Recoding addins (original) (raw)
The questionr packages provides addins for several recoding operations : recoding the levels of a factor or character variable, reordering the levels of a factor or character variable, dividing the range of a numeric variable into intervals.
The goal of these addins is to generate the recoding code with a small graphical interface. The code can then be inserted into a script and run (by design, nothing is executed by the addin in the global environment).
Launching an addin
There are three ways to launch one of the three addins :
- by clicking on its name in the Addins menu
- by launching its function name in the Console
- by selecting a variable name in a script and then clicking on its name in the Addins menu
- by launching its function name in the Console with a variable as argument
In the first two cases, you will have to select the variable to be recoded manually, in the two last it will be done automatically for you.
Note that if your cursor is in a script when you launch an addin with the Addins menu, the generated code will be automatically inserted at you cursor position when clicking on Done.
Levels recoding (irec)
The irec addin function can be launched with the_Levels recoding_ entry of the Addins menu.
Variable and settings
The first tab of the interface is called Variable and setings. Here you can select an object in you current environment, or a column in a data frame.
You can also select the name of the new object/data frame column, choose a recoding style, and the output object class.
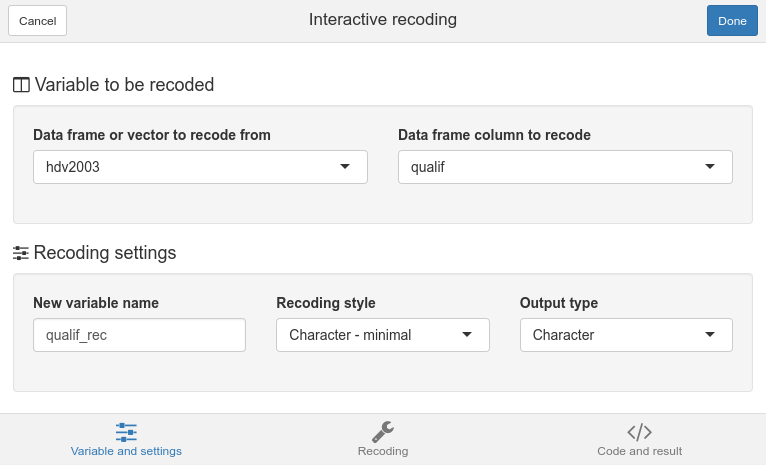
Variable and settings tab
Recoding
The Recoding tab is where you can make the correspondance between old and new values. If you want to recode an existing level toNA, just type NA in the recoding field.
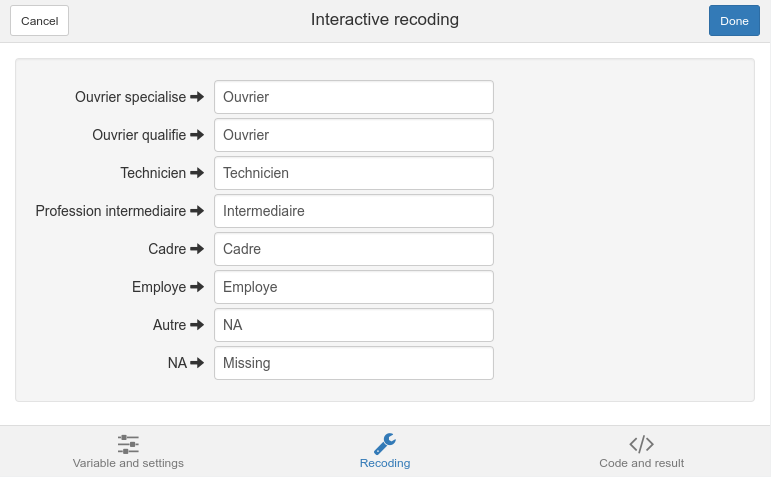
Recoding tab
Code and result
Finally, the Code and result tab lets you see the generated code, and a cross tabulation between the original and recoded variables, to check if everything seems correct. When your recoding is good, you can click on the Done button : the generated code will then be inserted in your script (if the cursor was in the script window when launching the addin) and pasted into the Console window.
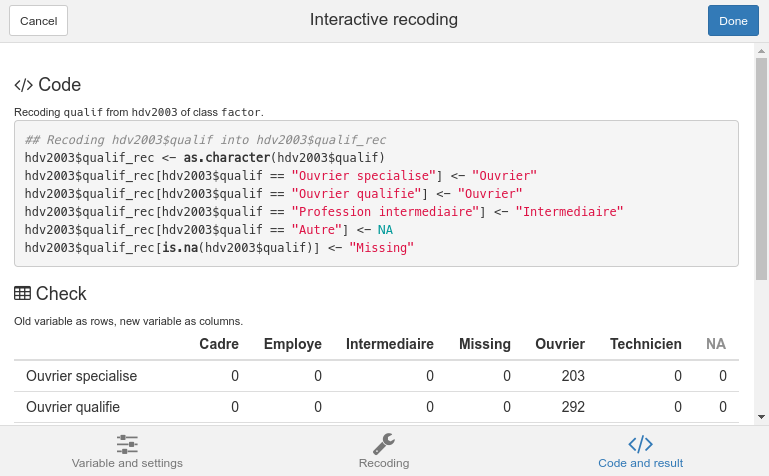
Code and result tab
Levels ordering (iorder)
The iorder addin function can be launched with the_Levels ordering_ entry of the Addins menu.
Variable and settings
The first tab of the interface is called Variable and setings. Here you can select an object in you current environment, or a column in a data frame. You can also select the name of the new object/data frame column which will get the reordered variable (by default it will just replace the original object).
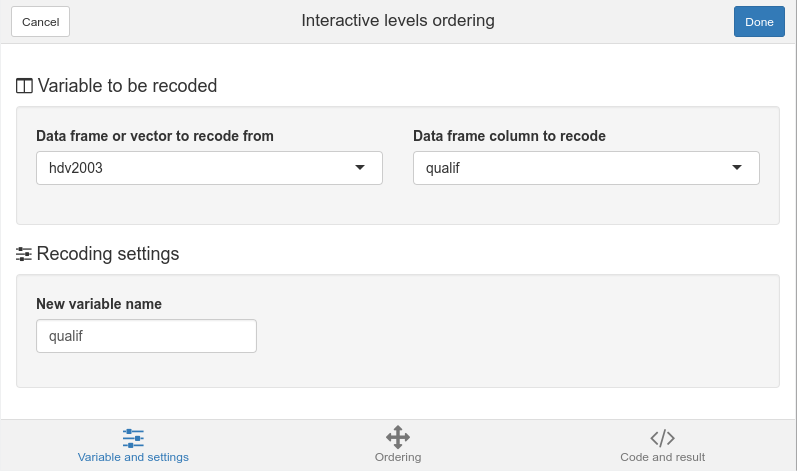
Variable and settings tab
Ordering
The Ordering tab is where you can reorder your levels. Just drag and drop them with your mouse.
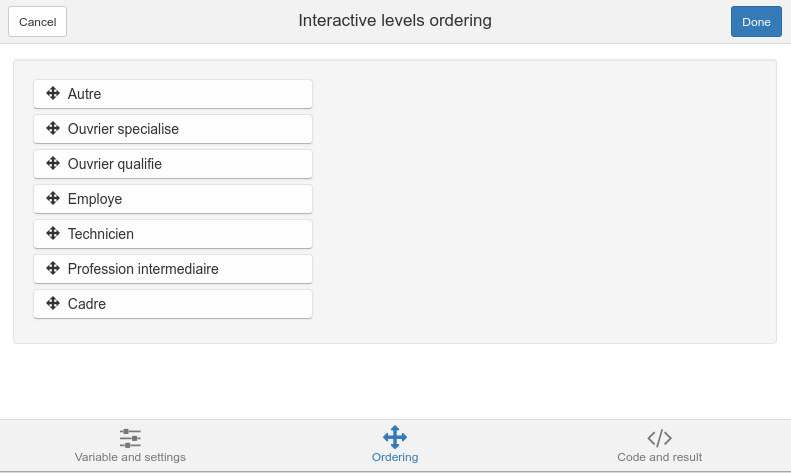
Ordering tab
Code and result
Finally, the Code and result tab lets you see the generated code, and a contingency table of the resulting factor. When your result is good, you can click on the Done button : the generated code will then be inserted in your script (if the cursor was in the script window when launching the addin) and pasted into the Console window.
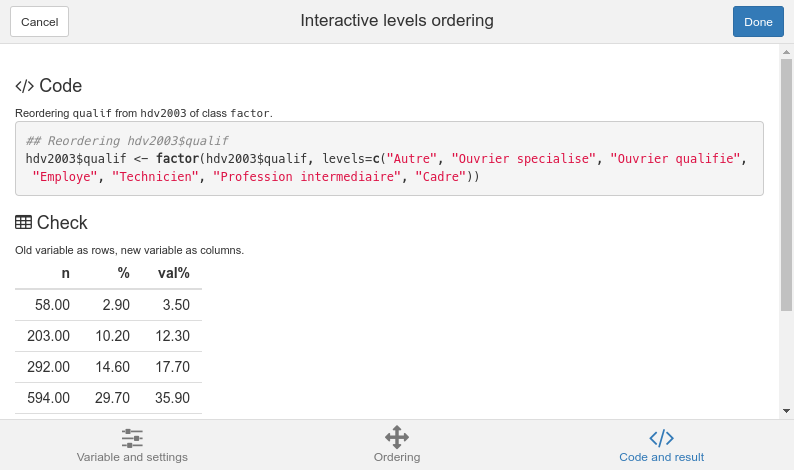
Code and result tab
Numeric range dividing (icut)
The iorder addin function can be launched with the_Numeric range dividing_ entry of the Addins menu.
Variable and settings
The first tab of the interface is called Variable and setings. Here you can select an object in you current environment, or a column in a data frame. You can also select the name of the new object/data frame column which will get the new variable.
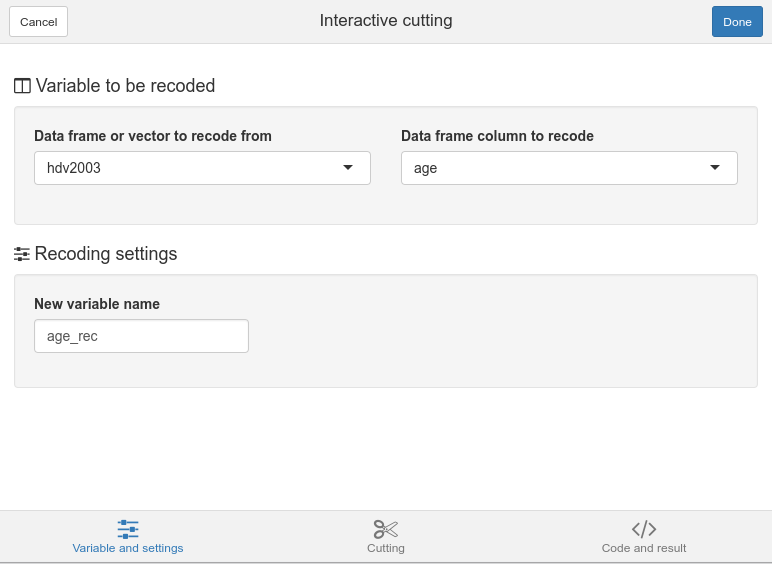
Variable and settings tab
Cutting
The Cutting tab is where you will define the way to divide the variable range. First select a cutting method (theManual method is the one used with the basecut function) and modify the options as you like. A dynamic histogram will show the class boundaries positions.
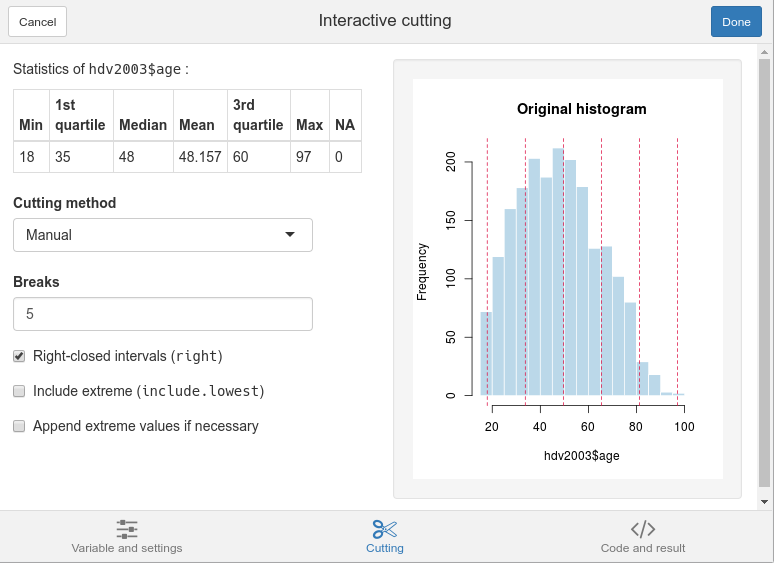
Cutting tab
Code and result
Finally, the Code and result tab lets you see the generated code, and a contingency table and a barplot of the resulting factor. When your result is good, you can click on the Done button : the generated code will then be inserted in your script (if the cursor was in the script window when launching the addin) and pasted into the Console window.
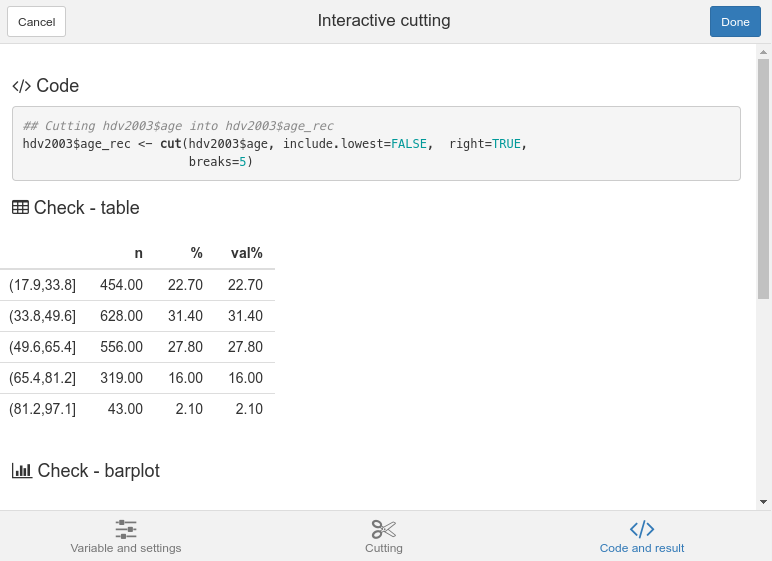
Code and result tab