ICT Services Trade in the BRICS Countries: Special and Common Features (original) (raw)
Abstract
Involvement in the global innovation system and the level of ICT influence the technological state of the Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa (BRICS) countries and their position in the world economy. Many studies were inspired that examined these economies from various prospective. However, only a few have specially focused on information and communication technologies (ICT), and particularly in services sectors. This paper aims to contribute to the analysis of the evolution of services ICT systems in BRICS. The main hypothesis of the article is that BRICS has made significant progress in economic cooperation, at the same time, the group has not been equally successful in designing and implementing their own agenda in the technology field. The BRICS are not released at a sufficient level of interaction and advocacy in ICT services, which would increase their role in international trade. The authors observe the retrospective of the process of formation of national innovation systems of the country participants of BRICS, consider current trends and challenges in the development of national markets for these services in each member country, and highlight future directions for the development. Then they provide an analysis of BRICS countries’ participation in the international ICT services trade. An estimation of revealed comparative advantage indicators allowed determining the dynamics in comparative advantage for ICT service trade in BRICS. Despite the increase in the volume of export operations in the trade in ICT services, their level of competitiveness is declining. The most vulnerable to the reduction of revealed comparative advantage was India, at the same time Brazil and South Africa showed the least volatile dynamics. It is argued that the policies aimed at promoting investment and enhancing conditions for trade in ICT services contributed significantly to services exports expansion in BRICS. Based on the analysis, a conclusion is made about the current problems and insufficient level of technical cooperation within the group.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
- Starting from 10 chapters or articles per month
- Access and download chapters and articles from more than 300k books and 2,500 journals
- Cancel anytime View plans
Buy Now
Price excludes VAT (USA)
Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
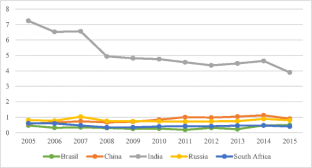
Fig. 1
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- ICT services comprise telecommunication, computer (including software) and information services (including news agencies), which corresponds to the 9th position in the harmonised system.
- GOELRO—Russian transliteration for ‘State Commission for Electrification of Russia’.
References
- Beausang, F. (2012). Globalization and the BRICs: why the BRICs will not rule the world for long (p. 215). New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
Book Google Scholar - Biryukova, O. V. (2014). Russian knowledge—intensive services in international trade. Studies on Russian Economic Development, 1, 77–83.
Article Google Scholar - Biziwick, M., Cattaneo, N., & Fryer, D. (2015). The rationale for and potential role of the BRICS contingent reserve arrangement. South African Journal of International Affairs, 22(3), 307–324.
Article Google Scholar - Bond P., Garcia A. (Eds.) (2015) BRICS: an anticapitalist critique. Auckland Park, South Africa : Jacana, p.300.
- Brazilian IT market grows 9.2 percent in 2015, 2016a, available at: http://www.zdnet.com/article/brazilian-it-market-grows-9-2-percent-in-2015/. Accessed 10 June 2017.
- Brazilian IT market, available at: http://tadviser.ru/a/145248. Accessed 27 February 2016b.
- BRICS Leaders Xiamen declaration (2017). China. available at: http://www.brics.utoronto.ca/docs/170904-xiamen.html . Accessed 17 September 2017.
- Central bank of Russian Federation. (2015). External Trade in Services, of Russian Federation, Statistical Compilation 2015, available at: http://www.cbr.ru/statistics/credit_statistics/External_Trade_in_Services_2015.pdf. Accessed 15 April 2016.
- China now world’s largest online gaming market, 2016, available at: https://america.cgtn.com/2016/01/08/china-now-worlds-largest-online-gaming-market. Accessed 10 June 2017.
- Crane, R. (2014). Building bridges among the BRICs (p. 198). Palgrave Macmillan UK.
- De Castro, T. (2012) EU-BRIC trade assessment: introversion, complementarity and RCA, Scientia et Societas, 8, 3, 68–80 ; De Castro, T. (2013) Trade Among BRICS Countries: Changes Towards Closer Cooperation?, Ekonomická Revue, 16, 3, 131–148.
- De Castro, T. (2013) Trade among BRICS Countries: Changes towards Closer Cooperation? Ekonomická Revue, 16, 3, 131–148.
- EU SME Centre (2015). The ICT Market in China, available at: http://www.ccilc.pt/sites/default/files/eu_sme_centre_report_-_the_ict_market_in_china_update_-_july_2015.pdf. Accessed 28 February 2016.
- Eurasian Development Bank, Centre for Integration Studies (2016) Monitoring of mutual investments in CIS countries 2016, available at: http://www.eabr.org/general/upload/reports/EDB_Centre_2016_Report_39_MIM_CIS_ENG.pdf.
- Gandhi, M. B. R. (2016). International trade and economic growth: evidences from the BRICS. Journal of Applied Economics and Business Research, 6(2), 150–160.
Google Scholar - Garcia, Juan A. and Werner, Sebastian E. V., Bond Risk Premia, Macroeconomic Factors and Financial Crisis in the Euro Area (June 15, 2015). Louvain School of Management Working Paper Series No. 2015/14. Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=2670913 or https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2670913.
- Gartner( 2015). Emerging market analysis: South Africa encounters challenges as a regional IT leader. available at: http://www.gartner.com/newsroom/id/3161319 . Accessed 28 February 2016.
- Gillwald, Moyo, Stork (2012) Understanding what is happening in ICT in South Africa: A supply- and demandside analysis of the ICT sector. Available at: http://www.researchictafrica.net/publications/Evidence_for_ICT_Policy_Action/Policy_Paper_7_-_Understanding_what_is_happening_in_ICT_in_South_Africa.pdf
- Goa Declaration (2016), India. available at: http://kremlin.ru/supplement/5139. Accessed 11 June 2017.
- Hmelevskaja, N.G. (2015) ‘Real'nye Kontury i Orientiry Valjutnogo Partnerstva BRIKS dlja Sodejstvija Torgovle i Investicijam [the real circuits and landmarks for BRICS currency cooperation for the purposes of fostering trade and investment]’, Vestnik Mezhdunarodnyh Organizacij: Obrazovanie, Nauka, Novaja Jekonomika [journal of international organizations: Education, science, new Eeconomy], 10, 2, 70-88.
- Hong P., Park Yo. (2014). Building network capabilities in turbulent competitive environments: business success stories from the BRICS. CRC Press; 1 edition. p. 244.
- IBGE (2015), Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatistica [Brasilian institute of geography and statistics]. Indicadores IBG [IBG indicators], available at: ftp://ftp.ibge.gov.br/Comercio_e_Servicos/Pesquisa_Mensal_de_Servicos/Fasciculo_Indicadores_IBGE/pms_201512caderno.pdf. Accessed 27 February 2016.
- IDC 2015 Top 10 predictions of China ICT market: 3rd platform pursuit of new growth during economic adjustment period, available at: http://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prCN25364315. Accessed: 28 February 2016.
- IoT India Industry Study - 2016, 2016, available at: http://iotindiamag.com/2016/09/iot-india-industry-study-2016/. Accessed 10 June 2017.
- Khatun, R. (2016). Relation between trade in financial services and economic growth in BRICS economies: cointegration and causality approach. Global Business Review, 17(1), 214–225.
Article Google Scholar - Kingah, S. and Quiliconi, C. (eds). 2016. Global and regional leadership of BRICS countries. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-22972-0
- Melville, A., & Mironyuk, M. (2016). Bad enough governance: state capacity and quality of institutions in post-soviet autocracies. Post-Soviet Affairs, 32(2), 132–151.
Article Google Scholar - Naud´e, W., Szirmai, A., and Haraguchi, N. (2015). Structural Change and Industrial Development in the BRICS. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Number of instant messaging services users in China from Deceomber 2012 to December 2016_,_ available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/321793/china-number-of-instant-messaging-users/. Accessed 10 June 2017.
- Sharma, S. K. & Kallummal, M. (2012). A GTAP Analysis of the Proposed BRICS Free Trade Agreement. Available at: https://www.gtap.agecon.purdue.edu/resources/download/5989.pdf. Accessed 9 February 2013.
- Simon J. P. (2011), The ICT landscape in BRICS countries: Brazil, India, China,. European Commission Joint Research Centre Institute for Prospective Technological Studies. Luxembourg.
- SITA Annual Report 2014/2015, available at: http://www.sita.co.za/docs/SITA%20Annual%20Report%202014-15.pdf. Accessed 1 March 2016.
- NACI (2014). South African Science, Technology and Innovation Indicators National Advisory Council on Innovation. Available at: http://www.naci.org.za/wp-content/uploads/South-African-STI-Indicators-2014.pdf. Accessed 1 March 2016.
- Structural Change and Industrial Development in the BRICS / edited by Wim Naude, Adam Szirmai and Nobuya Haraguchi. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- The Ministry of Economic Development of Russian Federation. The Forecast for Russian Federation Social and Economic Development between the Years 2016 and 2018, available at: http://economy.gov.ru/minec/about/structure/depmacro/20151026. Accessed 27 February 2016.
- Ufa Declaration (2015). VII BRICS Summit, the Russian Federation. available at: http://www.nkibrics.ru/system/asset_docs/data/559e/7a9a/6272/6943/0821/0000/original/VII_BRICS_SUMMIT_-_UFA_DECLARATION_JULY_9__2015_UFA__RUSSIA.pdf?1436449434. Accessed 11 June 2017.
- UNCTAD (2015) Handbook of Statistics (New York and Geneva United Nations).
- World Economic Forum (2015) The Global Information Technology Report 2015, available at: http://reports.weforum.org/global-information-technology-report-2015/. Accessed 27 February 2016.
- World Economic Forum (2016) The Global Information technology Report 2016_,_ available at: http://www3.weforum.org/docs/GITR2016/WEF_GITR_Full_Report.pdf. Accessed 10 June 2017.
- World Trade Organisation (2015) India. Trade Policy Review WT/TPR/S/313/Rev.1.
- Yao, X. N., Liu, J. N., (2011), The potential of economic growth and technology advancement in the BRICS. Proceedings of the 2011 international conference on machine learning and cybernetics, 10-13 July 2011, Guilin, 1067-1071.
- Yuan, H. & Zhao, Z. (2011). Comparative Analysis on Foreign Trade of the BRICs. M &D Forum: 166–172, available at: http://www.seiofbluemountain.com/upload/product/20 1112/2011jjzx05a2.pdf.
Acknowledgements
Support from the Research Program of the School of World Economy and International Affairs at National Research University Higher School of Economics is gratefully acknowledged, 2017-2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of World Economy, National Research University Higher School of Economics, 20 Myasnitskaya Str, Moscow, 101000, Russia
Ol’ga V. Biryukova & Anastasiia I. Matiukhina - Institute of Trade Policy, National Research University Higher School of Economics, 20 Myasnitskaya Str, Moscow, 101000, Russia
Ol’ga V. Biryukova
Authors
- Ol’ga V. Biryukova
- Anastasiia I. Matiukhina
Corresponding author
Correspondence toOl’ga V. Biryukova.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biryukova, O.V., Matiukhina, A.I. ICT Services Trade in the BRICS Countries: Special and Common Features.J Knowl Econ 10, 1080–1097 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-017-0517-6
- Received: 12 June 2017
- Accepted: 07 December 2017
- Published: 06 January 2018
- Version of record: 06 January 2018
- Issue date: 15 September 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-017-0517-6