Integrating LAN8720 with ESP32 for Ethernet Connectivity with plain (HTTP) and SSL (HTTPS) (original) (raw)
In the world of IoT and embedded systems, the ESP32 has emerged as a highly popular microcontroller due to its versatility and WiFi capabilities. However, for projects that require stable and fast network connections, Ethernet is often the preferred choice.

Integrating LAN8720 with ESP32 for Ethernet Connectivity with plain (HTTP) and SSL (HTTPS)
This is where the LAN8720 Ethernet PHY comes into play. In this guide, we’ll explore how to seamlessly integrate the LAN8720 module with an ESP32, providing a robust and reliable Ethernet connection for your IoT projects.
Here my selection of esp32 ESP32 Dev Kit v1 - TTGO T-Display 1.14 ESP32 - NodeMCU V3 V2 ESP8266 Lolin32 - NodeMCU ESP-32S - WeMos Lolin32 - WeMos Lolin32 mini - ESP32-CAM programmer - ESP32-CAM bundle - ESP32-WROOM-32 - ESP32-S
Toggle
lan8720 vs w5500
The W5500 and LAN8720 are both Ethernet controllers, but they serve different roles and have distinct features:
- W5500:
- Manufacturer: Wiznet
- Type: Full hardware TCP/IP stack Ethernet controller.
- Main Features:
* Integrated TCP/IP protocol stack which can handle TCP, UDP, IPv4, ICMP, ARP, IGMP, and PPPoE protocols.
* Supports up to 8 simultaneous socket connections.
* SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) for communication with host controllers.
* Internal 32Kbytes memory for TX/RX buffers.
* Suitable for embedded applications due to its ease of integration and minimal host processor loading.
* Typically used with microcontrollers like Arduino, STM32, etc.
- LAN8720:
- Manufacturer: Microchip Technology (previously SMSC)
- Type: Physical Layer Transceiver (PHY).
- Main Features:
* Operates at the physical layer of the OSI model.
* Supports 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX Ethernet standards.
* Uses RMII (Reduced Media Independent Interface) for communication with host controllers.
* Lower power consumption.
* Generally used in applications that require a separate MAC (Media Access Control) layer controller, often found in more complex systems like those with ARM processors.
Here a selection of the most widespread Ethernet devices w5500 lite - w5500 - enc26j60 mini - enc26j60 - lan8720
Key Differences:
- Functionality: The W5500 is a more integrated solution with a built-in TCP/IP stack, making it easier to handle network communications for simple microcontroller-based projects. The LAN8720, being a PHY layer device, requires a separate MAC controller and is more suited to complex applications.
- Interface: W5500 uses SPI, which is simpler and commonly found in microcontrollers. LAN8720 uses RMII, which is more complex but offers higher performance for systems that support it.
- Use Case: W5500 is preferred in simpler, microcontroller-based projects where ease of use and integration are key. LAN8720 is better for more advanced systems where a separate MAC is available and more control over the network stack is required.
Wiring
By default, the CHIP device has this wiring.
Common Pin Assignments from the official documentation
Using ESP32 internal MAC
- RMII PHY wiring is fixed and can not be changed through either IOMUX or GPIO Matrix. By default, they’re connected as follows:
| GPIO | RMII Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| GPIO21 | TX_EN | EMAC_TX_EN |
| GPIO19 | TX0 | EMAC_TXD0 |
| GPIO22 | TX1 | EMAC_TXD1 |
| GPIO25 | RX0 | EMAC_RXD0 |
| GPIO26 | RX1 | EMAC_RXD1 |
| GPIO27 | CRS_DV | EMAC_RX_DRV |
- One of the following GPIO pins can be used as RMII REF_CLK input/output:
| GPIO | Function | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| GPIO0 | EMAC_TX_CLK/CLK_OUT1 | input/output |
| GPIO16 | EMAC_CLK_OUT | output |
| GPIO17 | EMAC_CLK_180 | output |
- SMI (Serial Management Interface) wiring is not fixed. You may need to changed it according to your board schematic. By default, they’re connected as follows:
| GPIO | SMI Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| GPIO23 | MDC | Output to PHY |
| GPIO18 | MDIO | Bidirectional |
Wiring the prototyping board
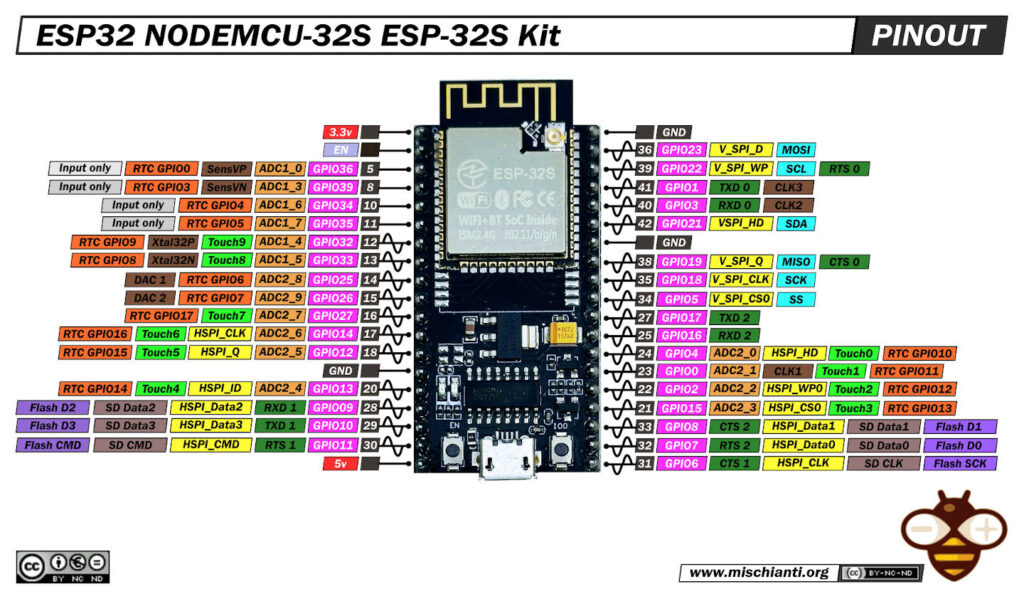
ESP32 NODEMCU-ESP-32S Kit pinout
Here is the wiring with an esp32 with 38 pins.
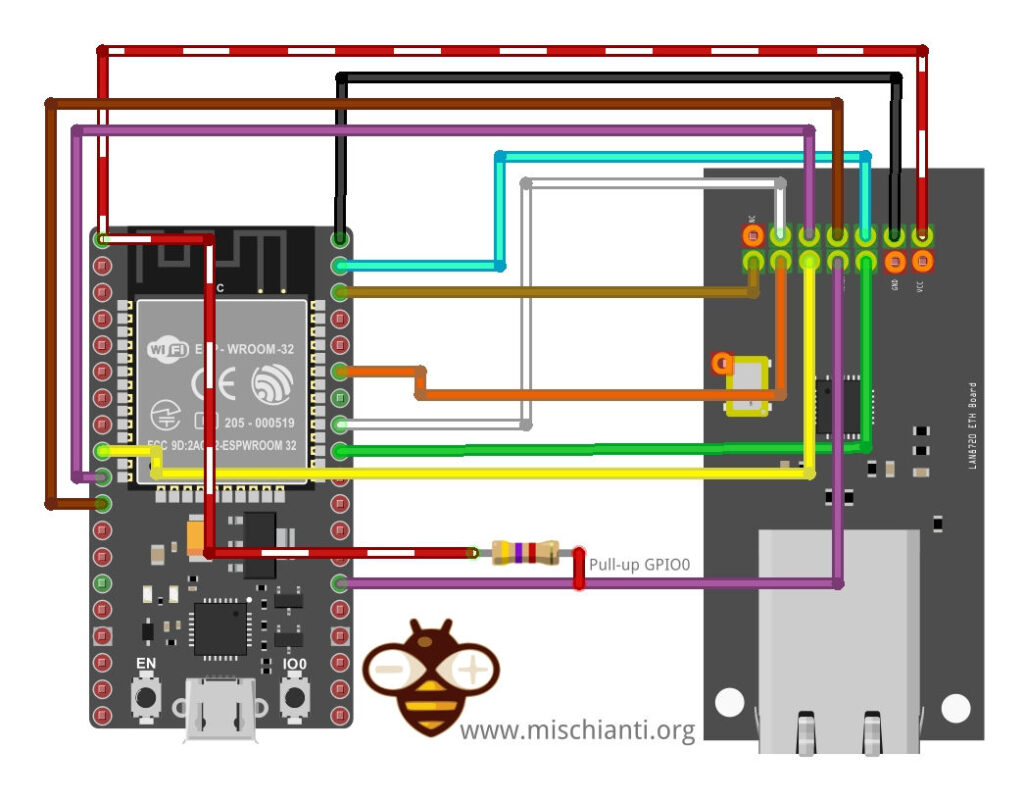
esp32 NODEMCU-ESP-32S and lan8720
In our prototype board, we start the wiring with this configuration (the standard one)
| esp32 | lan8720 |
|---|---|
| 3V3 | Vcc |
| GND | GND |
| GPIO18 | MDIO |
| GPIO19 | TXD0 |
| GPIO21 | TXEN |
| GPIO22 | TXD1 |
| GPIO23 | MDC |
| GPIO25 | RXD0 |
| GPIO26 | RXD1 |
| GPIO27 | CRS_DV |
| GPIO0 | nINT/RETCLM |
But with this version and China lan8720 board you can get a problem, rondomically you get a message like this.
mode:DIO, clock div:1 load:0x3fff0030,len:1184 load:0x40078000,len:13260 load:0x40080400,len:3028 entry 0x400805e4 ets Jul 29 2019 12:21:46
rst:0x1 (POWERON_RESET),boot:0x3 (DOWNLOAD_BOOT(UART0/UART1/SDIO_REI_REO_V2)) waiting for download ets Jul 29 2019 12:21:46
rst:0x1 (POWERON_RESET),boot:0x3 (DOWNLOAD_BOOT(UART0/UART1/SDIO_REI_REO_V2)) waiting for download
Some time works and other times not; this is because you attach GPIO0 to the Crystal Oscillator, and when the Oscillator is HIGH, GPIO0 puts your ESP32 on boot mode; if you are lucky and Oscillator is LOW, you boot normally.
To fix this problem you must solder a wire from the enable pin of the oscillator to the NC (Not connected) pin, and wire like so.
| esp32 | lan8720 patched |
|---|---|
| 3V3 | Vcc |
| GND | GND |
| GPIO18 | MDIO |
| GPIO19 | TXD0 |
| GPIO21 | TXEN |
| GPIO22 | TXD1 |
| GPIO23 | MDC |
| GPIO25 | RXD0 |
| GPIO26 | RXD1 |
| GPIO27 | CRS_DV |
| GPIO0 | nINT/RETCLM |
| GPIO17 | NC |
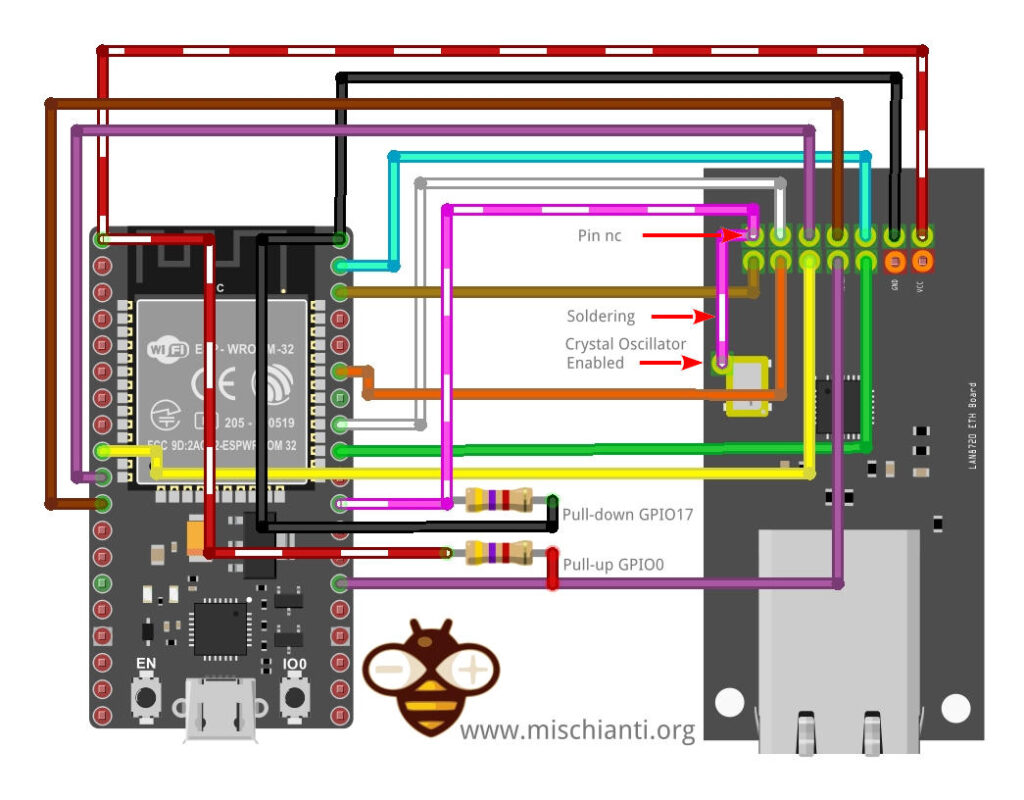
esp32 NODEMCU-ESP-32S and lan8720 patched with enable crystal oscillator
Here the patch on my device.

lan8720 for esp32 bottom crystal oscillator patch
Test the device
Standard connection without patch
First, the most common sketch you can find on the web without using the patch. Remember that you probably must reset more than one time to put in work without going into download mode.
/* This sketch shows how to use lan8720 with esp32 with minimal/standard configuration
You can set the parameter in begin function or at start with define before the import of ETH.h file, this way is preferible.
by Renzo Mischianti <mischianti.org> */
// I²C-address of Ethernet PHY (0 or 1 for LAN8720, 31 for TLK110) #define ETH_PHY_ADDR 1 // DEFAULT VALUE IS 0 YOU CAN OMIT IT // Type of the Ethernet PHY (LAN8720 or TLK110) #define ETH_PHY_TYPE ETH_PHY_LAN8720 // DEFAULT VALUE YOU CAN OMIT IT // Pin# of the enable signal for the external crystal oscillator (-1 to disable for internal APLL source) #define ETH_PHY_POWER -1 // DEFAULT VALUE YOU CAN OMIT IT // Pin# of the I²C clock signal for the Ethernet PHY #define ETH_PHY_MDC 23 // DEFAULT VALUE YOU CAN OMIT IT // Pin# of the I²C IO signal for the Ethernet PHY #define ETH_PHY_MDIO 18 // DEFAULT VALUE YOU CAN OMIT IT // External clock from crystal oscillator #define ETH_CLK_MODE ETH_CLOCK_GPIO0_IN // DEFAULT VALUE YOU CAN OMIT IT
#include <ETH.h>
static bool eth_connected = false;
void WiFiEvent(WiFiEvent_t event) { switch (event) { case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_START: Serial.println("ETH Started"); ETH.setHostname("esp32-mischianti-eth"); break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_CONNECTED: Serial.println("ETH Connected"); break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_GOT_IP: Serial.print("ETH MAC: "); Serial.print(ETH.macAddress()); Serial.print(", IPv4: "); Serial.print(ETH.localIP()); if (ETH.fullDuplex()) { Serial.print(", FULL_DUPLEX"); } Serial.print(", "); Serial.print(ETH.linkSpeed()); Serial.println("Mbps"); eth_connected = true; break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_DISCONNECTED: Serial.println("ETH Disconnected"); eth_connected = false; break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_STOP: Serial.println("ETH Stopped"); eth_connected = false; break; default: break; } }
void testClient(const char *host, uint16_t port) { Serial.print("\nconnecting to "); Serial.println(host);
WiFiClient client;
if (!client.connect(host, port)) {
Serial.println("connection failed");
return;
}
client.printf("GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: %s\r\n\r\n", host);
while (client.connected() && !client.available())
;
while (client.available()) {
Serial.write(client.read());
}
Serial.println("closing connection\n");
client.stop();}
void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); WiFi.onEvent(WiFiEvent); ETH.begin(); }
void loop() { if (eth_connected) { testClient("mischianti.org", 80); } delay(10000);
}
You can pass the same parameter also in the begin function like so (I add only as an example in this case).
/* This sketch shows how to use lan8720 with esp32 with minimal/standard configuration
Parameter in begin function
by Renzo Mischianti <mischianti.org> */
#include <ETH.h>
#define ETH_PARAM_PHY_ADDR 1 #define ETH_PARAM_PHY_TYPE ETH_PHY_LAN8720 #define ETH_PARAM_PHY_POWER -1 #define ETH_PARAM_PHY_MDC 23 #define ETH_PARAM_PHY_MDIO 18 #define ETH_PARAM_CLK_MODE ETH_CLOCK_GPIO0_IN
static bool eth_connected = false;
void WiFiEvent(WiFiEvent_t event) { switch (event) { case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_START: Serial.println("ETH Started"); ETH.setHostname("esp32-mischianti-eth"); break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_CONNECTED: Serial.println("ETH Connected"); break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_GOT_IP: Serial.print("ETH MAC: "); Serial.print(ETH.macAddress()); Serial.print(", IPv4: "); Serial.print(ETH.localIP()); if (ETH.fullDuplex()) { Serial.print(", FULL_DUPLEX"); } Serial.print(", "); Serial.print(ETH.linkSpeed()); Serial.println("Mbps"); eth_connected = true; break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_DISCONNECTED: Serial.println("ETH Disconnected"); eth_connected = false; break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_STOP: Serial.println("ETH Stopped"); eth_connected = false; break; default: break; } }
void testClient(const char *host, uint16_t port) { Serial.print("\nconnecting to "); Serial.println(host);
WiFiClient client;
if (!client.connect(host, port)) {
Serial.println("connection failed");
return;
}
client.printf("GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: %s\r\n\r\n", host);
while (client.connected() && !client.available())
;
while (client.available()) {
Serial.write(client.read());
}
Serial.println("closing connection\n");
client.stop();}
void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); WiFi.onEvent(WiFiEvent); ETH.begin(ETH_PARAM_PHY_ADDR, ETH_PARAM_PHY_POWER, ETH_PARAM_PHY_MDC, ETH_PARAM_PHY_MDIO, ETH_PARAM_PHY_TYPE, ETH_PARAM_CLK_MODE); }
void loop() { if (eth_connected) { testClient("mischianti.org", 80); } delay(10000);
}
The Output of the code is here.
ets Jul 29 2019 12:21:46
rst:0x1 (POWERON_RESET),boot:0x13 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT) configsip: 0, SPIWP:0xee clk_drv:0x00,q_drv:0x00,d_drv:0x00,cs0_drv:0x00,hd_drv:0x00,wp_drv:0x00 mode:DIO, clock div:1 load:0x3fff0030,len:1184 load:0x40078000,len:13260 load:0x40080400,len:3028 entry 0x400805e4 ETH Started ETH Connected ETH MAC: B8:D6:1A:68:E5:7F, IPv4: 192.168.1.115, FULL_DUPLEX, 100Mbps
connecting to mischianti.org HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently Connection: Keep-Alive Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100 content-type: text/html content-length: 3145 date: Fri, 02 Feb 2024 10:55:05 GMT server: LiteSpeed x-qc-pop: EU-FR-NTE-51 location: https://mischianti.org/
301 Moved Permanently301
Moved Permanently
The document has been permanently moved.
This page is generated by QUIC.cloud CDN on the EU-FR-NTE-51 server.
Connection of the device with the patch
If you do the patch, you need to manage the enable state of the Crystal Oscillator, you must set the GPIO17 as the power pin; this trick allows you to boot the device and, after the MCU boot operation, enable the Crystal Oscillator.
Probably with high-quality board, you don’t need that.
/* This sketch shows how to use patched lan8720 with esp32
Remeber you must connect the enable pin of Crystal Oscillator to the NC pin of the board
by Renzo Mischianti <mischianti.org> */
// I²C-address of Ethernet PHY (0 or 1 for LAN8720, 31 for TLK110) #define ETH_PHY_ADDR 1 // DEFAULT VALUE IS 0 YOU CAN OMIT IT // Pin# of the enable signal for the external crystal oscillator (-1 to disable for internal APLL source) #define ETH_PHY_POWER 17 // DEFAULT VALUE YOU CAN OMIT IT
#include <ETH.h>
static bool eth_connected = false;
void WiFiEvent(WiFiEvent_t event) { switch (event) { case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_START: Serial.println("ETH Started"); ETH.setHostname("esp32-mischianti-eth"); break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_CONNECTED: Serial.println("ETH Connected"); break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_GOT_IP: Serial.print("ETH MAC: "); Serial.print(ETH.macAddress()); Serial.print(", IPv4: "); Serial.print(ETH.localIP()); if (ETH.fullDuplex()) { Serial.print(", FULL_DUPLEX"); } Serial.print(", "); Serial.print(ETH.linkSpeed()); Serial.println("Mbps"); eth_connected = true; break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_DISCONNECTED: Serial.println("ETH Disconnected"); eth_connected = false; break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_STOP: Serial.println("ETH Stopped"); eth_connected = false; break; default: break; } }
void testClient(const char *host, uint16_t port) { Serial.print("\nconnecting to "); Serial.println(host);
WiFiClient client;
if (!client.connect(host, port)) {
Serial.println("connection failed");
return;
}
client.printf("GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: %s\r\n\r\n", host);
while (client.connected() && !client.available())
;
while (client.available()) {
Serial.write(client.read());
}
Serial.println("closing connection\n");
client.stop();}
void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); WiFi.onEvent(WiFiEvent); ETH.begin(); }
void loop() { if (eth_connected) { testClient("mischianti.org", 80); } delay(10000);
}
Make a raw GET request
First of all, we’ll try to make a simple HTTP request. I chose an online service created to test this kind of request to do this test.
I’m going to use a simple service given from httpbin.org, and you can use the same REST API in HTTP and HTTPS.
Remember that HTTP works on port 80 and HTTPS on 443, so you must validate a certificate to query the endpoint on the 443 port.
Here is the simple get request
/* This sketch shows how to use patched lan8720 with esp32
We are going to do a raw GET request to online service httpbin.org http://httpbin.org/get
by Renzo Mischianti <mischianti.org> */
// I²C-address of Ethernet PHY (0 or 1 for LAN8720, 31 for TLK110) #define ETH_PHY_ADDR 1 // DEFAULT VALUE IS 0 YOU CAN OMIT IT // Pin# of the enable signal for the external crystal oscillator (-1 to disable for internal APLL source) #define ETH_PHY_POWER 17 // DEFAULT VALUE YOU CAN OMIT IT
#include <ETH.h>
// if you don't want to use DNS (and reduce your sketch size) // use the numeric IP instead of the name for the server: //IPAddress server(74,125,232,128); // numeric IP for Google (no DNS) //char server[] = "www.google.com"; // name address for Google (using DNS) char server[] = "httpbin.org"; // name address for Google (using DNS)
// Initialize the Ethernet client library WiFiClient client;
// Variables to measure the speed unsigned long beginMicros, endMicros; unsigned long byteCount = 0; bool printWebData = true; // set to false for better speed measurement
static bool eth_connected = false;
void WiFiEvent(WiFiEvent_t event) { switch (event) { case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_START: Serial.println("ETH Started"); ETH.setHostname("esp32-mischianti-eth"); break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_CONNECTED: Serial.println("ETH Connected"); break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_GOT_IP: Serial.println(); Serial.print("ETH MAC: "); Serial.print(ETH.macAddress()); Serial.print(", IPv4: "); Serial.print(ETH.localIP()); if (ETH.fullDuplex()) { Serial.print(", FULL_DUPLEX"); } Serial.print(", "); Serial.print(ETH.linkSpeed()); Serial.println("Mbps"); eth_connected = true; break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_DISCONNECTED: Serial.println("ETH Disconnected"); eth_connected = false; break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_STOP: Serial.println("ETH Stopped"); eth_connected = false; break; default: break; } }
void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); WiFi.onEvent(WiFiEvent); ETH.begin();
while (!eth_connected) {
Serial.print(".");
delay(100);
}
// if you get a connection, report back via serial:
if (client.connect(server, 80)) {
Serial.println("Connected!");
// Make a HTTP request:
client.println("GET /get HTTP/1.1");
client.println("Host: httpbin.org");
client.println("Connection: close");
client.println();
} else {
// if you didn't get a connection to the server:
Serial.println("connection failed");
}
beginMicros = micros();}
void loop() { // if there are incoming bytes available // from the server, read them and print them: int len = client.available(); if (len > 0) { byte buffer[80]; if (len > 80) len = 80; client.read(buffer, len); if (printWebData) { Serial.write(buffer, len); // show in the serial monitor (slows some boards) } byteCount = byteCount + len; }
// if the server's disconnected, stop the client:
if (len == 0 && !client.connected()) {
endMicros = micros();
Serial.println();
Serial.println("disconnecting.");
client.stop();
Serial.print("Received ");
Serial.print(byteCount);
Serial.print(" bytes in ");
float seconds = (float)(endMicros - beginMicros) / 1000000.0;
Serial.print(seconds, 4);
float rate = (float)byteCount / seconds / 1000.0;
Serial.print(", rate = ");
Serial.print(rate);
Serial.print(" kbytes/second");
Serial.println();
// do nothing forevermore:
while (true) {
delay(1);
}
}}
And here is the result.
ETH Started ETH Connected ........... ETH MAC: B8:D6:1A:68:E5:7F, IPv4: 192.168.1.115, FULL_DUPLEX, 100Mbps Connected! HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Fri, 02 Feb 2024 15:44:00 GMT Content-Type: application/json Content-Length: 199 Connection: close Server: gunicorn/19.9.0 Access-Control-Allow-Origin: * Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
{ "args": {}, "headers": { "Host": "httpbin.org", "X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-65bd0dc0-4ea2c7a33ad187b40ac5cda8" }, "origin": "84.221.199.122", "url": "http://httpbin.org/get" }
disconnecting. Received 424 bytes in 0.2767, rate = 1.53 kbytes/second
Now, an HTTPS request.
If we change only the port from
if (client.connect(server, 80)) {to
if (client.connect(server, 443)) {we receive an explicit error like this.
ETH Started ETH Connected . ETH MAC: B8:D6:1A:68:E5:7F, IPv4: 192.168.1.115, FULL_DUPLEX, 100Mbps Connected! HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request Server: awselb/2.0 Date: Fri, 02 Feb 2024 16:25:02 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 220 Connection: close
400 The plain HTTP request was sent to HTTPS port400 Bad Request
The plain HTTP request was sent to HTTPS portdisconnecting. Received 370 bytes in 0.2764, rate = 1.34 kbytes/second
First of all, we must use the WiFiClientSecure that implements the SSL layer. But if you substitute the line
// Initialize the Ethernet client library WiFiClient client;
with
// Initialize the Ethernet client library WiFiClientSecure client;
we obtain
ETH Started ETH Connected . ETH MAC: B8:D6:1A:68:E5:7F, IPv4: 192.168.1.115, FULL_DUPLEX, 100Mbps connection failed
disconnecting. Received 0 bytes in 0.0000, rate = 0.00 kbytes/second
This is because the layer SSL needs to validate the remote server via the Certification Authority, but if you are a bad guy, you can ask the library to avoid the control of the certificate with this command.
The complete sketch becomes.
/* This sketch shows how to use patched lan8720 with esp32
We are going to do a raw GET request to online service httpbin.org http://httpbin.org/get
by Renzo Mischianti <mischianti.org> */
// I²C-address of Ethernet PHY (0 or 1 for LAN8720, 31 for TLK110) #define ETH_PHY_ADDR 1 // DEFAULT VALUE IS 0 YOU CAN OMIT IT // Pin# of the enable signal for the external crystal oscillator (-1 to disable for internal APLL source) #define ETH_PHY_POWER 17 // DEFAULT VALUE YOU CAN OMIT IT
#include <ETH.h> #include <WiFiClientSecure.h>
// if you don't want to use DNS (and reduce your sketch size) // use the numeric IP instead of the name for the server: //IPAddress server(74,125,232,128); // numeric IP for Google (no DNS) //char server[] = "www.google.com"; // name address for Google (using DNS) char server[] = "httpbin.org"; // name address for Google (using DNS)
// Initialize the Ethernet client library WiFiClientSecure client;
// Variables to measure the speed unsigned long beginMicros, endMicros; unsigned long byteCount = 0; bool printWebData = true; // set to false for better speed measurement
static bool eth_connected = false;
void WiFiEvent(WiFiEvent_t event) { switch (event) { case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_START: Serial.println("ETH Started"); ETH.setHostname("esp32-mischianti-eth"); break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_CONNECTED: Serial.println("ETH Connected"); break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_GOT_IP: Serial.println(); Serial.print("ETH MAC: "); Serial.print(ETH.macAddress()); Serial.print(", IPv4: "); Serial.print(ETH.localIP()); if (ETH.fullDuplex()) { Serial.print(", FULL_DUPLEX"); } Serial.print(", "); Serial.print(ETH.linkSpeed()); Serial.println("Mbps"); eth_connected = true; break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_DISCONNECTED: Serial.println("ETH Disconnected"); eth_connected = false; break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_STOP: Serial.println("ETH Stopped"); eth_connected = false; break; default: break; } }
void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); WiFi.onEvent(WiFiEvent); ETH.begin();
while (!eth_connected) {
Serial.print(".");
delay(100);
}
client.setInsecure();
// if you get a connection, report back via serial:
if (client.connect(server, 443)) {
Serial.println("Connected!");
// Make a HTTP request:
client.println("GET /get HTTP/1.1");
client.println("Host: httpbin.org");
client.println("Connection: close");
client.println();
} else {
// if you didn't get a connection to the server:
Serial.println("connection failed");
}
beginMicros = micros();}
void loop() { // if there are incoming bytes available // from the server, read them and print them: int len = client.available(); if (len > 0) { byte buffer[80]; if (len > 80) len = 80; client.read(buffer, len); if (printWebData) { Serial.write(buffer, len); // show in the serial monitor (slows some boards) } byteCount = byteCount + len; }
// if the server's disconnected, stop the client:
if (len == 0 && !client.connected()) {
endMicros = micros();
Serial.println();
Serial.println("disconnecting.");
client.stop();
Serial.print("Received ");
Serial.print(byteCount);
Serial.print(" bytes in ");
float seconds = (float)(endMicros - beginMicros) / 1000000.0;
Serial.print(seconds, 4);
float rate = (float)byteCount / seconds / 1000.0;
Serial.print(", rate = ");
Serial.print(rate);
Serial.print(" kbytes/second");
Serial.println();
// do nothing forevermore:
while (true) {
delay(1);
}
}}
And now the result is this.
ETH Started ETH Connected .......... ETH MAC: B8:D6:1A:68:E5:7F, IPv4: 192.168.1.115, FULL_DUPLEX, 100Mbps Connected! HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Fri, 02 Feb 2024 16:36:00 GMT Content-Type: application/json Content-Length: 200 Connection: close Server: gunicorn/19.9.0 Access-Control-Allow-Origin: * Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
{ "args": {}, "headers": { "Host": "httpbin.org", "X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-65bd19f0-36775c160826895f26d52da8" }, "origin": "84.221.199.122", "url": "https://httpbin.org/get" }
disconnecting. Received 425 bytes in 0.1594, rate = 2.67 kbytes/second
Ok, now we try to be a good guy; we are going to download the Certification Authority certificate to validate the host.
So in the httpbin page click on setting of the site.
Select setting of the site
Then you must select the connection information.
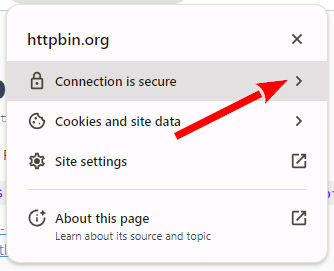
Select connection security
Now click on the certificate.
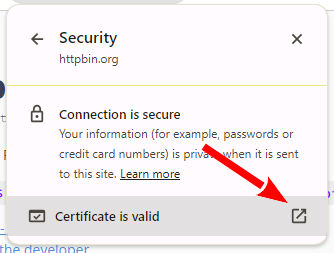
Select the certificate settings
And finally, select the line at the top of the list (the root certificate).
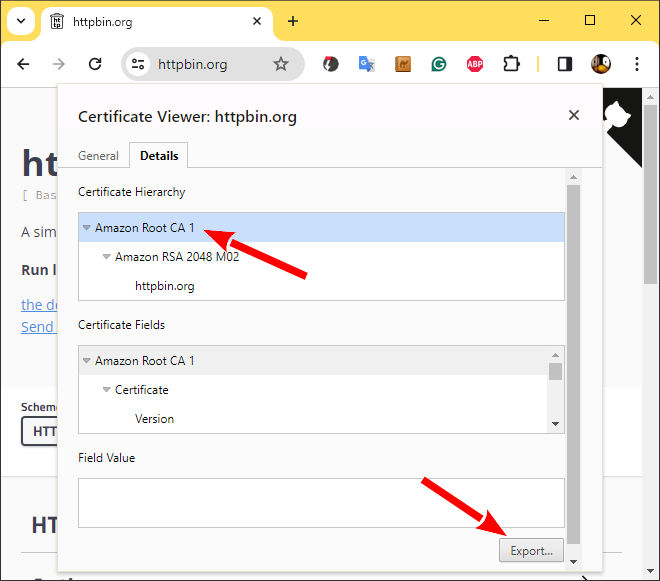
Select the root certificate and export in crt format
Export the certificate and open the file, copy the content and put all in a char array variable.
const char* rootCA= R""""(-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDQTCCAimgAwIBAgITBmyfz5m/jAo54vB4ikPmljZbyjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsF ADA5MQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEPMA0GA1UEChMGQW1hem9uMRkwFwYDVQQDExBBbWF6 b24gUm9vdCBDQSAxMB4XDTE1MDUyNjAwMDAwMFoXDTM4MDExNzAwMDAwMFowOTEL MAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxDzANBgNVBAoTBkFtYXpvbjEZMBcGA1UEAxMQQW1hem9uIFJv b3QgQ0EgMTCCASIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEPADCCAQoCggEBALJ4gHHKeNXj ca9HgFB0fW7Y14h29Jlo91ghYPl0hAEvrAIthtOgQ3pOsqTQNroBvo3bSMgHFzZM 9O6II8c+6zf1tRn4SWiw3te5djgdYZ6k/oI2peVKVuRF4fn9tBb6dNqcmzU5L/qw IFAGbHrQgLKm+a/sRxmPUDgH3KKHOVj4utWp+UhnMJbulHheb4mjUcAwhmahRWa6 VOujw5H5SNz/0egwLX0tdHA114gk957EWW67c4cX8jJGKLhD+rcdqsq08p8kDi1L 93FcXmn/6pUCyziKrlA4b9v7LWIbxcceVOF34GfID5yHI9Y/QCB/IIDEgEw+OyQm jgSubJrIqg0CAwEAAaNCMEAwDwYDVR0TAQH/BAUwAwEB/zAOBgNVHQ8BAf8EBAMC AYYwHQYDVR0OBBYEFIQYzIU07LwMlJQuCFmcx7IQTgoIMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUA A4IBAQCY8jdaQZChGsV2USggNiMOruYou6r4lK5IpDB/G/wkjUu0yKGX9rbxenDI U5PMCCjjmCXPI6T53iHTfIUJrU6adTrCC2qJeHZERxhlbI1Bjjt/msv0tadQ1wUs N+gDS63pYaACbvXy8MWy7Vu33PqUXHeeE6V/Uq2V8viTO96LXFvKWlJbYK8U90vv o/ufQJVtMVT8QtPHRh8jrdkPSHCa2XV4cdFyQzR1bldZwgJcJmApzyMZFo6IQ6XU 5MsI+yMRQ+hDKXJioaldXgjUkK642M4UwtBV8ob2xJNDd2ZhwLnoQdeXeGADbkpy rqXRfboQnoZsG4q5WTP468SQvvG5 -----END CERTIFICATE-----)"""";
Now we can set the certificate of Certification Autority, needed to validate the server httpbin to the WiFiClientSecure to be able to do the check.
The code become so.
/* This sketch shows how to use patched lan8720 with esp32
We are going to do a raw GET request to online service httpbin.org http://httpbin.org/get
by Renzo Mischianti <mischianti.org> */
// I²C-address of Ethernet PHY (0 or 1 for LAN8720, 31 for TLK110) #define ETH_PHY_ADDR 1 // DEFAULT VALUE IS 0 YOU CAN OMIT IT // Pin# of the enable signal for the external crystal oscillator (-1 to disable for internal APLL source) #define ETH_PHY_POWER 17 // DEFAULT VALUE YOU CAN OMIT IT
#include <ETH.h> #include <WiFiClientSecure.h>
// if you don't want to use DNS (and reduce your sketch size) // use the numeric IP instead of the name for the server: //IPAddress server(74,125,232,128); // numeric IP for Google (no DNS) //char server[] = "www.google.com"; // name address for Google (using DNS) char server[] = "httpbin.org"; // name address for Google (using DNS)
const char* rootCA= R""""(-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDQTCCAimgAwIBAgITBmyfz5m/jAo54vB4ikPmljZbyjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsF ADA5MQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEPMA0GA1UEChMGQW1hem9uMRkwFwYDVQQDExBBbWF6 b24gUm9vdCBDQSAxMB4XDTE1MDUyNjAwMDAwMFoXDTM4MDExNzAwMDAwMFowOTEL MAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxDzANBgNVBAoTBkFtYXpvbjEZMBcGA1UEAxMQQW1hem9uIFJv b3QgQ0EgMTCCASIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEPADCCAQoCggEBALJ4gHHKeNXj ca9HgFB0fW7Y14h29Jlo91ghYPl0hAEvrAIthtOgQ3pOsqTQNroBvo3bSMgHFzZM 9O6II8c+6zf1tRn4SWiw3te5djgdYZ6k/oI2peVKVuRF4fn9tBb6dNqcmzU5L/qw IFAGbHrQgLKm+a/sRxmPUDgH3KKHOVj4utWp+UhnMJbulHheb4mjUcAwhmahRWa6 VOujw5H5SNz/0egwLX0tdHA114gk957EWW67c4cX8jJGKLhD+rcdqsq08p8kDi1L 93FcXmn/6pUCyziKrlA4b9v7LWIbxcceVOF34GfID5yHI9Y/QCB/IIDEgEw+OyQm jgSubJrIqg0CAwEAAaNCMEAwDwYDVR0TAQH/BAUwAwEB/zAOBgNVHQ8BAf8EBAMC AYYwHQYDVR0OBBYEFIQYzIU07LwMlJQuCFmcx7IQTgoIMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUA A4IBAQCY8jdaQZChGsV2USggNiMOruYou6r4lK5IpDB/G/wkjUu0yKGX9rbxenDI U5PMCCjjmCXPI6T53iHTfIUJrU6adTrCC2qJeHZERxhlbI1Bjjt/msv0tadQ1wUs N+gDS63pYaACbvXy8MWy7Vu33PqUXHeeE6V/Uq2V8viTO96LXFvKWlJbYK8U90vv o/ufQJVtMVT8QtPHRh8jrdkPSHCa2XV4cdFyQzR1bldZwgJcJmApzyMZFo6IQ6XU 5MsI+yMRQ+hDKXJioaldXgjUkK642M4UwtBV8ob2xJNDd2ZhwLnoQdeXeGADbkpy rqXRfboQnoZsG4q5WTP468SQvvG5 -----END CERTIFICATE-----)"""";
// Initialize the Ethernet client library WiFiClientSecure client;
// Variables to measure the speed unsigned long beginMicros, endMicros; unsigned long byteCount = 0; bool printWebData = true; // set to false for better speed measurement
static bool eth_connected = false;
void WiFiEvent(WiFiEvent_t event) { switch (event) { case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_START: Serial.println("ETH Started"); ETH.setHostname("esp32-mischianti-eth"); break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_CONNECTED: Serial.println("ETH Connected"); break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_GOT_IP: Serial.println(); Serial.print("ETH MAC: "); Serial.print(ETH.macAddress()); Serial.print(", IPv4: "); Serial.print(ETH.localIP()); if (ETH.fullDuplex()) { Serial.print(", FULL_DUPLEX"); } Serial.print(", "); Serial.print(ETH.linkSpeed()); Serial.println("Mbps"); eth_connected = true; break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_DISCONNECTED: Serial.println("ETH Disconnected"); eth_connected = false; break; case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_STOP: Serial.println("ETH Stopped"); eth_connected = false; break; default: break; } }
void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); WiFi.onEvent(WiFiEvent); ETH.begin();
while (!eth_connected) {
Serial.print(".");
delay(100);
}
client.setCACert(rootCA);
// if you get a connection, report back via serial:
if (client.connect(server, 443)) {
Serial.println("Connected!");
// Make a HTTP request:
client.println("GET /get HTTP/1.1");
client.println("Host: httpbin.org");
client.println("Connection: close");
client.println();
} else {
// if you didn't get a connection to the server:
Serial.println("connection failed");
}
beginMicros = micros();}
void loop() { // if there are incoming bytes available // from the server, read them and print them: int len = client.available(); if (len > 0) { byte buffer[80]; if (len > 80) len = 80; client.read(buffer, len); if (printWebData) { Serial.write(buffer, len); // show in the serial monitor (slows some boards) } byteCount = byteCount + len; }
// if the server's disconnected, stop the client:
if (len == 0 && !client.connected()) {
endMicros = micros();
Serial.println();
Serial.println("disconnecting.");
client.stop();
Serial.print("Received ");
Serial.print(byteCount);
Serial.print(" bytes in ");
float seconds = (float)(endMicros - beginMicros) / 1000000.0;
Serial.print(seconds, 4);
float rate = (float)byteCount / seconds / 1000.0;
Serial.print(", rate = ");
Serial.print(rate);
Serial.print(" kbytes/second");
Serial.println();
// do nothing forevermore:
while (true) {
delay(1);
}
}}
The result is the same, but the world needs a lot of good guys.
Thanks
- ESP32: pinout, specs and Arduino IDE configuration
- ESP32: integrated SPIFFS Filesystem
- ESP32: manage multiple Serial and logging
- ESP32 practical power saving
- ESP32 practical power saving: manage WiFi and CPU
- ESP32 practical power saving: modem and light sleep
- ESP32 practical power saving: deep sleep and hibernation
- ESP32 practical power saving: preserve data, timer and touch wake up
- ESP32 practical power saving: external and ULP wake up
- ESP32 practical power saving: UART and GPIO wake up
- ESP32: integrated LittleFS FileSystem
- ESP32: integrated FFat (Fat/exFAT) FileSystem
- ESP32-wroom-32
- ESP32-CAM
- ESP32: use ethernet w5500 with plain (HTTP) and SSL (HTTPS)
- ESP32: use ethernet enc28j60 with plain (HTTP) and SSL (HTTPS)
- How to use SD card with esp32
- esp32 and esp8266: FAT filesystem on external SPI flash memory
- Firmware and OTA update management
- Firmware management
- OTA update with Arduino IDE
- OTA update with Web Browser
- Self OTA uptate from HTTP server
- Non-standard Firmware update
- Integrating LAN8720 with ESP32 for Ethernet Connectivity with plain (HTTP) and SSL (HTTPS)
- Connecting the EByte E70 to ESP32 c3/s3 devices and a simple sketch example
- ESP32-C3: pinout, specs and Arduino IDE configuration
- Integrating W5500 with ESP32 Using Core 3: Native Ethernet Protocol Support with SSL and Other Features
- Integrating LAN8720 with ESP32 Using Core 3: Native Ethernet Protocol Support with SSL and Other Features
- Dallas ds18b20:
- Guide to I2C on ESP32: Communication with Heterogeneous 5V and 3.3V Devices, Additional Interface Management and Scanner
- Display