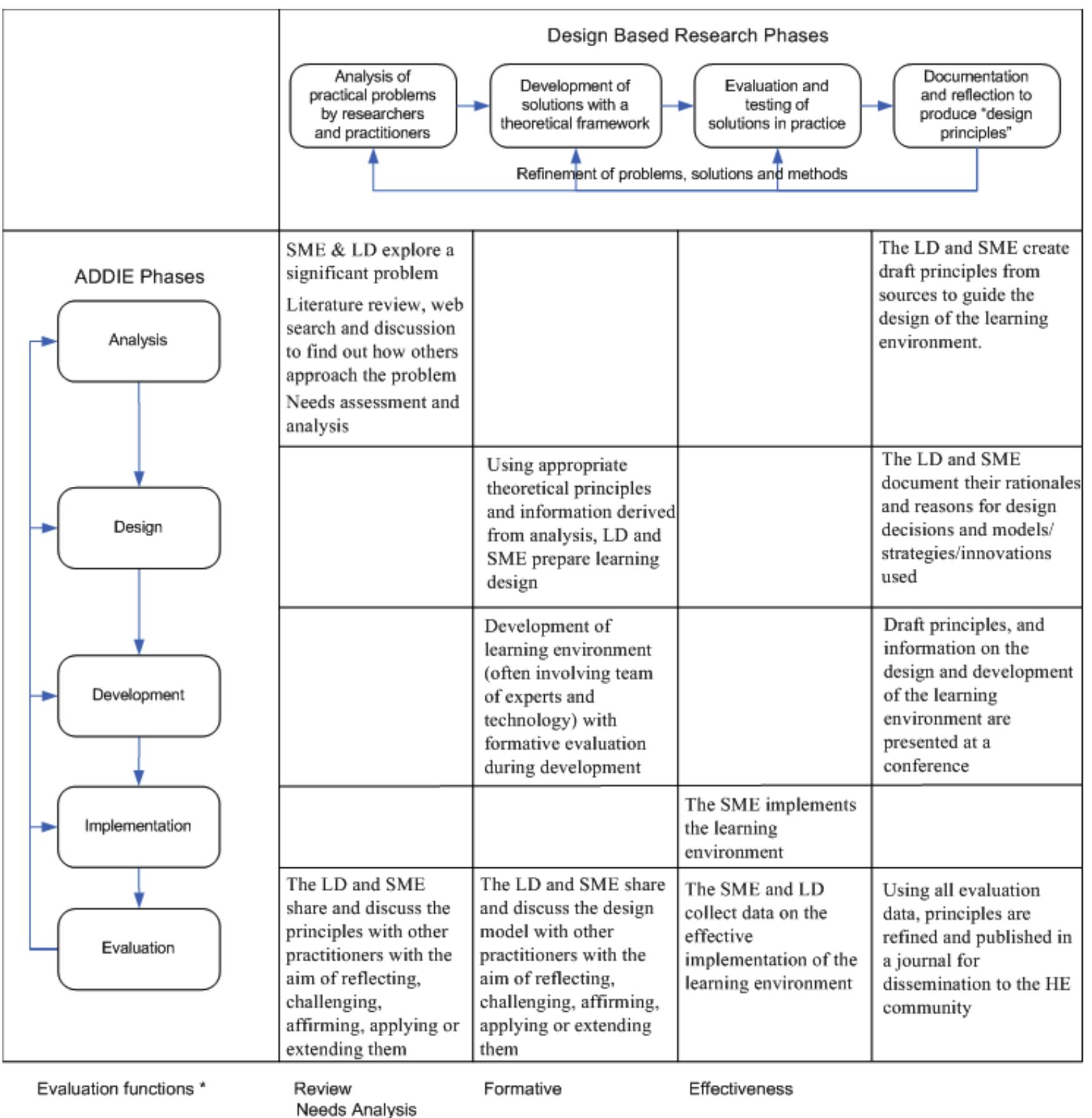
![Figure 1. Creative Industries Workplace Learning Industry Partners Portal: Integration of Institutional Systems [1] WOr For these reasons, design decisions were made to house the QUT CI Industry Partner Portal on the Faculty’s web- based corporate homepage, with all program information readily available to potential and existing industry partners. The final platform architecture decision for the QUT Portal comprised Blackboard, a web-based portal. and third-party job-posting and employment software (Fig. 1). Affordances of Blackboard for enrolled students include efficient access to program information and assignment submission. However, the LMS authentication process does not readily support external access from multiple industry partners. A web portal linked to the Faculty’s site addresses th is need and affords opportunities for industry partners to seek information about the kplace learning program. Hosting the Portal on the Faculty’s home page brings with it the added benefits of a URL which is easy for industry partners to remember. Moreover, industry partners could use search engines to find the Portal, which would not be possible if the Portal existed behind university firewalls. The Portal link will be clearly named “Industry Portal for Creative Industries Workplace Learning” so that industry partners can locate it easi and site wor placement positions listed y on the homepage. T kplace learning Black he Industry Portal will link to the existing QUT Careers and Employment jobs-posting employment site through which industry partners can enter placement position descriptions. This single sign-on will allow CI workplace learning academic staff to access and approve placement descriptions. A link on the board site will allow enrolled students access to the approved workplace learning on the Careers and Employment site. A third-party job-posting and employment application linked to the Portal is efficient in terms of time and development that workplace learning program designers will save in building a dynamic interface and database to collect and make available placement position descriptions.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/107171408/figure_001.jpg) ](
](