H. Merdjan - Academia.edu (original) (raw)
Papers by H. Merdjan
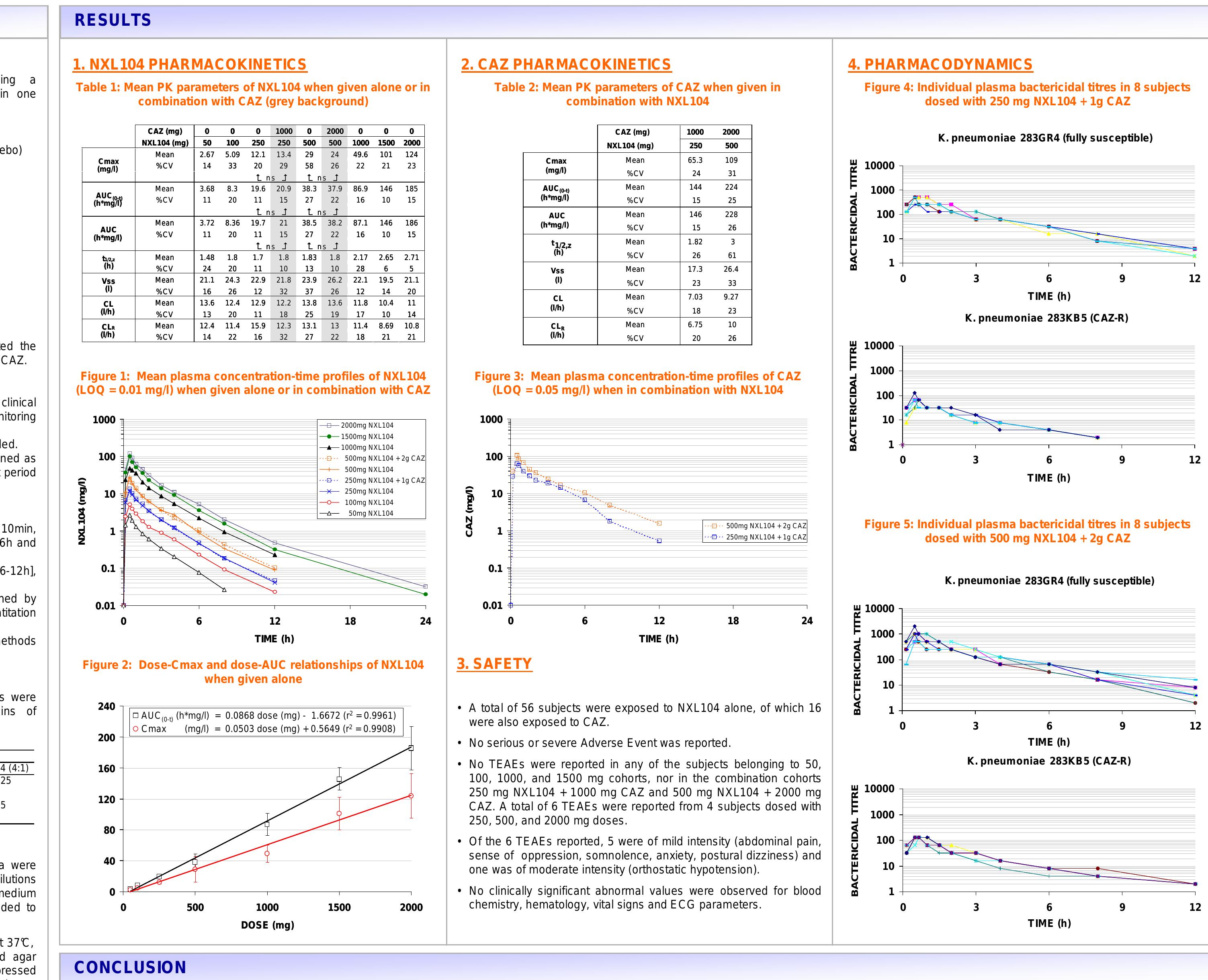
NXL104 administered alone (up to 2000 mg) or in combination with CAZ was safe and well tolerated,... more NXL104 administered alone (up to 2000 mg) or in combination with CAZ was safe and well tolerated, both systemically and locally.
[Pharmacokinetics of ornidazole in the patient with renal failure; influence of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis]
Presse médicale (Paris, France : 1983), Jan 14, 1983
Prediction of Hemodynamic Responses in Hypertensive and Elderly Subjects from Healthy Volunteer Data
Drugs and the Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2002
Determination of ivabradine and its N-demethylated metabolite in human plasma and urine, and in rat and dog plasma by a validated high-performance liquid chromatographic method with fluorescence detection
Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1998
A sensitive and selective high-performance liquid chromatographic method with native detection of... more A sensitive and selective high-performance liquid chromatographic method with native detection of fluorescence was developed and validated for the quantitation of ivabradine and its N-demethylated metabolite in plasma (rat, dog, human) and human urine. The procedure involves the use of an analogue as internal standard, solid-phase extraction on cyano cartridges, separation on a Nova-Pak C8 column and fluorescence detection. Calibration curves are linear in the concentration ranges from 0.5 to 100 ng/ml in plasma and 2.0 to 500 ng/ml in urine with a limit of quantitation set at 0.5 and 2.0 ng/ml in plasma and urine, respectively. The analysis of plasma and urine samples (spiked with the analytes at low, medium and high concentrations of the calibration range) demonstrates that both analytes can be measured with precision and accuracy within acceptable limits. Quality controls spiked with analyte concentrations up to 10000 ng/ml can also be analysed with excellent precision and accuracy after dilution of the samples. The parent drug and its metabolite are stable in plasma and urine after short-term storage (24 h at room temperature and after three freeze-thaw cycles) as well as after long-term storage at -20 degrees C (at least 6 months in animal plasma and 12 months in human plasma and urine). The method has been used to quantify both compounds in plasma and urine samples from clinical and non-clinical studies with ivabradine.
Rapid determination of pyrazinamide in biological fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography
Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1985
Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1985
Alminoprofen is a derivative of propionic acid (2-methylallylaminophenyl propionic acid) with the... more Alminoprofen is a derivative of propionic acid (2-methylallylaminophenyl propionic acid) with the following molecular structure:
Moxalactam kinetics during chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 1983
Moxalactam kinetics in renal failure were followed in eight patients undergoing chronic ambulator... more Moxalactam kinetics in renal failure were followed in eight patients undergoing chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) after a single 1-gm IV infusion. Elimination t 1/2 was 16.7 +/- 2.1 hr, with an apparent volume of distribution of 0.21 +/- 0.01 l/kg and plasma clearance of 10.6 +/- 2 ml/min. In 24 hr, 17.4 +/- 3.1% of the dose was present in the dialysis fluids, and 14.6 +/- 5.7% was excreted in the urine. Renal and peritoneal clearance values were thus 2.3 +/- 1.1 and 2.7 +/- 0.5 ml/min. Peritoneal concentrations were high (22.7 +/- 2.2 micrograms/ml). A recommended dosage schedule is proposed on the basis of moxalactam kinetics during CAPD.
Measurement of ornidazole by high-performance liquid chromatography
Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1983
Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1986
Clofibrate IS the ethyl ester of p-chlorophenoxylsobutyrlc acid, the actlve metabohte of which IS... more Clofibrate IS the ethyl ester of p-chlorophenoxylsobutyrlc acid, the actlve metabohte of which IS clofrbnc acid, and 1s used m the treatment of hyperhpoprotemaemla [l] Determmatlon of cloflbrate levels m plasma by hlgh-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has been reported by BJOrMOn et al and Robmson et al. Other authors have reported an HPLC method or a radlolsotoplc method measuring the glucuromde conJugated in plasma and urme [4,53
A mathematical model for dynamics of cardiovascular drug action: Application to intravenous dihydropyridines in healthy volunteers
Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics, 1993
A physiologically based mathematical model was built to describe the pharmacodynamic effects in r... more A physiologically based mathematical model was built to describe the pharmacodynamic effects in response to the administration of intravenous (iv) dihydropyridine drugs in healthy volunteers. This model incorporates a limited number of hemodynamic variables, namely, mean arterial blood pressure (MAP), cardiac output (CO) or heart rate (HR), stroke volume (SV), and total peripheral resistance (TPR), into a closed-loop system supposed to represent essential features of the cardiovascular regulation. We also defined an additional auxiliary control variable (U) which is thought to represent primarily the role of the baroreceptor reflex. It was assumed that the variable U was related to MAP changes through both deviation- and rate-sensitive mechanisms. Other model parameters are the baseline levels for MAP, CO (or HR), and TPR, as well as time constants to account for further temporal aspects of the regulation. Finally, TPR was assumed to be linked to the plasma concentrations of dihydropyridine drugs via a conventional pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) model, relying upon an effect compartment and a linear, hyperbolic, or sigmoidal relationship between the reduction in TPR and the drug concentrations at the effect site. The model characteristics were explored by studying the influence of various parameters, including baseline levels and deviation- and rate-sensitive control parameters, on the hemodynamic responses to a fictive constant rate i.v. infusion of a vasodilator drug. Attempts were also made to mimic literature data with nifedipine, following i.v. administration under both constant and exponentially decreasing infusion rates. The applicability of the model was demonstrated by fitting hemodynamic data following i.v. infusion of nicardipine to healthy volunteers, under experimental conditions similar to those described above for nifedipine. The effect model for the action of nicardipine on TPR, combined with the physiological model including a feedback control loop, allowed an adequate quantitative description of time profiles for both cardiac output and mean arterial pressure. The suggested model is a useful tool for integrated data analysis of hemodynamic responses to vasodilator drugs in healthy volunteers. Computer simulations suggest that a graded variation of a few model parameters--including baseline levels of TPR and MAP and the deviation-sensitive parameter of the arterial pressure control--would also be able to account for the pattern of hemodynamic response observed in hypertensive patients, which is qualitatively different to that seen in normotensive subjects. Extrapolation of drug response from the healthy volunteer to the hypertensive patient is allowed by our model. Its usefulness for an early evaluation of drug efficacy during drug development is under current investigation.
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 2007
Tianeptine and its main metabolite. Disposition in chronic renal failure and haemodialysis
Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology, 1990
The disposition of the antidepressant tianeptine and its MC5 metabolite (pentanoic acid analogue ... more The disposition of the antidepressant tianeptine and its MC5 metabolite (pentanoic acid analogue of tianeptine) was studied following a single 12.5 mg oral dose of tianeptine sodium salt in 20 patients with chronic renal failure. In 12 patients (group I) having a creatinine clearance of less than 19 ml.min-1 the pharmacokinetics parameters for tianeptine and MC5 metabolite were determined and compared with those obtained in a matched control group (group II). The other 8 patients (group III) were functionally anephric and were studied during 1 dialysis to assess the haemodialysis clearances of tianeptine and MC5 metabolite. The comparison between groups I and II showed that renal failure did not appear to affect the disposition of parent tianeptine. However, the MC5 metabolite terminal half-life was found to be increased in renal patients compared to controls (14.2 +/- 9.3 h vs 4.9 +/- 1.7 h). Due to a large interindividual variability the difference did not reach a significant level (P = 0.054). According to the antidepressant activity of the MC5 metabolite in pharmacological tests, the sustained rise in its plasma level suggests that a reduced daily dose should be administered and 12.5 mg of tianeptine should be given twice daily to patients with chronic renal failure. In patients from group III elimination of the compounds by haemodialysis was found to be low. The dialysis clearances were 3.9 +/- 9.9 ml.min-1 and 19.2 +/- 8.6 ml.min-1 for tianeptine and its MC5 metabolite respectively. This low dialysability has 2 clinical implications. Firstly, patients currently undergoing haemodialysis and treated by tianeptine could be given the drug without taking dialysis into account. Secondly, haemodialysis does not appear to be an effective method for tianeptine elimination in cases of overdosage.
Acute effects of clometacin on renal prostaglandin biosynthesis in healthy subjects
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 1986
In 6 healthy subjects the effect of clometacin on renal function, sodium and water excretion, pla... more In 6 healthy subjects the effect of clometacin on renal function, sodium and water excretion, plasma renin activity and urinary excretion of prostaglandins has been studied. After four days of treatment with clometacin, the excretion of urinary prostaglandins E2, F2 alpha and 6 keto F1 alpha and thromboxane B2 were reduced by 61.2, 41.2, 59 and 42%, respectively. 62% reduction in plasma renin activity was also observed. There was no significant change in mean blood pressure, heart rate, body weight, creatinine clearance or urinary excretion of sodium. It is concluded that clometacin is an efficient cyclooxygenase inhibitor in healthy individuals with a normal sodium intake, and that caution is required when giving clometacin to patients at risk of developing renal failure during treatment with a cyclooxygenase inhibitor.
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 1985
1 The pharmacokinetics of ornidazole (Tiberal®) was studied after intravenous administration of a... more 1 The pharmacokinetics of ornidazole (Tiberal®) was studied after intravenous administration of a single 500 mg dose in eight patients with advanced chronic renal failure (ACRF) (creatinine clearance 2-16 ml/min), in seven patients treated by haemodialysis (residual renal creatinine clearance 0-5 ml/min) and in five patients treated by continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) (residual renal creatinine clearance 0-6 ml/min). 2 In ACRF patients, the half-life of ornidazole was 10.8 ± 1.4 h, the total plasma clearance 46.3 ± 2.3 ml/min and the volume of distribution 0.73 ± 0.06 1/kg. 3 During haemodialysis, ornidazole was partly removed: the dialyser extraction ratio was 42 ± 5% and the dialysis clearance 64 ± 7 ml/min. 4 During CAPD, peritoneal excretion was low: the dialysis clearance was 3.0 ± 0.4 ml/ min and in 48 h 6.0 ± 1.1% of the administered dose was found in the peritoneal fluids. In these patients, the half-life of ornidazole was 11.8 ± 0.8 h and total plasma clearance was 48.3 ± 5.5 ml/min, values which were close to those determined in non dialysed patients. 5 In patients with end-stage renal disease, the half-life of ornidazole is comparable to that of subjects with normal renal function. This is due to the predominantly extra-renal elimination of the drug. Therefore, there is no need to modify the usual dosage of ornidazole for these patients. Because of the large elimination of the drug during haemodialysis it is necessary to administer the drug after the dialysis session.
The Activity of Ceftazidime and Avibactam Against -Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in a Hollow-Fiber Pharmacodynamic Model
Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2014
Avibactam is a novel non-β-lactam β-lactamase inhibitor that is currently undergoing phase 3 clin... more Avibactam is a novel non-β-lactam β-lactamase inhibitor that is currently undergoing phase 3 clinical trials in combination with ceftazidime. Ceftazidime is hydrolyzed by a broad range of β-lactamases, but avibactam is able to inhibit the majority of these enzymes. The studies described here attempt to provide insight into the amount of avibactam required to suppress bacterial growth in an environment where the concentrations of both agents are varying as they would when administered to humans. Following the simulation of a single intravenous dose of the drug, ceftazidime alone had no effect on any test organism, but a ceftazidime-avibactam combination resulted in rapid killing of all of the strains, with growth suppressed for the 8 h of the study. For seven of eight strains, this was achieved with a 1-g-250-mg profile, but a 2-g-500-mg profile was necessary to completely suppress a high-level-AmpC-producing isolate. When ceftazidime was infused continuously for 24 h with a single bolus dose of avibactam, rapid killing of all of the strains was again observed, with growth suppressed for 10 to >24 h. Regrowth appeared to commence once the avibactam concentration dropped below a critical concentration of approximately 0.3 μg/ml. In a third series of studies, ceftazidime was administered every 8 h for 24 h with avibactam administered at fixed concentrations for short periods during each ceftazidime dose profile. Simulating a 1-g dose of ceftazidime, an avibactam pulse of >0.25 and <0.5 μg/ml was required to suppress growth for 24 h.
Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1986
A specific and sensitive high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the measurement of su... more A specific and sensitive high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the measurement of sulpiride in plasma is described. The internal standard used was veralipride, a structurally related substituted benzamide. A fluorescence detector with maximum excitation at 300 nm and maximum emission at 365 nm was used for quantitation. After an alkaline extraction procedure, the benzamides were separated on a B-pm ODS column using a large organic counter ion in the mobile phase. The detector response was linear from 10 to 1000 ng/ml and the detection limit was 10 ng/ml, which is sensitive enough for pharmacokinetic studies. The suitability of the method for the analysis of biological samples was tested by studying the variation with time of plasma concentrations of sulpiride in normal human volunteers after a single therapeutic 200-mg oral dose of three different formulations of sulpiride. 0378-4347/86/$03.50 0 1986 Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.
NXL104 administered alone (up to 2000 mg) or in combination with CAZ was safe and well tolerated,... more NXL104 administered alone (up to 2000 mg) or in combination with CAZ was safe and well tolerated, both systemically and locally.
[Pharmacokinetics of ornidazole in the patient with renal failure; influence of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis]
Presse médicale (Paris, France : 1983), Jan 14, 1983
Prediction of Hemodynamic Responses in Hypertensive and Elderly Subjects from Healthy Volunteer Data
Drugs and the Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2002
Determination of ivabradine and its N-demethylated metabolite in human plasma and urine, and in rat and dog plasma by a validated high-performance liquid chromatographic method with fluorescence detection
Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1998
A sensitive and selective high-performance liquid chromatographic method with native detection of... more A sensitive and selective high-performance liquid chromatographic method with native detection of fluorescence was developed and validated for the quantitation of ivabradine and its N-demethylated metabolite in plasma (rat, dog, human) and human urine. The procedure involves the use of an analogue as internal standard, solid-phase extraction on cyano cartridges, separation on a Nova-Pak C8 column and fluorescence detection. Calibration curves are linear in the concentration ranges from 0.5 to 100 ng/ml in plasma and 2.0 to 500 ng/ml in urine with a limit of quantitation set at 0.5 and 2.0 ng/ml in plasma and urine, respectively. The analysis of plasma and urine samples (spiked with the analytes at low, medium and high concentrations of the calibration range) demonstrates that both analytes can be measured with precision and accuracy within acceptable limits. Quality controls spiked with analyte concentrations up to 10000 ng/ml can also be analysed with excellent precision and accuracy after dilution of the samples. The parent drug and its metabolite are stable in plasma and urine after short-term storage (24 h at room temperature and after three freeze-thaw cycles) as well as after long-term storage at -20 degrees C (at least 6 months in animal plasma and 12 months in human plasma and urine). The method has been used to quantify both compounds in plasma and urine samples from clinical and non-clinical studies with ivabradine.
Rapid determination of pyrazinamide in biological fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography
Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1985
Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1985
Alminoprofen is a derivative of propionic acid (2-methylallylaminophenyl propionic acid) with the... more Alminoprofen is a derivative of propionic acid (2-methylallylaminophenyl propionic acid) with the following molecular structure:
Moxalactam kinetics during chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 1983
Moxalactam kinetics in renal failure were followed in eight patients undergoing chronic ambulator... more Moxalactam kinetics in renal failure were followed in eight patients undergoing chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) after a single 1-gm IV infusion. Elimination t 1/2 was 16.7 +/- 2.1 hr, with an apparent volume of distribution of 0.21 +/- 0.01 l/kg and plasma clearance of 10.6 +/- 2 ml/min. In 24 hr, 17.4 +/- 3.1% of the dose was present in the dialysis fluids, and 14.6 +/- 5.7% was excreted in the urine. Renal and peritoneal clearance values were thus 2.3 +/- 1.1 and 2.7 +/- 0.5 ml/min. Peritoneal concentrations were high (22.7 +/- 2.2 micrograms/ml). A recommended dosage schedule is proposed on the basis of moxalactam kinetics during CAPD.
Measurement of ornidazole by high-performance liquid chromatography
Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1983
Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1986
Clofibrate IS the ethyl ester of p-chlorophenoxylsobutyrlc acid, the actlve metabohte of which IS... more Clofibrate IS the ethyl ester of p-chlorophenoxylsobutyrlc acid, the actlve metabohte of which IS clofrbnc acid, and 1s used m the treatment of hyperhpoprotemaemla [l] Determmatlon of cloflbrate levels m plasma by hlgh-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has been reported by BJOrMOn et al and Robmson et al. Other authors have reported an HPLC method or a radlolsotoplc method measuring the glucuromde conJugated in plasma and urme [4,53
A mathematical model for dynamics of cardiovascular drug action: Application to intravenous dihydropyridines in healthy volunteers
Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics, 1993
A physiologically based mathematical model was built to describe the pharmacodynamic effects in r... more A physiologically based mathematical model was built to describe the pharmacodynamic effects in response to the administration of intravenous (iv) dihydropyridine drugs in healthy volunteers. This model incorporates a limited number of hemodynamic variables, namely, mean arterial blood pressure (MAP), cardiac output (CO) or heart rate (HR), stroke volume (SV), and total peripheral resistance (TPR), into a closed-loop system supposed to represent essential features of the cardiovascular regulation. We also defined an additional auxiliary control variable (U) which is thought to represent primarily the role of the baroreceptor reflex. It was assumed that the variable U was related to MAP changes through both deviation- and rate-sensitive mechanisms. Other model parameters are the baseline levels for MAP, CO (or HR), and TPR, as well as time constants to account for further temporal aspects of the regulation. Finally, TPR was assumed to be linked to the plasma concentrations of dihydropyridine drugs via a conventional pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) model, relying upon an effect compartment and a linear, hyperbolic, or sigmoidal relationship between the reduction in TPR and the drug concentrations at the effect site. The model characteristics were explored by studying the influence of various parameters, including baseline levels and deviation- and rate-sensitive control parameters, on the hemodynamic responses to a fictive constant rate i.v. infusion of a vasodilator drug. Attempts were also made to mimic literature data with nifedipine, following i.v. administration under both constant and exponentially decreasing infusion rates. The applicability of the model was demonstrated by fitting hemodynamic data following i.v. infusion of nicardipine to healthy volunteers, under experimental conditions similar to those described above for nifedipine. The effect model for the action of nicardipine on TPR, combined with the physiological model including a feedback control loop, allowed an adequate quantitative description of time profiles for both cardiac output and mean arterial pressure. The suggested model is a useful tool for integrated data analysis of hemodynamic responses to vasodilator drugs in healthy volunteers. Computer simulations suggest that a graded variation of a few model parameters--including baseline levels of TPR and MAP and the deviation-sensitive parameter of the arterial pressure control--would also be able to account for the pattern of hemodynamic response observed in hypertensive patients, which is qualitatively different to that seen in normotensive subjects. Extrapolation of drug response from the healthy volunteer to the hypertensive patient is allowed by our model. Its usefulness for an early evaluation of drug efficacy during drug development is under current investigation.
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 2007
Tianeptine and its main metabolite. Disposition in chronic renal failure and haemodialysis
Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology, 1990
The disposition of the antidepressant tianeptine and its MC5 metabolite (pentanoic acid analogue ... more The disposition of the antidepressant tianeptine and its MC5 metabolite (pentanoic acid analogue of tianeptine) was studied following a single 12.5 mg oral dose of tianeptine sodium salt in 20 patients with chronic renal failure. In 12 patients (group I) having a creatinine clearance of less than 19 ml.min-1 the pharmacokinetics parameters for tianeptine and MC5 metabolite were determined and compared with those obtained in a matched control group (group II). The other 8 patients (group III) were functionally anephric and were studied during 1 dialysis to assess the haemodialysis clearances of tianeptine and MC5 metabolite. The comparison between groups I and II showed that renal failure did not appear to affect the disposition of parent tianeptine. However, the MC5 metabolite terminal half-life was found to be increased in renal patients compared to controls (14.2 +/- 9.3 h vs 4.9 +/- 1.7 h). Due to a large interindividual variability the difference did not reach a significant level (P = 0.054). According to the antidepressant activity of the MC5 metabolite in pharmacological tests, the sustained rise in its plasma level suggests that a reduced daily dose should be administered and 12.5 mg of tianeptine should be given twice daily to patients with chronic renal failure. In patients from group III elimination of the compounds by haemodialysis was found to be low. The dialysis clearances were 3.9 +/- 9.9 ml.min-1 and 19.2 +/- 8.6 ml.min-1 for tianeptine and its MC5 metabolite respectively. This low dialysability has 2 clinical implications. Firstly, patients currently undergoing haemodialysis and treated by tianeptine could be given the drug without taking dialysis into account. Secondly, haemodialysis does not appear to be an effective method for tianeptine elimination in cases of overdosage.
Acute effects of clometacin on renal prostaglandin biosynthesis in healthy subjects
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 1986
In 6 healthy subjects the effect of clometacin on renal function, sodium and water excretion, pla... more In 6 healthy subjects the effect of clometacin on renal function, sodium and water excretion, plasma renin activity and urinary excretion of prostaglandins has been studied. After four days of treatment with clometacin, the excretion of urinary prostaglandins E2, F2 alpha and 6 keto F1 alpha and thromboxane B2 were reduced by 61.2, 41.2, 59 and 42%, respectively. 62% reduction in plasma renin activity was also observed. There was no significant change in mean blood pressure, heart rate, body weight, creatinine clearance or urinary excretion of sodium. It is concluded that clometacin is an efficient cyclooxygenase inhibitor in healthy individuals with a normal sodium intake, and that caution is required when giving clometacin to patients at risk of developing renal failure during treatment with a cyclooxygenase inhibitor.
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 1985
1 The pharmacokinetics of ornidazole (Tiberal®) was studied after intravenous administration of a... more 1 The pharmacokinetics of ornidazole (Tiberal®) was studied after intravenous administration of a single 500 mg dose in eight patients with advanced chronic renal failure (ACRF) (creatinine clearance 2-16 ml/min), in seven patients treated by haemodialysis (residual renal creatinine clearance 0-5 ml/min) and in five patients treated by continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) (residual renal creatinine clearance 0-6 ml/min). 2 In ACRF patients, the half-life of ornidazole was 10.8 ± 1.4 h, the total plasma clearance 46.3 ± 2.3 ml/min and the volume of distribution 0.73 ± 0.06 1/kg. 3 During haemodialysis, ornidazole was partly removed: the dialyser extraction ratio was 42 ± 5% and the dialysis clearance 64 ± 7 ml/min. 4 During CAPD, peritoneal excretion was low: the dialysis clearance was 3.0 ± 0.4 ml/ min and in 48 h 6.0 ± 1.1% of the administered dose was found in the peritoneal fluids. In these patients, the half-life of ornidazole was 11.8 ± 0.8 h and total plasma clearance was 48.3 ± 5.5 ml/min, values which were close to those determined in non dialysed patients. 5 In patients with end-stage renal disease, the half-life of ornidazole is comparable to that of subjects with normal renal function. This is due to the predominantly extra-renal elimination of the drug. Therefore, there is no need to modify the usual dosage of ornidazole for these patients. Because of the large elimination of the drug during haemodialysis it is necessary to administer the drug after the dialysis session.
The Activity of Ceftazidime and Avibactam Against -Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in a Hollow-Fiber Pharmacodynamic Model
Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2014
Avibactam is a novel non-β-lactam β-lactamase inhibitor that is currently undergoing phase 3 clin... more Avibactam is a novel non-β-lactam β-lactamase inhibitor that is currently undergoing phase 3 clinical trials in combination with ceftazidime. Ceftazidime is hydrolyzed by a broad range of β-lactamases, but avibactam is able to inhibit the majority of these enzymes. The studies described here attempt to provide insight into the amount of avibactam required to suppress bacterial growth in an environment where the concentrations of both agents are varying as they would when administered to humans. Following the simulation of a single intravenous dose of the drug, ceftazidime alone had no effect on any test organism, but a ceftazidime-avibactam combination resulted in rapid killing of all of the strains, with growth suppressed for the 8 h of the study. For seven of eight strains, this was achieved with a 1-g-250-mg profile, but a 2-g-500-mg profile was necessary to completely suppress a high-level-AmpC-producing isolate. When ceftazidime was infused continuously for 24 h with a single bolus dose of avibactam, rapid killing of all of the strains was again observed, with growth suppressed for 10 to >24 h. Regrowth appeared to commence once the avibactam concentration dropped below a critical concentration of approximately 0.3 μg/ml. In a third series of studies, ceftazidime was administered every 8 h for 24 h with avibactam administered at fixed concentrations for short periods during each ceftazidime dose profile. Simulating a 1-g dose of ceftazidime, an avibactam pulse of >0.25 and <0.5 μg/ml was required to suppress growth for 24 h.
Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1986
A specific and sensitive high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the measurement of su... more A specific and sensitive high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the measurement of sulpiride in plasma is described. The internal standard used was veralipride, a structurally related substituted benzamide. A fluorescence detector with maximum excitation at 300 nm and maximum emission at 365 nm was used for quantitation. After an alkaline extraction procedure, the benzamides were separated on a B-pm ODS column using a large organic counter ion in the mobile phase. The detector response was linear from 10 to 1000 ng/ml and the detection limit was 10 ng/ml, which is sensitive enough for pharmacokinetic studies. The suitability of the method for the analysis of biological samples was tested by studying the variation with time of plasma concentrations of sulpiride in normal human volunteers after a single therapeutic 200-mg oral dose of three different formulations of sulpiride. 0378-4347/86/$03.50 0 1986 Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.

![Research paper thumbnail of [Pharmacokinetics of ornidazole in the patient with renal failure; influence of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis]](https://a.academia-assets.com/images/blank-paper.jpg) ](
](



