Physiological roles of zinc transporters: molecular and genetic importance in zinc homeostasis (original) (raw)
Abstract
Zinc (Zn) is an essential trace mineral that regulates the expression and activation of biological molecules such as transcription factors, enzymes, adapters, channels, and growth factors, along with their receptors. Zn deficiency or excessive Zn absorption disrupts Zn homeostasis and affects growth, morphogenesis, and immune response, as well as neurosensory and endocrine functions. Zn levels must be adjusted properly to maintain the cellular processes and biological responses necessary for life. Zn transporters regulate Zn levels by controlling Zn influx and efflux between extracellular and intracellular compartments, thus, modulating the Zn concentration and distribution. Although the physiological functions of the Zn transporters remain to be clarified, there is growing evidence that Zn transporters are related to human diseases, and that Zn transporter-mediated Zn ion acts as a signaling factor, called “Zinc signal”. Here we describe critical roles of Zn transporters in the body and their contribution at the molecular, biochemical, and genetic levels, and review recently reported disease-related mutations in the Zn transporter genes.
Keywords: Zinc, Transporter, Zinc signaling, Physiology, Disease
Zinc homeostasis is essential for life
Bioinformatics analysis of the human genome reveals that zinc (Zn) can bind ~10% of all of the proteins found in the human body [1, 2]. This remarkable finding highlights the physiological importance of Zn in molecules involved in cellular processes. Zn is required for the normal function of numerous enzymes, transcriptional factors, and other proteins [3–6]. These proteins can potentially interact with Zn through specific regions such as Zn-finger domains, LIM domains, and RING finger domains. The skeletal muscles and bones serve as major tissue reservoirs for Zn [7, 8] (Fig. 1) but cannot store more Zn than the body needs. Therefore, we must take in Zn daily from our diet to maintain proper Zn-related cellular processes. While the toxicity of Zn is quite low, and it is generally non-harmful, a deficiency or excess of Zn can cause severe symptoms [4]. Zn deficiency causes eye and skin lesions, hair loss, immune dysfunction, taste abnormalities, and growth retardation, and excessively high Zn exhibits its toxicity as nausea, vomiting, fever, and headaches [9]. Symptoms of Zn deficiency are improved by Zn supplementation [4], confirming that Zn is an essential trace mineral and that Zn homeostasis is a crucial physiological process [10–15].
Fig. 1.
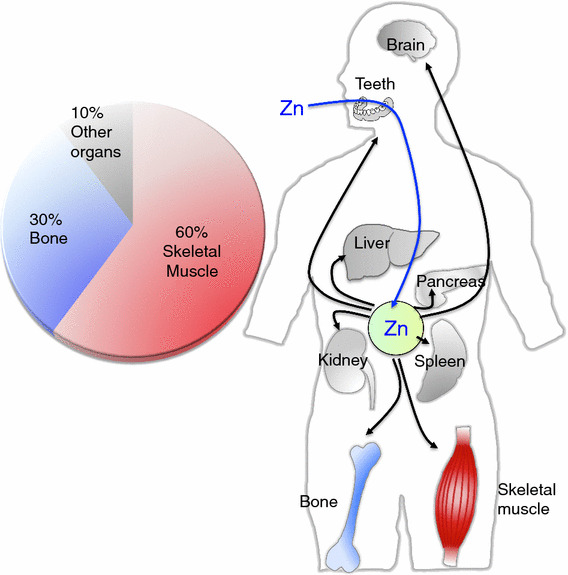
Zn storage and distribution in the body. Dietary Zn is absorbed from the small intestine and distributed to the organs. Bones and skeletal muscles act as major Zn reservoir tissues
Zn is important for development, differentiation, immune responses, neurological functions, and protein synthesis. Supplementation of Zn and Zn complex with some other compounds are reported to have some beneficial effects on our health [16–18]. Recent studies provide evidence for a growing number of physiological functions of chelatable Zn in cellular responses. Zn acts as a neuromodulator in synaptic transmissions [19, 20], and as an intracellular signal transducer in multiple cellular functions, which is regulated by Zn transporters [21–23]. A number of Zn transporters regulate Zn homeostasis and are crucial for proper cellular functions. Recent studies indicate that impaired Zn transporter function is strongly linked to clinical human diseases. There are a number of evidences about the membrane transporters having the great potential for drug targets [24–31]. Hence, Zn and Zn transporters should be considered as novel therapeutic targets.
We here describe the physiological and molecular functions of Zn transporters, which regulate Zn homeostasis and are involved in cellular biology, signal transduction, development, and human diseases.
Systemic Zn homeostasis
The adult human body contains ~2–3 g Zn. The skeletal muscle, bone, and liver/skin store 60, 30, and 5% of the total Zn, respectively, and ~2–3% is stored in other tissues [7] (Fig. 1). Less than 1% of the total Zn is found in the serum; 80% of the serum Zn is bound to serum albumin, and 20% is strongly bound to α2-macroglobulin [32, 33]. The body can adjust to up to a ten-fold increase in daily Zn intake and maintain homeostasis [34]. Approximately 0.1% of the total Zn is supplemented by daily food intake (or for infants, breast milk). Zn from food is absorbed mainly in the small intestine, and the body’s ability to absorb Zn increases up to 90% when the availability of Zn is limited [35]. When too much Zn is taken in, Zn is secreted from the gastrointestinal tract and is also disposed of through sloughing epithelial cells in the mucosa [36, 37]. As Zn is distributed within the body, each Zn transporter tightly regulates Zn levels according to the tissue, cell type, and organelle level. In terms of Zn distribution in the cellular compartments, the cytoplasm, the nucleus, and the plasma and organelle membranes contain 50, 30–40, and 10%, respectively, of the total cellular Zn [21, 38]. Although the intracellular Zn concentration reaches 10–100 μM [39–41], the actual concentration of Zn in the cytosol is estimated to be quite low, perhaps in the pico-molar to low nano-molar range, because Zn binds a number of functional proteins in the cytosol and organelles and is also distributed into vesicles in the cytosol [42–45]. Zn concentrations have been reported for mitochondria (0.14 pM) [46], the mitochondrial matrix (0.2 pM) [47], the ER (0.9 pM–5 nM), and the Golgi (0.2 pM) [48, 49] (Fig. 2, top). However, there are dramatic differences in the concentrations in some cases, which could be due to environmental differences such as oxidative conditions, protein folding, Zn interactions with other proteins, and the methods of measurement. When Zn acts as a signaling molecule, as in the Zn spark or Zn wave [50, 51], the cellular Zn concentration fluctuates in response to various biological stimuli. The further development of advanced methods for monitoring Zn levels both in vitro and in vivo will help to reveal the importance of these fluctuations in Zn levels.
Fig. 2.
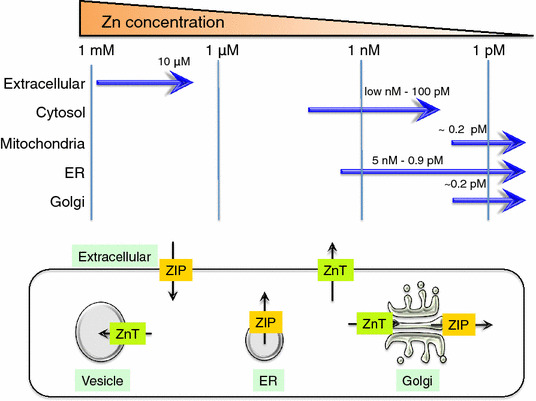
Zn storage and distribution in intracellular compartments. The upper diagram shows Zn concentrations in the extracellular region and the cellular compartments (cytosol, mitochondria, ER, and Golgi). The lower diagram shows the direction of Zn transport (black arrows) elicited by ZIP (orange) and ZnT (green) proteins expressed on these cellular compartments
Structure, function, and mechanism of Zn transporters
The Zn ion is a stable divalent cation in living organisms, and thus does not require a redox reaction for membrane transport, unlike copper or iron [52, 53]. Thus, the expression level of Zn transporters at the sites where they normally operate directly defines the net cellular Zn transport. There is growing evidence that the membrane proteins involved in Zn transport are crucial for a variety of biological processes. Although some types of permeable-channel proteins, including calcium channels, assist in moving Zn across cellular membranes, the Zn transporter (ZnT)/SLC30A family and the Zrt/Irt-like protein/solute carrier family 39 (ZIP/SLC39A) are the primary Zn-transport proteins in metazoa, and are thus closely related to Zn physiology and pathogenesis [53–57]. The mammalian genome encodes nine ZnT and 14 ZIP transporters; higher and lower numbers are encoded in other species, such as Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila melanogaster, and Gallus gallus [53, 58]. In general, ZnT-family members, which are mammalian cation-diffusion facilitator (CDF) proteins, are efflux transporters that reduce cytosolic Zn levels by transporting Zn directly out of the cell or into intracellular compartments, while ZIP-family proteins are influx transporters that elevate cytosolic Zn levels by pulling Zn into the cytosol from the extracellular fluid or from intracellular vesicles (Fig. 2, bottom).
Structural and biochemical studies reveal that ZnT transporters and their homologs act as Zn2+/H+ antiporters [59–61], which is reasonable for ZnT transporters, especially for ZnT2, ZnT3, ZnT4, and ZnT8, which localize to acidic compartments and to vesicles such as endosomes/lysosomes, synaptic vesicles, and insulin granules. However, it is still not clear how ZIP-family members transport Zn. Zn-uptake studies suggest a mode of Zn/bicarbonate symport [62–64], but this has not yet been confirmed by other methods. An in vitro study using reconstituted proteoliposomes suggested that ZIP proteins transport Zn by a selective electrodiffusional channel mechanism [65].
ZnT-family structural properties
In general, ZnT transporters form homodimers to transport Zn across cellular membranes [66, 67]. Each protomer is thought to have a topology of six transmembrane domains (TMDs) with cytosolic amino- and carboxyl-termini, based on hydropathy plots and biochemical characterization [53, 54]. Each protomer has two histidine (His) and two aspartic acid (Asp) residues in TMDs II and V (HDHD core motif) [68–70], which are thought to form an intramembranous tetrahedral Zn-binding site, because they are indispensable for Zn-transport activity (Fig. 3) [68–70]. These structural characteristics almost coincide with those of the Escherichia coli homolog YiiP, which is the only ZnT-family protein whose overall three-dimensional structure has been verified [71, 72]. YiiP’s 3D structure shows a Y-shaped homodimer in which each protomer has 6 TMDs [71–74]. These TMDs are grouped into a compact four-helix (TMDs I, II, IV, and V) bundle and a two-helix pair (TMDs III and VI). The compact four-helix bundle forms an inner core that creates a channel, where the intramembranous tetrahedral Zn-binding site (site A) is formed by four hydrophilic residues (a DDHD core motif) in TMDs II and V, while the two-helix pair forms an antiparallel configuration outside the bundle. Each protomer’s cytosolic carboxyl-terminal domain, which consists of two α helixes and three β sheets, has two Zn-binding sites (site C) and adopts the structure of a metallochaperone-like fold. This metallochaperone-like structure is highly conserved in other bacterial ZnT homologs despite a high degree of sequence variety [75–77], and is expected to be conserved in metazoan ZnT transporters. Although there is much evidence to support the importance of this structure, the recent discovery of CDF proteins lacking this region raises questions about its precise role [78]. Another Zn-binding site is located at the interface between the membrane and the cytoplasmic domains (site B) in YiiP, but this site is not conserved among ZnT transporters.
Fig. 3.
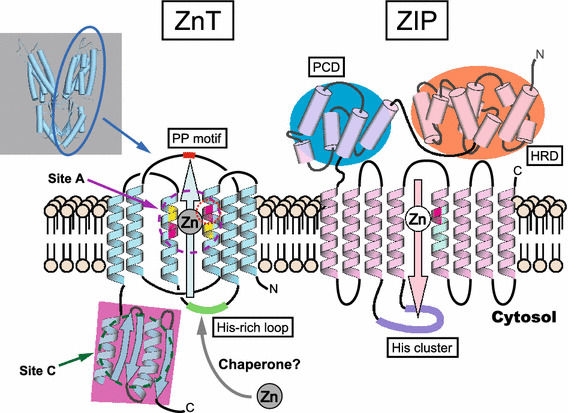
The putative structures of ZnT and ZIP transporters. Left side: the putative topology of ZnT transporters. ZnT transporters efflux Zn from the cytosol to the extracellular space or to the lumen of intracellular compartments. ZnT transporters are thought to have six TMDs consisting of two bundles of a compact four-helix (TMDs I, II, IV, and V) and a two-helix pair (TMDs III and VI). They are thought to function as Y-shaped dimers for Zn transport, based on the structural information of E. coli YiiP (shown in _top_-left panel, PDB 3H90) [71–74]. Most ZnT transporters have an indispensable intramembranous Zn-binding site (site A, indicated in magenta circle) consisting of two His (magenta) and two Asp (yellow) residues (HDHD core motif). The position of the His residue (red circle) is speculated to regulate metal substrate specificity. The cytosolic carboxyl-terminal domain (pink square) contains the cytosolic Zn-binding site (site C, indicated in dark green circle), and is thought to consist of two α helixes and three β sheets (αββαβ). The Zn-binding site corresponding to site B in YiiP is omitted because this site is not conserved among ZnT transporters. The cytosolic His-rich loop is indicated in green. The PP motif in the luminal loop in ZnT5 and ZnT7, which is important for TNAP activation [139], is shown in red. Putative Zn chaperon proteins in the cytosol may transfer Zn to the ZnT transporters (see text). Right side: the putative topology of ZIP transporters. This diagram is based on the information available for ZIP4, which is in the LIV-1 subfamily [93, 95]. ZIP transporters mobilize Zn in a direction opposite to that of ZnT transporters. ZIP transporters are thought to have eight TMDs and to function as dimers (not shown). The His residue (magenta) in TMD V is speculated to form part of an intramembranous Zn-binding site, and this position may be involved in specifying the substrate metal. ZIP transporters of the LIV-1 subfamily are characterized by a long extracellular amino-terminal portion containing the helix-rich domain (HRD, orange) and the PAL motif–containing domain (PCD, blue). A potential metalloprotease motif (HEXPHEXGD) is embedded in TM helix V (pale green). Some ZIP transporters have a His cluster (purple) in the cytosolic loop between TMDs III and IV
Several mechanistic models have been proposed to explain how YiiP transports Zn. An autoregulation model proposes that YiiP’s Zn-transport activity is regulated by an allosteric mechanism: the cytosolic carboxyl-terminal domain containing site C senses and binds the Zn ion, which induces a scissor-like movement of the homodimers that interlocks the TMDs at the dimer interface, thereby modulating the coordination geometry of the intramembranous Zn (site A) for Zn transport [71, 72]. Another model proposes an alternative-access mechanism in the Zn2+/H+ exchange, in which TMDs of YiiP can adopt cytosolic-facing and periplasm-facing conformations, both of which can bind Zn ions (in site A) or protons, and the extracellular proton provides a driving force for exporting the Zn ions from the cytosol [73, 74]. In this mechanism, Zn binding to the cytosolic carboxyl-terminal portion (site C) might induce conformational changes in the TMDs for Zn transport in alternative-access mechanism [77], and is important for stabilizing the homodimers [73, 74]. Most ZnT transporters and their homologs have a characteristic cytosolic loop between TMDs IV and V that is enriched in His residues. The His-rich loop is thought to be essential for modulating Zn transport and for metal substrate specificity [59, 79], and thus might deliver Zn from the cytosol to the Zn-binding site (site A) within the TMDs as a key Zn-binding motif.
Although all ZnT transporters have an intramembranous tetrahedral Zn-binding site (site A) in the HDHD core motif [68–71], ZnT10 is unique in having an Asn residue instead of a His residue in TMD II (the NDHD core motif in TMDs), which enables ZnT10 to transport manganese (Mn) [80]. An S. pneumonia ZnT homolog, the Mn-specific transporter MntE, has an Asn residue in the corresponding position in TMD II (NDDD core motif), and this residue is required for its ability to transport Mn [81]. These results suggest that this position in TMD II is critical for regulating metal substrate specificity. Consistent with this possibility, replacing the His residues in TMD II with Asp residues (i.e., an alteration from the HDHD motif to the DDHD core motif) allows ZnT5 and ZnT8 to transport cadmium as well as Zn [68]. Based on their phylogenetic relationships and metal substrate specificities, CDF transporters are classified as Zn-CDF, Zn/Fe-CDF, or Mn-CDF transporters. All ZnT transporters belong to the Zn-CDF group [69, 82], and they are further subdivided into four groups: (1) ZnT1 and ZnT10; (2) ZnT2, ZnT3, ZnT4, and ZnT8; (3) ZnT5 and ZnT7; and (4) ZnT6 [58, 69, 83]. This system does not place ZnT10 in the Mn-CDF family, despite its ability to transport Mn; therefore, its classification might have to be reconsidered.
While most ZnT transporters form homodimers to transport Zn, ZnT5 and ZnT6 (and their orthologs) form heterodimers [66, 84–86]. In the ZnT5-ZnT6 heterodimer, ZnT6 functions as an auxiliary subunit because it lacks Zn-transport activity; it may have a modulatory function for Zn transport [86]. In addition to ZnT5 and ZnT6, other ZnT transporters were recently found to form heterodimers [87, 88] that might regulate Zn homeostasis under physiological and pathological conditions in manners distinct from their respective homodimers [87]. Covalent dityrosine bonds within the cytosolic carboxyl-terminal domain are proposed to regulate the homo- and heterodimerization of ZnT transporters [88]; thus, clarifying the molecular mechanism by which these covalent dityrosine bonds are created would help us understand how the heterodimers form.
ZIP-family structural properties
Although the structure of ZIP-family transporters has proven elusive [89], recent studies have added to our understanding of their structural and mechanistic characteristics. As with ZnT transporters, ZIP transporters form homodimers or heterodimers to transport Zn [65, 90–92]. Each protomer is thought to have eight TMDs and a membrane topology in which the amino- and carboxyl-terminal ends are both located outside the plasma membrane or in the lumen of a subcellular compartment (Fig. 3). Recent computational studies present a structural model for ZIP4 that predicts eight TMDs and a homodimer structure [93]. Based on their phylogenetic relationships, ZIP transporters can be classified into subfamilies (I, II, LIV-1, and gufA) [62, 94]. Most mammalian ZIP-family members are classified into the LIV-1 subfamily, which is characterized by a potential metalloprotease motif (HEXPHEXGD) in TMD V and a CPALLY (PAL) motif immediately preceding the first TMD. A recent study of the crystal structure of the long extracellular amino-terminal portion of ZIP4 revealed that the portion forms a homodimer centered around the PAL motif-containing domain (PCD) [95]. Each protomer (extracellular portion) consists of two structurally independent subdomains (PCD and a helix-rich domain: HRD), both of which play pivotal but distinct roles in Zn transport, although it has not been revealed whether the structure is altered by Zn binding. Zn transport by ZIP4 across the plasma membrane requires extracellular His residues [96], raising the interesting possibility that His residues in the extracellular portion may alter the homodimer conformation through Zn binding. The PAL motif is found in most LIV-1 members except for ZIP7 and ZIP13; thus, ZIP4’s structure provides clues to the structure and function of the extracellular portions of other proteins in the LIV-1 subfamily. Based on the sequence similarity of the extracellular portion, the LIV-1 subfamily proteins are divided into four subgroups: (I) ZIP4 and ZIP12; (II) ZIP8 and ZIP14; (III) ZIP5, ZIP6, and ZIP10; and (IV) ZIP7 and ZIP13. Proteins in the subgroup III have a unique domain called a prion fold in the extracellular region proximal to the membrane, indicating an evolutionary link between these ZIP proteins and the prion protein family [97]. Proteins in the subgroup IV have a degenerate PAL motif. The extracellular portion of the LIV-1 subfamily is thought to be important for dimer formation, but may have different dimerization properties in different subgroup members. In ZIP4, the extracellular portion forms homodimers without an intermolecular disulfide bond, while that of ZIP14 is predicted to form a disulfide bond at the dimerization interface [95]. As with ZnT transporters, ZIP transporters may operate as heterodimers [92], in which the extracellular portion regulates dimerization. ZIP transporters mobilize not only Zn, but also iron, Mn, and cadmium across the cellular membranes. The activity of ZIP8 and ZIP14 in transporting these ions has been well investigated through in vitro kinetic evaluation [63, 64, 98] and by physiology and pathology studies in vivo [99–103]. In ZIP8 and ZIP14, the Glu residue in TMD V rather than a His residue may recognize these metals. However, the molecular mechanism of this recognition has not yet been clarified, and other common mechanisms may help regulate the metal specificities of the ZIP transporters.
Mechanisms of Zn transporter expression and modification
Because Zn transporters play physiological roles in a wide range of cellular processes, increases or decreases in Zn-transporter expression must be precisely timed for proper Zn transport. The expression of ZnT and ZIP transporters is sophisticatedly coordinated by transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulations—including transcriptional activation, mRNA stabilization, protein modifications, trafficking to target organelles, and degradation—in response to various stimuli, including hormones, cytokines, ER stress, oxidative stress, and hypoxia [104–115], all of which is conducted in a cell- and tissue-specific or a differentiation and developmentally regulated manner. For instance, _Zip_6 upregulation by the transcriptional factor STAT3 leads to the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is critical in development [116]. Recent studies revealed that microRNAs control the expression of ZnT and ZIP transporters [117–119]. These expression controls all contribute to cellular Zn homeostasis, and thus a normal physiological state, and are involved in disease pathogenesis in some cases. This review focuses only on the regulation of Zn transporters by Zn status; other stimuli that affect Zn transporter expression are reviewed elsewhere [52–55, 57, 120–123].
In vertebrates, the rapid Zn-responsive transcriptional control of some ZnT transporters requires the Zn-sensing transcription factor MTF-1 (metal response element-binding transcription factor-1). MTF-1 increases ZnT1 transcription, as does metallothionein, by binding metal-responsive elements (MREs) in response to excessive Zn [15, 124]. A similar regulatory mechanism functions in the Zn-responsive increase of ZnT2 transcription [104]. However, ZIP10 transcription is repressed via MTF-1 binding to MREs, by which MTF-1 pauses Pol II transcription [12, 125]. Another Zn-finger transcription factor, ZNF658, also regulates Zn-responsive Zn transporter expression [126]. Because transcriptional regulation by ZNF658 is completely independent of MTF-1, ZNF658 is likely to be important in Zn homeostasis in a unique manner, although this point needs to be clarified.
The expression of ZIP and ZnT transporters is regulated posttranslationally in a Zn-dependent manner. This is exemplified in ZIP4 expression, which increases significantly in response to Zn deficiency, causing an accumulation of ZIP4 protein at the apical surface of intestinal epithelial cells. When cytosolic Zn levels are sufficiently elevated, the accumulated ZIP4 on the plasma membrane is rapidly endocytosed and then degraded [127–131]. A similar endocytosis in response to excessive Zn has been found for several ZIP transporters [132]. The endocytosed ZIP4 and other ZIP transporters are degraded in the ubiquitin–proteasome or lysosomal degradation pathway, suggesting that a conserved Zn-responsive endocytosis mechanism may maintain Zn homeostasis by controlling the expression of ZIP transporters. Severe Zn deficiency causes ZIP4 to be processed so that the extracellular amino-terminal portion is proteolytically cleaved [129, 133]. A similar proteolytic processing mechanism is found in ZIP10 in response to Zn deficiency [134] and in ZIP6 for its trafficking to the plasma membrane [134]. Since the cleaved ZIP transporters (the 8 TM helices lacking the amino-terminal portion) can still transport Zn [95, 129], it is possible that the extracellular portion of these ZIP proteins modulates Zn-transport activity, and that the proteolytic processing of the amino-terminal portion is a crucial mechanism for regulating Zn uptake. Intriguingly, this processing also occurs in ZIP10 in the prion-infected mouse brain [134]. The posttranslational regulation of ZnT transporters in response to Zn status is poorly understood. However, it is interesting that some ZnT transporters (ZnT4 and ZnT6) traffic Zn from intracellular compartments to the cell periphery when Zn levels are high [135]. The regulation of Zn-induced ZnT translocation mechanisms is important for proper cellular Zn homeostasis, as is also true for copper, for which the transporters ATP7A and ATP7B are important regulators [136].
Zn transporters regulate Zn enzyme activation and maturation
There is growing evidence that Zn transporters contribute to various physiological events and to disease pathogeneses by mobilizing Zn ions across biological membranes. One crucial function of Zn transporters is the activation of Zn enzymes, which is mediated by Zn coordination at the enzyme’s active site. In this section, we will briefly summarize the sophisticated molecular mechanism by which Zn transporters activate Zn enzymes by describing the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP) activation process.
Many ZnT transporters pass through the ER and Golgi apparatus, and can thus carry Zn from the cytosol into the lumen. However, the luminal Zn mobilized by a specific ZnT transporter is probably limited to a very specific, critical role, if any, in these organelles. For example, ZnT5–ZnT6 heterodimers and ZnT7 homodimers are indispensable for activating TNAP, a Zn-requiring ectoenzyme, by supplying Zn to the _apo_-TNAP protein [137, 138]. Interestingly, both complexes (even mutant ZnT5–ZnT6 heterodimers that cannot transport Zn) stabilize the TNAP protein, indicating that the processes of protein stabilization and metalation can be divided in Zn–TNAP interactions. TNAP activity is severely diminished in cells lacking both ZnT5–ZnT6 heterodimers and ZnT7 homodimers, and is not restored by excess Zn supplementation in the culture medium [137]. Thus, ZnT5–ZnT6 heterodimers and ZnT7 homodimers probably control TNAP activation through an elaborate two-step regulation mechanism: the TNAP protein (_apo_-TNAP) is first stabilized in the early secretory pathway, after which the _apo_-TNAP protein is converted to _holo_-TNAP by Zn that is supplied by ZnT5–ZnT6 heterodimers or ZnT7 homodimers.
In this two-step mechanism, the Pro-Pro (PP) motif in the luminal loop of ZnT5–ZnT6 heterodimers and ZnT7 homodimers (Fig. 3) is suggested to be important [139]. The PP motif is highly conserved in ZnT5 and ZnT7 across multiple species, but is not conserved in other ZnTs. A double Ala substitution in ZnT5’s PP motif severely impairs its ability to activate TNAP, but does not appear to significantly impair its ability to transport Zn. The PP motif is thought to be located just above the HDHD core motif in ZnT5 and ZnT7, suggesting that a unique cooperative mechanism may operate between these two motifs. Interestingly, ZnT5 with mutations in the amino acids of the HDHD core motif (e.g., H451D or D599E) fails to activate TNAP [139], although neither mutation impairs ZnT5’s ability to transport Zn [68, 70], suggesting that the HDHD core motif is important for enzyme activation in addition to determining metal specificity [68, 80].
Many Zn-requiring ectoenzymes probably become functional by binding Zn in the secretory pathway, which suggests that disturbing the cytosolic Zn metabolism may affect their activation. This idea is based on the activation process of copper-requiring ectoenzymes, in which the cytosolic copper chaperone Atox1 is crucial for transferring cytosolic copper to the ectoenzyme for its metalation through _trans_-Golgi network-resident copper-transporting P-type ATPases (ATP7A and ATP7B). Thus, copper-requiring ectoenzymes are not fully activated in cells lacking Atox1 [140], even though cytosolic copper levels are elevated [141]. Interestingly, disturbing cytosolic Zn metabolism by disrupting the ZnT1, ZnT4, and metallothionein genes significantly impaired TNAP activation despite elevated cytosolic Zn [142]. Considering the similar enzyme-activation defects in cells lacking Atox1 and those lacking ZnT1, ZnT4, and metallothionein, it is attractive to hypothesize that putative Zn chaperone proteins, controlled by the cooperative functions of ZnT1, ZnT4, and metallothionein, may function in the transfer of cytosolic Zn to ZnT transporters such as the ZnT5–ZnT6 heterodimers or ZnT7 homodimers [142] (Fig. 3).
Zn transporters mediate Zn signaling
A number of cellular proteins interact with Zn in a specific domain to exert their biological functions. Studies have revealed that Zn acts not only as an accessory molecule for proteins but also as a signaling molecule, much like cAMP and calcium [22, 143], and thus regulates various signaling pathways such those mediated by growth factors, hormones, [144], or Toll-like or cytokine receptors [108, 112, 116, 145]. Consider the following examples:
- ZIP6: ZIP6-regulated Zn transport suppresses E-cadherin transcription via SNAIL, and this suppression is important in the embryogenesis of the zebrafish gastrula [116, 146]. ZIP6 also adjusts TLR-signal-mediated immune responses [108].
- ZIP8: ZIP8 transcription is controlled by NF-κB. ZIP8-mediated Zn transport decreases proinflammatory responses by suppressing IκB activity [110].
- ZIP10: ZIP10 inhibits caspase activity, in turn promoting cell survival in B cell development [112]. ZIP10 also regulates B-cell antigen-receptor (BCR) signaling, which includes CD45 phosphatase activity [147].
- ZIP13: ZIP13-mediated Zn transport regulates BMP/TGF-β signaling by controlling SMAD’s nuclear translocation [148].
- ZIP14: ZIP14-mediated Zn transport negatively regulates phosphodiesterase (PDE), to maintain cAMP levels within GPCR signaling pathways [147, 148]. In addition, ZIP14 modulates protein tyrosine phosphatase 1b (PTP1B) to promote c-Met phosphorylation and contribute to liver regeneration [149].
These functions of ZIP-family members indicate their principal relationships to systemic growth and bone homeostasis. Interestingly, the Zn signals mediated by each Zn transporter regulate not only the influx or efflux of Zn ions, but also specific cellular events. Therefore, a deeper understanding of the biological functions of each Zn transporter will provide further insight into the Zn transporter–Zn axis as a crucial physiological system.
Physiology and pathophysiology of ZnT and ZIP-family members
Various biological functions have been reported for ZnT and ZIP-family members (Fig. 4; Tables 1, 2). Knockout (KO) studies in mice and human genetic studies have revealed unique physiopathological roles of each ZnT and ZIP protein, as follows.
Fig. 4.
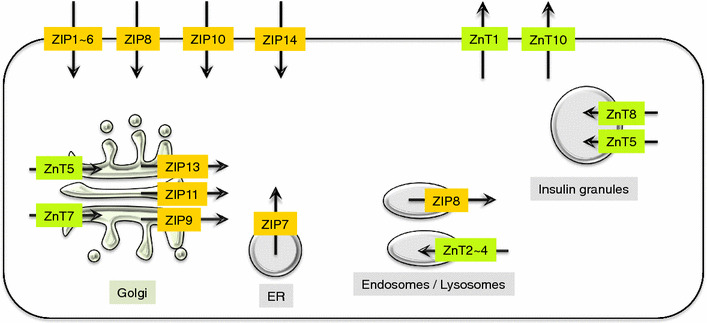
ZnT and ZIP intracellular localizations. The diagram shows the localization of ZnT (green) and ZIP (yellow) proteins, and the direction of Zn transport (black arrows) for each organelle and plasma membrane. In terms of Zn homeostasis, ZnT and ZIP maintain the influx and efflux of Zn ions between the cell and extracellular spaces, or between the cytosol and the organelle compartments, thereby maintaining appropriate Zn concentrations in the cells
Table 1.
Genetic evidence for the biological relevance of ZnT transporters
| Official symbol | Protein | Mutation type | OMIM Gene locus/ phenotype | Abnormality (*Phenotypes in human) | Expression | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slc30a1 | ZnT1 | KO | 609521/ - | Embryonic lethal | Ubiquitous | [150] |
| Slc30a2 | ZnT2 | *Mutation | 609617/ 608118 | *Low Zn in milk | Widely distributed | [151–154] |
| Slc30a3 | ZnT3 | KO | 602878/ - | Prone to seizures; similar to the synaptic and memory deficits of Alzheimer’s disease; required for pre-synaptic Erk activation and hippocampus-dependent memory | Brain | [155, 156] |
| Slc30a4 | ZnT4 | Mutation | 602095/ - | Lethal milk mutant: low Zn in milk | Ubiquitous | [157] |
| Slc30a5 | ZnT5 | KO | 607819/ - | Growth retardation, osteopenia and male-specific cardiac death; impaired mast cell functions | Ubiquitous | [158, 159] |
| Slc30a6 | ZnT6 | 611148/ - | Widely distributed | |||
| Slc30a7 | ZnT7 | KO | 611149/ - | Growth retardation, low body Zn status and low fat accumulation | Widely distributed | [160, 161] |
| Slc30a8 | ZnT8 | KO; *SNP | 611145/ 125853 | Impairment of insulin secretion and insulin-crystal formation; *type I and II diabetes mellitus | Pancreas | [162, 167] |
| Slc30a10 | ZnT10 | *Mutation | 611146/ 613280 | *Parkinsonism, hypermanganesemia, syndrome of hepatic cirrhosis, dystonia, polycythemia | Small intestine Liver Brain | [169, 170] |
ZnT: physiology and pathophysiology
- ZnT1: genetic _Znt1_-KO mice show embryonic lethality [150].
- ZnT2: the genetic loss of ZnT2 function reduces Zn levels in breast milk [151] and causes Zn-deficiency-related symptoms in infants [152–154].
- ZnT3: _Znt3_-KO mice have Alzheimer’s-like memory impairment, indicating that ZnT3 is involved in maintaining memory [155, 156].
- ZnT4: mice with a genetic loss of Znt4 function (called lethal-milk mutant mice) produce milk with markedly low Zn content [157]. ZnT4’s function in regulating the Zn content of breast milk in mice is similar to that of ZnT2 in humans. The lethal-milk phenotype of these mice clearly demonstrated that sufficient dietary Zn is indispensable for the development and growth of the pups.
- ZnT5: _Znt5_-KO mice have impaired mast-cell-mediated immune responses [158], severe osteopenia, and bradyarrhythmia-induced male-specific sudden death [159].
- ZnT7: in _Znt7_-KO mice, both growth and the accumulation of body fat are impaired [160]. In addition, male KO mice fed a high-fat diet have symptoms of metabolic disorders such as insulin and glucose intolerance and hyperglycemia [161].
- ZnT8: bioinformatic analysis showed that the ZnT8 gene is strongly related to type I and II diabetes [162, 163]. ZnT8 expressed in pancreatic β cells is involved in secreting insulin, forming crystals [164–166], and eliminating insulin by the liver [167].
- ZnT10: the loss of ZnT10 function results in Parkinsonism and dystonia-like symptoms with hypermanganesemia, chronic liver dysfunction, and hematopoiesis disorders such as polycythemia [103, 168–170].
ZIP: physiology and pathophysiology
While the biochemical characterization of ZIP transporters is less complete than that of ZnT transporters, their physiological significance is evident (Fig. 4). Knockout studies of ZIP-family genes have reported many unique phenotypes (Table 2).
- ZIP1, ZIP2, and ZIP3: KO studies of Zip1, Zip2, and Zip3 in mice did not reveal any phenotypes; however, embryonic development was abnormal if the mother’s Zn intake was limited. Therefore, during pregnancy, lacks of the ZIP1, ZIP2, and ZIP3 genes are thought to be more susceptible to Zn deficiencies [171–174].
- ZIP4: ZIP4’s physiological functions are well characterized in both mice and humans. A genetically mutated SLC39A4/ZIP4 allele that loses ZIP4 function results in a rare autosomal recessive disorder (acrodermatitis enteropathica) characterized by severe Zn-deficiency symptoms such as periorificial and acral dermatitis, alopecia, and diarrhea in infants [175–177]. Zn supplements improve these symptoms, and allow the patient to survive; without supplementation, the patients die within two years [175]. ZIP4 expressed on the apical membrane of enterocytes regulates Zn absorption [127]. ZIP4 also supports embryonic development by incorporating Zn into the embryo [178].
- ZIP5: ZIP5 loss-of-function mutations are associated with autosomal-dominant nonsyndromic high-grade myopia [179].
- ZIP7: the genetic disruption of Zip7 in mouse intestine enhances ER stress signaling, which associates with cell death occurred in intestinal epithelium by loss of ZIP7 [180], which is discussed in the next part.
- ZIP8: ZIP8 increases the expression of matrix-degrading enzymes by controlling Zn influx into chondrocytes, inducing osteoarthritis in mice and humans [107]. Z_ip8_-KO mice are embryonic lethal because of abnormal organ morphogenesis and hematopoiesis [181]. ZIP8 variants affect the function of Mn-dependent enzymes, which is related to glycosylation [102]. In addition, ZIP8 has a non-synonymous variant that is linked with schizophrenia [182]. The single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis in the patients of inflammatory bowel disease reveals that a ZIP8 variant is associated with Crohn’s disease and gut microbiome composition [183].
- ZIP9: ZIP9 is expressed in breast cancer and prostate cancer cell lines. Testosterone treatment increases intracellular Zn concentrations, thereby upregulating a gene related to apoptosis. These findings suggest that ZIP9 is important for the mechanisms of cellular functions in cancer cells [184].
- ZIP10: _Zip10_-KO B cells in mice are developmentally and functionally impaired, which disrupts immune responses [112, 147]. ZIP10 expressed in breast cancer and renal carcinoma cells affects cancer progression [185, 186].
- ZIP12: the genetic disruption of Zip12 attenuates the development of pulmonary hypertension in a hypoxic atmosphere in rats [114].
- ZIP13: bone, tooth, and connective tissues development and systemic growth are impaired in _Zip13_-KO mice and in patients with loss of functions of ZIP13 proteins [148].
- ZIP14: as in _Zip13_-KO mice, _Zip14_-KO mice have defects in bone development and systemic growth [187]. ZIP14 is also associated with hepatocyte proliferation, decreased insulin signals, and increased production of leptin and other adipokines [188]. One very recent study suggested that the genetic loss of ZIP14 function is involved in Parkinsonism-dystonia with neurodegeneration and hypermanganesemia in childhood [103].
Table 2.
Genetic evidence for the biological relevance of ZIP transporters
| Official symbol | Protein | Mutation type | OMIM Gene locus/ phenotype | Abnormality (*Phenotypes in human) | Expression | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slc39a1 | ZIP1 | KO | 604740/ – | Abnormal embryonic development | Ubiquitous | [172] |
| Slc39a2 | ZIP2 | KO | 612166/ – | Abnormal embryonic development | Liver, ovary, skin, dendritic cell | [173] |
| Slc39a3 | ZIP3 | KO | 612168/ – | Abnormal embryonic and T-cell development | Widely distributed | [171] |
| Slc39a4 | ZIP4 | KO; *Mutation | 607059/ 201100 | Embryonic lethal, *acrodermatitis enteropathica | Small intestine | [95, 175–177] |
| Slc39a5 | ZIP5 | KO; *Mutation | 608730/ 615946 | Intestinal Zn excretion; Pancreatic Zn accumulation. *Nonsymptomatic high myopia | Small intestine, kidney, pancreas | [179] |
| Slc39a6 | ZIP6 Liv1 | 608731/ – | Abnormal gonad formation and E-cadherin expression. Glial cell migration in Drosophila | Widely distributed | [92, 146] | |
| Slc39a7 | ZIP7 Ke4 | 601416/ – | Impaired melanin synthesis, FGFR and Notch signaling in Drosophila. Colon epithelial cell differentiation and proliferation in mouse | Widely distributed Colon | [180, 205, 206] | |
| Slc39a8 | ZIP 8 | KO; *Mutation | 608732/ 616721 | Cdm mouse: Resistance to cadmium-induced testicular damage, Crohn’s disease. *Disorder of Mn transporter and glycosylation | Widely distributed | [99, 102, 182, 183] |
| Slc39a9 | ZIP9 | Expressed in breast and prostate cancer cell lines. Apoptosis regulation | Widely distributed | [184] | ||
| Slc39a10 | ZIP 10 | KO | 608733/ – | B-cell development. Breast cancer progression | Widely distributed. Renal cell carcinoma B-cell | [92, 147, 185, 186] |
| Slc39a13 | ZIP13 | KO *Mutation | 608735/ 612350 | Growth retardation, abnormal hard and connective tissue development. *Spondylocheiro dysplastic Ehlers–Danlos syndrome | Hard and connective tissues | [148, 196] |
| Slc39a14 | ZIP14 | KO *Mutation | 608736/ 617013 | Growth retardation and impaired GPCR signaling. Impaired Mn homeostasis. Adipokine production. *Childhood-onset Parkinsonism-dystonia | Widely distributed. Bone and cartilage | [103, 187, 188] |
Among the ZIP family, we introduce the most current information about selected ZIP-family members as follows.
ZIP7: role of Zn signaling in the self-renewal of intestinal epithelial cells
Ohashi et al. demonstrated that ZIP7, which predominantly localizes to the ER membrane, promotes rapid cell proliferation in intestinal crypts by maintaining ER function [180]. The continuous self-renewal of the intestinal epithelium depends on precisely regulated stem-cell activity and the vigorous proliferation of progenitor daughter cells [189]. A growing body of evidence indicates that the unfolded protein response (UPR) plays a crucial role in regulating the proliferation of the intestinal epithelium, whereas excessive UPR induces ER stress, leading to cell death [190–193]. Therefore, the balance of UPR signaling must be finely tuned for the self-renewal of intestinal epithelial cells. However, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear.
Ohashi et al. recently found that mice with an intestinal-epithelium-specific Zip7 deletion exhibited extensive apoptosis in the stem-cell-derived transit-amplifying (TA) cells due to increased ER stress. This abnormality causes the loss of intestinal stem cells and irreversibly impairs the induction of self-renewal of the intestinal epithelium, and is consequently lethal within a week after Zip7 deletion. Taken together, the TA cells in the lower region of the intestinal crypt enhance UPR signaling to support vigorous cell proliferation. The UPR signaling then upregulates ZIP7, which maintains Zn homeostasis under ER stress and facilitates epithelial proliferation. This mechanism is important for maintaining intestinal stemness, because stem cells are highly susceptible to the ER-stress-induced death of neighboring cells. Hence, ZIP7 is considered a novel regulator of the homeostasis of the intestinal epithelium [180].
ZIP10: role of Zn signaling in B-cell function and embryonic development
ZIP10 is expressed in the spleen, thymus, and lymph nodes. Among the various immune cells, ZIP10 is highly expressed in B cells, especially in early B cell stages [147]. The deletion of Zip10 gene specifically in pro-B cells reduces the B-cell counts and plasma Ig levels in mice [112]. A B-cell-specific Zip10 deficiency impairs B-cell differentiation and increases some types of caspase activity leading to apoptosis; the same result is obtained by treating cells with a chemical Zn-ion chelation compound. The expression levels of other ZIP-family members are unchanged in _Zip10_-KO mice, indicating that ZIP10 signaling specifically regulates caspase activity, thereby promoting the survival of pro-B cells. ZIP10 is also required for functions of mature B cells. Namely, BCR-induced B-cell proliferation is abolished in _Zip10_-KO mice, due to that ZIP10-Zn signaling regulates activity of CD45, a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPase), which is needed for BCR signal transduction, which contributes to antibody-mediated immune responses. [147]. Therefore, ZIP10 is a key player to fine-tune both early and late B cell stages.
Taylor et al. reported that ZIP10’s physiological function is also required for embryonic development and cell migration in fish. Zip10 knockdown causes head, eye, heart, and tail deformities in zebrafish. They also demonstrated that ZIP10 and ZIP6, the closest molecular relative of ZIP10, form a heteromer to become functional. Since ZIP6 is involved in cell migration during embryogenesis of zebrafish [116] so ZIP6 and ZIP10 may cooperate their functions in some cases [92].
ZIP13: role of Zn signaling in the development of hard and connective tissues
ZIP13 forms a homodimer and localizes to the Golgi apparatus. ZIP13 mobilizes Zn from the Golgi to the cytosolic compartment, contributing to Zn homeostasis [90, 91, 148]. ZIP13 is involved in the development of hard and connective tissues [148, 194, 195], in the following ways. (1) Bone formation: _Zip13_-KO mice have growth impairments such as osteopenia and growth retardation. Some processes required for bone elongation, such as osteoblast-mediated bone formation and endochondral ossification, are also impaired [148]. (2) Skin morphology: _Zip13_-KO mice have fragile skin caused by a decrease in the fibril-associated collagen layer [148, 194]. (3) Odontological morphology: _Zip13_-KO mice have odontological defects such as malocclusion, deformity, and incisor-tooth breakage [148, 194].
In _Zip13_-KO mice, the functional genes related to cell adhesion and polarity are decreased in primary osteoblasts and chondrocytes [148]. The RNA expression of Msh homeobox2 (Msx2), which regulates the development of bones and teeth by BMP signaling, and of dermal type 1 collagen mRNA, is decreased in cells prepared from _Zip13_-KO mice. In contrast, the mRNA of Runt-related transcriptional factor 2 (Runx2), which affects osteoblast maturation, accumulates excessively. BMP4 does not induce Msx2 mRNA in _Zip13_-KO primary osteoblasts; however, it dramatically increases Runx2 mRNA expression. TGF-β induces Smad7 mRNA and reduces type 1 collagen (Col1a2) in _Zip13_-KO primary dermal fibroblasts. Ectopic ZIP13 overexpression in _Zip13_-KO primary cells rescues impaired BMP4/TGF-β signaling. Interestingly, the TGF-β–mediated nuclear translocation of SMAD, but not its phosphorylation, is inhibited in the _Zip13_-KO cells, concomitant with the increase and decrease of Zn levels in the Golgi and nucleus, respectively. A short-term Zn deficiency in rats increases the Zip13 mRNA; however, BMP2 is suppressed in the bones, causing defective bone formation. The ZIP13 molecule is therefore significant in BMP/TGF-β signaling.
The abnormal phenotypes in dermal, skeletal, ocular, and dental tissues of _Zip13_-KO mice are clinically similar to human Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS), a genetic disorder that causes the abnormal development of connective tissues [196]. Notably, loss-of-function mutations in the ZIP13 gene have been identified in patients with the spondylocheirodysplastic form of EDS (SCD-EDS), specifically a G64D mutation at the c.221 nucleotide and a frameshift mutation with a deletion between the c.483–491 nucleotides [148, 196]. ZIP13-mutant proteins are susceptible to degradation by the valosin-containing protein (VCP)-linked ubiquitin (Ub)-proteasome pathway, and this degradation process is suppressed by proteasome-inhibitor treatment [91]. Since ZIP13 mutants are susceptible to Ub-proteasome pathways, Zn homeostasis via ZIP13 is impaired, leading to the severe SCD-EDS pathogenesis [91, 197].
ZIP14: role of Zn signaling in systemic growth
ZIP14, which is encoded by the SLC39A14 gene, is expressed in the plasma membrane [187, 198]. ZIP14 is expressed in chondrocytes and pituitary cells, and is crucial for bone elongation and growth-hormone production [199, 200]. _Zip14_-KO mice show dwarfism, scoliosis, osteopenia, and shortened long bones [187].
Chondrocytes differentiate into prehypertrophic cells that mature into hypertrophic chondrocytes [199]. Mice with a chondrocyte-specific Zip14 KO are morphologically abnormal, with excessive hypertrophy in proliferative and hypertrophic zones. This phenotype is similar to that of mice with a chondrocyte-specific deletion of parathyroid hormone 1 receptor (PTH1R) [201]. PTH1R signaling increases cAMP levels, which contributes to the translocation of the catalytic subunit alpha of protein kinase A (PKA-Cα) to the nucleus. PKA-Cα translocation activates c-fos transcription [202]. Consistent with this finding, the PKA-Cα–mediated c-fos transcription in PTH1R signaling is reduced in Zip14 gene-deficient chondrocytes with low intracellular Zn levels. In _Zip14_-deficient cells, the cAMP levels are restored by Zn supplementation or ectopic ZIP14 expression. ZIP14 signaling is therefore linked to PTH1R signaling, and has an additive effect [187].
ZIP14-mediated Zn signaling also regulates somatic growth. The Zn and cAMP levels are reduced in the pituitary gland of _Zip14_-KO mice. Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), which induces the release of GH from pituitary somatotrophs, does not increase the plasma GH levels in _Zip14_-KO mice. Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in plasma and the transcription of its encoding gene, igf1, in hepatocytes [203, 204] are reduced in _Zip14_-KO mice, and the expression of the GH receptor is slightly altered in the pituitary gland. Taken together, ZIP14 contributes to GPCR signaling related to endochondral ossification and to GH production, and is thus important for regulating systemic growth in vertebrates.
Zip13 and Zip14 knockouts in mice have demonstrated that these Zn transporters regulate Zn signaling that is linked to specific physiological functions, and the impairment of these Zn-signaling axes causes abnormalities in systemic growth and bone homeostasis. Each of these Zn transporters is likely to trigger signal pathways that regulate specific Zn-dependent outcomes (Fig. 5). ZIP14 is also an important transporter for Mn. In zebrafish, a ZIP14 mutation impairs Mn transport and homeostasis, leading to abnormal locomotor activity [103]. Interestingly, Mn accumulations have been observed in patients with rapidly progressive childhood-onset Parkinsonism-dystonia, and reducing the blood Mn level improves clinical symptoms. Moreover, ZIP14 mediates non-transferrin bound iron into liver, which possibly involves in iron overload [100]. Thus, homeostasis of multiple metals regulated by ZIP14 might also be important in disease pathology.
Fig. 5.
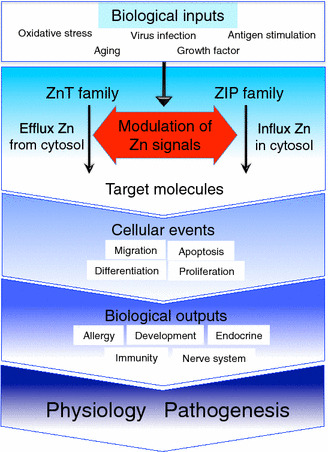
Summary of Zn transporters in physiology and pathogenesis. Biological inputs such as oxidative stress, antigen stimulation, aging, growth factors, and virus infection trigger various intracellular processes (blue square on upper side). “Modulation of Zn signals” intends the Zn ion, which is transported through individual Zn transporters, modulates various intracellular processes followed by the regulation of molecular status of their target molecules (r_ed arrow area in the middle_). Zn signal affects numerous cellular events such as migration, differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis, etc. These cellular events contribute to induce specific biological outputs such as allergy, development, immunity, nerve system and endocrine, etc. (dark blue area on lower side). The impairment of Zn transporter-mediated Zn signal will cause the progression and initiation of various diseases. Please refer to Tables 1 and 2 for reviewing individual biological functions of zinc transporters
Conclusions and perspectives
In the past few decades, physiological and genetic studies of mice and humans have demonstrated the importance of Zn and Zn transporters in health and disease. Although much has been learned about the roles of Zn transporters, their precise physiological functions are not clear. In particular, there are still major questions about the Zn transporter families that have yet to be resolved. These questions can be answered by analyzing (1) the expression profiles, transcription mechanisms, and activation mechanisms of Zn transporter family members in various tissues and organelles; (2) the structure of each Zn transporter and how the structure is related to the actual Zn influx/efflux mechanisms; and (3) the signal-transduction mechanism of each Zn transporter that reflects the Zn ion as a signal molecule. These analyses require the development of methods for detecting Zn and Zn transporters at high resolution both in vitro and in vivo. It would also be helpful to identify chemical compounds that specifically modulate Zn-transporter functions; in addition, these compounds would be candidate therapies for Zn-related disorders.
Zn homeostasis is likely to involve Zn-transporting molecules besides the ZnT and ZIP families, and these should be identified. Some Zn transporters also mobilize another trace metal, indicating that two or more metal ions might regulate cellular functions via identical membrane transporters. Thus, we should focus not only on Zn, but also on Mn, iron, and other trace metals, and further studies of Zn transporters will provide a comprehensive picture of systemic metallomics and of their therapeutic potential. Recent studies have revealed important relationships between Zn transporters and human diseases, indicating the potential of Zn transporters as therapeutic targets (Fig. 5). Further investigation of the functions of Zn transporters will provide novel insights into their roles in cellular functions and in mammalian health and disease.
Acknowledgements
We thank our many colleagues for their excellent works.
Compliance with ethical standards
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (#23592239 to T. F. and #15H04501 to T. K.), the Fuji Foundation for Protein Research (T. K.), the Sumitomo Foundation (T. F.), and the Naito Foundation (T. F.).
Conflict of interest
Author Takafumi Hara declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Taka-aki Takeda declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Teruhisa Takagishi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Kazuhisa Fukue declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Taiho Kambe declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Toshiyuki Fukada declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This review article contains data of our studies involving human participants, which were approved by the Ethics Committee of Kyoto University Graduate School and Faculty of Medicine (Nos. G352 and G573) with written informed consents, and studies using mice cared for according to guidelines approved by the RIKEN Yokohama institutional Animal Care and Experiments committee (K24-007).
Footnotes
T. Hara and T. Takeda equally contributed to this work.
Contributor Information
Taiho Kambe, Phone: +81-75-753-6273, Email: kambe1@kais.kyoto-u.ac.jp.
Toshiyuki Fukada, Phone: +81-88-602-8593, Email: fukada@ph.bunri-u.ac.jp.
References
- 1.Andreini C, Bertini I. A bioinformatics view of zinc enzymes. J Inorg Biochem. 2012;111:150–156. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2011.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Andreini C, Bertini I, Rosato A. Metalloproteomes: a bioinformatic approach. Acc Chem Res. 2009;42:1471–1479. doi: 10.1021/ar900015x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Maret W, Li Y. Coordination dynamics of zinc in proteins. Chem Rev. 2009;109:4682–4707. doi: 10.1021/cr800556u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Prasad AS. Zinc: an overview. Nutr Burbank Los Angel Cty Calif. 1995;11:93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vallee BL, Auld DS. Cocatalytic zinc motifs in enzyme catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:2715–2718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vallee BL, Falchuk KH. The biochemical basis of zinc physiology. Physiol Rev. 1993;73:79–118. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jackson MJ (1989) Physiology of Zinc: general aspects. In: Mills CF (ed) Zinc in human biology. Springer, London, pp 1–14
- 8.Wapnir RA (1990) Protein Nutrition and mineral absorption. CRC Press, Boca Raton. https://www.crcpress.com/Protein-Nutrition-and-Mineral-Absorption/Wapnir/p/book/9780849352270. Accessed 10 Sep 2016
- 9.Broun ER, Greist A, Tricot G, Hoffman R. Excessive zinc ingestion. A reversible cause of sideroblastic anemia and bone marrow depression. JAMA. 1990;264:1441–1443. doi: 10.1001/jama.1990.03450110087033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Andrews GK. Cellular zinc sensors: MTF-1 regulation of gene expression. Biometals Int J Role Met Ions Biol Biochem Med. 2001;14:223–237. doi: 10.1023/A:1012932712483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Eide DJ. The SLC39 family of metal ion transporters. Pflügers Arch Eur J Physiol. 2004;447:796–800. doi: 10.1007/s00424-003-1074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lichtlen P, Schaffner W (2001) The “metal transcription factor” MTF-1: biological facts and medical implications. Swiss Med Wkly 131:647–652. doi:2001/45/smw-09672 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 13.Palmiter RD. Protection against zinc toxicity by metallothionein and zinc transporter 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:4918–4923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401022101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vallee BL. The function of metallothionein. Neurochem Int. 1995;27:23–33. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(94)00165-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gefeller EM, Bondzio A, Aschenbach JR, et al. Regulation of intracellular Zn homeostasis in two intestinal epithelial cell models at various maturation time points. J Physiol Sci. 2015;65:317–328. doi: 10.1007/s12576-015-0369-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Korkmaz-Icöz S, Atmanli A, Radovits T, et al. Administration of zinc complex of acetylsalicylic acid after the onset of myocardial injury protects the heart by upregulation of antioxidant enzymes. J Physiol Sci. 2016;66:113–125. doi: 10.1007/s12576-015-0403-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Barnett JB, Dao MC, Hamer DH, et al. Effect of zinc supplementation on serum zinc concentration and T cell proliferation in nursing home elderly: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;103:942–951. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.115.115188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Goldenberg RL, Tamura T, Neggers Y, et al. The effect of zinc supplementation on pregnancy outcome. JAMA. 1995;274:463–468. doi: 10.1001/jama.1995.03530060037030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Frederickson CJ, Koh J-Y, Bush AI. The neurobiology of zinc in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:449–462. doi: 10.1038/nrn1671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sensi SL, Paoletti P, Bush AI, Sekler I. Zinc in the physiology and pathology of the CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:780–791. doi: 10.1038/nrn2734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Haase H, Ober-Blöbaum JL, Engelhardt G, et al. Zinc signals are essential for lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction in monocytes. J Immunol. 2008;181:6491–6502. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.9.6491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hirano T, Murakami M, Fukada T, et al. Roles of zinc and zinc signaling in immunity: zinc as an intracellular signaling molecule. Adv Immunol. 2008;97:149–176. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)00003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Maret W. Zinc coordination environments in proteins as redox sensors and signal transducers. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006;8:1419–1441. doi: 10.1089/ars.2006.8.1419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Oda K, Umemura M, Nakakaji R, et al. Transient receptor potential cation 3 channel regulates melanoma proliferation and migration. J Physiol Sci. 2016 doi: 10.1007/s12576-016-0480-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Takada T, Takata K, Ashihara E. Inhibition of monocarboxylate transporter 1 suppresses the proliferation of glioblastoma stem cells. J Physiol Sci. 2016;66:387–396. doi: 10.1007/s12576-016-0435-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mizuno H, Suzuki Y, Watanabe M, et al. Potential role of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels in bladder cancer cells. J Physiol Sci. 2014;64:305–314. doi: 10.1007/s12576-014-0319-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shima T, Jesmin S, Matsui T, et al. Differential effects of type 2 diabetes on brain glycometabolism in rats: focus on glycogen and monocarboxylate transporter 2. J Physiol Sci. 2016 doi: 10.1007/s12576-016-0508-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Takaishi M, Uchida K, Suzuki Y, et al. Reciprocal effects of capsaicin and menthol on thermosensation through regulated activities of TRPV1 and TRPM8. J Physiol Sci. 2016;66:143–155. doi: 10.1007/s12576-015-0427-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bu H, Yang C, Wang M, et al. K(ATP) channels and MPTP are involved in the cardioprotection bestowed by chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia in the developing rat. J Physiol Sci. 2015;65:367–376. doi: 10.1007/s12576-015-0376-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Suzuki Y, Watanabe M, Saito CT, Tominaga M. Expression of the TRPM6 in mouse placental trophoblasts; potential role in maternal-fetal calcium transport. J Physiol Sci. 2017;67:151–162. doi: 10.1007/s12576-016-0449-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shimizu S, Akiyama T, Kawada T, et al. Sodium ion transport participates in non-neuronal acetylcholine release in the renal cortex of anesthetized rabbits. J Physiol Sci. 2016 doi: 10.1007/s12576-016-0489-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Barnett JP, Blindauer CA, Kassaar O, et al. Allosteric modulation of zinc speciation by fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1830:5456–5464. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.05.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Reyes JG. Zinc transport in mammalian cells. Am J Physiol. 1996;270:C401–C410. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.270.2.C401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.King JC, Shames DM, Woodhouse LR. Zinc homeostasis in humans. J Nutr. 2000;130:1360S–1366S. doi: 10.1093/jn/130.5.1360S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Taylor CM, Bacon JR, Aggett PJ, Bremner I. Homeostatic regulation of zinc absorption and endogenous losses in zinc-deprived men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991;53:755–763. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/53.3.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hambidge M, Krebs NF. Interrelationships of key variables of human zinc homeostasis: relevance to dietary zinc requirements. Annu Rev Nutr. 2001;21:429–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.21.1.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Krebs NF. Update on zinc deficiency and excess in clinical pediatric practice. Ann Nutr Metab. 2013;62(Suppl 1):19–29. doi: 10.1159/000348261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Thiers RE, Vallee BL. Distribution of metals in subcellular fractions of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1957;226:911–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Colvin RA, Bush AI, Volitakis I, et al. Insights into Zn2+ homeostasis in neurons from experimental and modeling studies. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008;294:C726–C742. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00541.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Krezel A, Maret W. Zinc-buffering capacity of a eukaryotic cell at physiological pZn. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2006;11:1049–1062. doi: 10.1007/s00775-006-0150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Palmiter RD, Findley SD. Cloning and functional characterization of a mammalian zinc transporter that confers resistance to zinc. EMBO J. 1995;14:639–649. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Outten CE, O’Halloran TV. Femtomolar sensitivity of metalloregulatory proteins controlling zinc homeostasis. Science. 2001;292:2488–2492. doi: 10.1126/science.1060331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sensi SL, Canzoniero LM, Yu SP, et al. Measurement of intracellular free zinc in living cortical neurons: routes of entry. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci. 1997;17:9554–9564. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-24-09554.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Vinkenborg JL, Nicolson TJ, Bellomo EA, et al. Genetically encoded FRET sensors to monitor intracellular Zn2+ homeostasis. Nat Methods. 2009;6:737–740. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Qin Y, Miranda JG, Stoddard CI, et al. Direct comparison of a genetically encoded sensor and small molecule indicator: implications for quantification of cytosolic Zn(2+) ACS Chem Biol. 2013;8:2366–2371. doi: 10.1021/cb4003859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Besnard P, Niot I, Poirier H, et al. New insights into the fatty acid-binding protein (FABP) family in the small intestine. Mol Cell Biochem. 2002;239:139–147. doi: 10.1023/A:1020505512364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.McCranor BJ, Bozym RA, Vitolo MI, et al. Quantitative imaging of mitochondrial and cytosolic free zinc levels in an in vitro model of ischemia/reperfusion. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2012;44:253–263. doi: 10.1007/s10863-012-9427-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Qin Y, Dittmer PJ, Park JG, et al. Measuring steady-state and dynamic endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi Zn2+ with genetically encoded sensors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:7351–7356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015686108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Chabosseau P, Tuncay E, Meur G, et al. Mitochondrial and ER-targeted eCALWY probes reveal high levels of free Zn2+ . ACS Chem Biol. 2014;9:2111–2120. doi: 10.1021/cb5004064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kim AM, Bernhardt ML, Kong BY, et al. Zinc sparks are triggered by fertilization and facilitate cell cycle resumption in mammalian eggs. ACS Chem Biol. 2011;6:716–723. doi: 10.1021/cb200084y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yamasaki S, Sakata-Sogawa K, Hasegawa A, et al. Zinc is a novel intracellular second messenger. J Cell Biol. 2007;177:637–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200702081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kambe T (2013) Regulation of zinc transport. Encycl Inorg Bioinorg Chem 301–309
- 53.Kambe T, Tsuji T, Hashimoto A, Itsumura N. The physiological, biochemical, and molecular roles of zinc transporters in zinc homeostasis and metabolism. Physiol Rev. 2015;95:749–784. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00035.2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Fukada T, Kambe T. Molecular and genetic features of zinc transporters in physiology and pathogenesis. Metallomics. 2011;3:662–674. doi: 10.1039/c1mt00011j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Fukada T, Yamasaki S, Nishida K, et al. Zinc homeostasis and signaling in health and diseases : zinc signaling. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2011;16:1123–1134. doi: 10.1007/s00775-011-0797-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kimura T, Kambe T. The functions of metallothionein and ZIP and ZnT transporters: an overview and perspective. Int J Mol Sci. 2016 doi: 10.3390/ijms17030336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lichten LA, Cousins RJ. Mammalian zinc transporters: nutritional and physiologic regulation. Annu Rev Nutr. 2009;29:153–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-033009-083312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kambe T, Suzuki T, Nagao M, Yamaguchi-Iwai Y. Sequence similarity and functional relationship among eukaryotic ZIP and CDF transporters. Genom Proteom Bioinform. 2006;4:1–9. doi: 10.1016/S1672-0229(06)60010-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kawachi M, Kobae Y, Mimura T, Maeshima M. Deletion of a histidine-rich loop of AtMTP1, a vacuolar Zn(2+)/H(+) antiporter of Arabidopsis thaliana, stimulates the transport activity. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:8374–8383. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707646200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ohana E, Hoch E, Keasar C, et al. Identification of the Zn2+ binding site and mode of operation of a mammalian Zn2+ transporter. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:17677–17686. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.007203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Shusterman E, Beharier O, Shiri L, et al. ZnT-1 extrudes zinc from mammalian cells functioning as a Zn(2+)/H(+) exchanger. Metallomics. 2014;6:1656–1663. doi: 10.1039/C4MT00108G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gaither LA, Eide DJ. Functional expression of the human hZIP2 zinc transporter. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:5560–5564. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.8.5560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Girijashanker K, He L, Soleimani M, et al. Slc39a14 gene encodes ZIP14, a metal/bicarbonate symporter: similarities to the ZIP8 transporter. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;73:1413–1423. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.043588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.He L, Girijashanker K, Dalton TP, et al. ZIP8, member of the solute-carrier-39 (SLC39) metal-transporter family: characterization of transporter properties. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;70:171–180. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.024521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lin W, Chai J, Love J, Fu D. Selective electrodiffusion of zinc ions in a Zrt-, Irt-like protein, ZIPB. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:39013–39020. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.180620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Lasry I, Golan Y, Berman B, et al. In situ dimerization of multiple wild type and mutant zinc transporters in live cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:7275–7292. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.533786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Salazar G, Falcon-Perez JM, Harrison R, Faundez V. SLC30A3 (ZnT3) oligomerization by dityrosine bonds regulates its subcellular localization and metal transport capacity. PLoS One. 2009;4:e5896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hoch E, Lin W, Chai J, et al. Histidine pairing at the metal transport site of mammalian ZnT transporters controls Zn2+ over Cd2+ selectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:7202–7207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1200362109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kambe T. Molecular architecture and function of ZnT transporters. Curr Top Membr. 2012;69:199–220. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394390-3.00008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ohana E, Hoch E, Keasar C, et al. Identification of the Zn2+ binding site and mode of operation of a mammalian Zn2+ transporter. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:17677–17686. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.007203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Lu M, Fu D. Structure of the zinc transporter YiiP. Science. 2007;317:1746–1748. doi: 10.1126/science.1143748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Lu M, Chai J, Fu D. Structural basis for autoregulation of the zinc transporter YiiP. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009;16:1063–1067. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Coudray N, Valvo S, Hu M, et al. Inward-facing conformation of the zinc transporter YiiP revealed by cryoelectron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:2140–2145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215455110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Gupta S, Chai J, Cheng J, et al. Visualizing the kinetic power stroke that drives proton-coupled zinc(II) transport. Nature. 2014;512:101–104. doi: 10.1038/nature13382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Cherezov V, Hofer N, Szebenyi DM, et al. Insights into the mode of action of a putative zinc transporter CzrB in Thermus thermophilus . Structure. 2008;16:1378–1388. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2008.05.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Higuchi T, Hattori M, Tanaka Y, et al. Crystal structure of the cytosolic domain of the cation diffusion facilitator family protein. Proteins. 2009;76:768–771. doi: 10.1002/prot.22444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Zeytuni N, Uebe R, Maes M, et al. Cation diffusion facilitators transport initiation and regulation is mediated by cation induced conformational changes of the cytoplasmic domain. PLoS One. 2014;9:e92141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Kolaj-Robin O, Russell D, Hayes KA, et al. Cation diffusion facilitator family: structure and function. FEBS Lett. 2015;589:1283–1295. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Blindauer CA, Schmid R. Cytosolic metal handling in plants: determinants for zinc specificity in metal transporters and metallothioneins. Metallomics. 2010;2:510–529. doi: 10.1039/c004880a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Nishito Y, Tsuji N, Fujishiro H, et al. Direct comparison of manganese detoxification/efflux proteins and molecular characterization of ZnT10 as a manganese transporter. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:14773–14787. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.728014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Martin JE, Giedroc DP. Functional determinants of metal ion transport and selectivity in paralogous cation diffusion facilitator transporters CzcD and MntE in Streptococcus pneumoniae . J Bacteriol. 2016;198:1066–1076. doi: 10.1128/JB.00975-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Montanini B, Blaudez D, Jeandroz S, et al. Phylogenetic and functional analysis of the cation diffusion facilitator (CDF) family: improved signature and prediction of substrate specificity. BMC Genom. 2007;8:107. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Gustin JL, Zanis MJ, Salt DE. Structure and evolution of the plant cation diffusion facilitator family of ion transporters. BMC Evol Biol. 2011;11:76. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ellis CD, Macdiarmid CW, Eide DJ. Heteromeric protein complexes mediate zinc transport into the secretory pathway of eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:28811–28818. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505500200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Fujiwara T, Kawachi M, Sato Y, et al. A high molecular mass zinc transporter MTP12 forms a functional heteromeric complex with MTP5 in the Golgi in Arabidopsis thaliana . FEBS J. 2015;282:1965–1979. doi: 10.1111/febs.13252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Fukunaka A, Suzuki T, Kurokawa Y, et al. Demonstration and characterization of the heterodimerization of ZnT5 and ZnT6 in the early secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:30798–30806. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.026435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Golan Y, Berman B, Assaraf YG. Heterodimerization, altered subcellular localization, and function of multiple zinc transporters in viable cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:9050–9063. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.617332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Zhao Y, Feresin RG, Falcon-Perez JM, Salazar G. Differential targeting of SLC30A10/ZnT10 heterodimers to endolysosomal compartments modulates EGF-induced MEK/ERK1/2 activity. Traffic Cph Den. 2016;17:267–288. doi: 10.1111/tra.12371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Hojyo S, Fukada T. Zinc transporters and signaling in physiology and pathogenesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016 doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.06.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Bin B-H, Fukada T, Hosaka T, et al. Biochemical characterization of human ZIP13 protein: a homo-dimerized zinc transporter involved in the spondylocheiro dysplastic Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:40255–40265. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.256784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bin B-H, Hojyo S, Hosaka T, et al. Molecular pathogenesis of spondylocheirodysplastic Ehlers–Danlos syndrome caused by mutant ZIP13 proteins. EMBO Mol Med. 2014;6:1028–1042. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201303809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Taylor KM, Muraina IA, Brethour D, et al. Zinc transporter ZIP10 forms a heteromer with ZIP6 which regulates embryonic development and cell migration. Biochem J. 2016;473:2531–2544. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Antala S, Ovchinnikov S, Kamisetty H, et al. Computation and functional studies provide a model for the structure of the zinc transporter hZIP4. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:17796–17805. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.617613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Taylor KM, Nicholson RI. The LZT proteins; the LIV-1 subfamily of zinc transporters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1611:16–30. doi: 10.1016/S0005-2736(03)00048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Zhang T, Sui D, Hu J. Structural insights of ZIP4 extracellular domain critical for optimal zinc transport. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11979. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Antala S, Dempski RE. The human ZIP4 transporter has two distinct binding affinities and mediates transport of multiple transition metals. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2012;51:963–973. doi: 10.1021/bi201553p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Ehsani S, Huo H, Salehzadeh A, et al. Family reunion—the ZIP/prion gene family. Prog Neurobiol. 2011;93:405–420. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Nam H, Wang CY, Zhang L, et al. ZIP14 and DMT1 in the liver, pancreas, and heart are differentially regulated by iron deficiency and overload: implications for tissue iron uptake in iron-related disorders. Haematologica. 2013;98:1049–1057. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.072314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Boycott KM, Beaulieu CL, Kernohan KD, et al. Autosomal-recessive intellectual disability with cerebellar atrophy syndrome caused by mutation of the manganese and zinc transporter gene SLC39A8. Am J Hum Genet. 2015;97:886–893. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Jenkitkasemwong S, Wang CY, Coffey R, et al. SLC39A14 is required for the development of hepatocellular iron overload in murine models of hereditary hemochromatosis. Cell Metab. 2015;22:138–150. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Jorge-Nebert LF, Galvez-Peralta M, Landero Figueroa J, et al. Comparing gene expression during cadmium uptake and distribution: untreated versus oral Cd-treated wild-type and ZIP14 knockout mice. Toxicol Sci. 2015;143:26–35. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Park JH, Hogrebe M, Gruneberg M, et al. SLC39A8 deficiency: a disorder of manganese transport and glycosylation. Am J Hum Genet. 2015;97:894–903. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Tuschl K, Meyer E, Valdivia LE, et al. Mutations in SLC39A14 disrupt manganese homeostasis and cause childhood-onset parkinsonism-dystonia. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11601. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Guo L, Lichten LA, Ryu M-S, et al. STAT5-glucocorticoid receptor interaction and MTF-1 regulate the expression of ZnT2 (Slc30a2) in pancreatic acinar cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:2818–2823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914941107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Homma K, Fujisawa T, Tsuburaya N, et al. SOD1 as a molecular switch for initiating the homeostatic ER stress response under zinc deficiency. Mol Cell. 2013;52:75–86. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Ishihara K, Yamazaki T, Ishida Y, et al. Zinc transport complexes contribute to the homeostatic maintenance of secretory pathway function in vertebrate cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:17743–17750. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602470200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Kim J-H, Jeon J, Shin M, et al. Regulation of the catabolic cascade in osteoarthritis by the zinc-ZIP8-MTF1 axis. Cell. 2014;156:730–743. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Kitamura H, Morikawa H, Kamon H, et al. Toll-like receptor-mediated regulation of zinc homeostasis influences dendritic cell function. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:971–977. doi: 10.1038/ni1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Kong BY, Duncan FE, Que EL, et al. Maternally-derived zinc transporters ZIP6 and ZIP10 drive the mammalian oocyte-to-egg transition. Mol Hum Reprod. 2014;20:1077–1089. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gau066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Liu M-J, Bao S, Gálvez-Peralta M, et al. ZIP8 regulates host defense through zinc-mediated inhibition of NF-κB. Cell Rep. 2013;3:386–400. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.01.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Liuzzi JP, Lichten LA, Rivera S, et al. Interleukin-6 regulates the zinc transporter Zip14 in liver and contributes to the hypozincemia of the acute-phase response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:6843–6848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502257102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Miyai T, Hojyo S, Ikawa T, et al. Zinc transporter SLC39A10/ZIP10 facilitates antiapoptotic signaling during early B-cell development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:11780–11785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323549111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Ryu M-S, Lichten LA, Liuzzi JP, Cousins RJ. Zinc transporters ZnT1 (Slc30a1), Zip8 (Slc39a8), and Zip10 (Slc39a10) in mouse red blood cells are differentially regulated during erythroid development and by dietary zinc deficiency. J Nutr. 2008;138:2076–2083. doi: 10.3945/jn.108.093575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Zhao L, Oliver E, Maratou K, et al. The zinc transporter ZIP12 regulates the pulmonary vascular response to chronic hypoxia. Nature. 2015;524:356–360. doi: 10.1038/nature14620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Kinazaki A, Chen H, Koizumi K, et al. Putative role of intracellular Zn(2 +) release during oxidative stress: a trigger to restore cellular thiol content that is decreased by oxidative stress. J Physiol Sci. 2011;61:403–409. doi: 10.1007/s12576-011-0160-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Yamashita S, Miyagi C, Fukada T, et al. Zinc transporter LIVI controls epithelial-mesenchymal transition in zebrafish gastrula organizer. Nature. 2004;429:298–302. doi: 10.1038/nature02545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Song J, Kim D, Lee CH, et al. MicroRNA-488 regulates zinc transporter SLC39A8/ZIP8 during pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. J Biomed Sci. 2013;20:31. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-20-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Weaver BP, Andrews GK. Regulation of zinc-responsive Slc39a5 (Zip5) translation is mediated by conserved elements in the 3′-untranslated region. Biometals. 2012;25:319–335. doi: 10.1007/s10534-011-9508-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Zhang Y, Yang J, Cui X, et al. A novel epigenetic CREB-miR-373 axis mediates ZIP4-induced pancreatic cancer growth. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5:1322–1334. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201302507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Cousins RJ, Liuzzi JP, Lichten LA. Mammalian zinc transport, trafficking, and signals. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:24085–24089. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R600011200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Fukada T, Kambe T. Zinc signals in cellular functions and disorders. Tokyo: Springer; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 122.Kambe T, Hashimoto A, Fujimoto S. Current understanding of ZIP and ZnT zinc transporters in human health and diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71:3281–3295. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1617-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Kambe T, Weaver BP, Andrews GK. The genetics of essential metal homeostasis during development. Genesis (N.Y.: 2000) 2008;46:214–228. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Langmade SJ, Ravindra R, Daniels PJ, Andrews GK. The transcription factor MTF-1 mediates metal regulation of the mouse ZnT1 gene. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:34803–34809. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007339200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Wimmer U, Wang Y, Georgiev O, Schaffner W. Two major branches of anti-cadmium defense in the mouse: MTF-1/metallothioneins and glutathione. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:5715–5727. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Ogo OA, Tyson J, Cockell SJ, et al. The zinc finger protein ZNF658 regulates the transcription of genes involved in zinc homeostasis and affects ribosome biogenesis through the zinc transcriptional regulatory element. Mol Cell Biol. 2015;35:977–987. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01298-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Dufner-Beattie J, Wang F, Kuo YM, et al. The acrodermatitis enteropathica gene ZIP4 encodes a tissue-specific, zinc-regulated zinc transporter in mice. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:33474–33481. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305000200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Hashimoto A, Ohkura K, Takahashi M, et al. Soybean extracts increase cell surface ZIP4 abundance and cellular zinc levels: a potential novel strategy to enhance zinc absorption by ZIP4 targeting. Biochem J. 2015;472:183–193. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Kambe T, Andrews GK. Novel proteolytic processing of the ectodomain of the zinc transporter ZIP4 (SLC39A4) during zinc deficiency is inhibited by acrodermatitis enteropathica mutations. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:129–139. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00963-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Kim BE, Wang F, Dufner-Beattie J, et al. Zn2+ stimulated endocytosis of the mZIP4 zinc transporter regulates its location at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:4523–4530. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310799200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Weaver BP, Dufner-Beattie J, Kambe T, Andrews GK. Novel zinc-responsive post-transcriptional mechanisms reciprocally regulate expression of the mouse Slc39a4 and Slc39a5 zinc transporters (Zip4 and Zip5) Biol Chem. 2007;388:1301–1312. doi: 10.1515/BC.2007.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Wang F, Dufner-Beattie J, Kim B-E, et al. Zinc-stimulated endocytosis controls activity of the mouse ZIP1 and ZIP3 zinc uptake transporters. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:24631–24639. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400680200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Hashimoto A, Nakagawa M, Tsujimura N, et al. Properties of Zip4 accumulation during zinc deficiency and its usefulness to evaluate zinc status: a study of the effects of zinc deficiency during lactation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2016;310:R459–R468. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00439.2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Ehsani S, Salehzadeh A, Huo H, et al. LIV-1 ZIP ectodomain shedding in prion-infected mice resembles cellular response to transition metal starvation. J Mol Biol. 2012;422:556–574. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.06.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Huang L, Kirschke CP, Gitschier J. Functional characterization of a novel mammalian zinc transporter, ZnT6. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:26389–26395. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200462200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Lutsenko S, Barnes NL, Bartee MY, Dmitriev OY. Function and regulation of human copper-transporting ATPases. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:1011–1046. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00004.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Fukunaka A, Kurokawa Y, Teranishi F, et al. Tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase is activated via a two-step mechanism by zinc transport complexes in the early secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:16363–16373. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.227173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Kambe T. An overview of a wide range of functions of ZnT and Zip zinc transporters in the secretory pathway. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011;75:1036–1043. doi: 10.1271/bbb.110056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Fujimoto S, Tsuji T, Fujiwara T, et al. The PP-motif in luminal loop 2 of ZnT transporters plays a pivotal role in TNAP activation. Biochem J. 2016;473:2611–2621. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Jeney V, Itoh S, Wendt M, et al. Role of antioxidant-1 in extracellular superoxide dismutase function and expression. Circ Res. 2005;96:723–729. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000162001.57896.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Hamza I, Faisst A, Prohaska J, et al. The metallochaperone Atox1 plays a critical role in perinatal copper homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:6848–6852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.111058498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Fujimoto S, Itsumura N, Tsuji T, et al. Cooperative Functions of ZnT1, metallothionein and ZnT4 in the cytoplasm are required for full activation of TNAP in the early secretory pathway. PLoS One. 2013;8:e77445. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Maret W. Metals on the move: zinc ions in cellular regulation and in the coordination dynamics of zinc proteins. Biometals Int J Role Met Ions Biol Biochem Med. 2011;24:411–418. doi: 10.1007/s10534-010-9406-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Haase H, Maret W. Intracellular zinc fluctuations modulate protein tyrosine phosphatase activity in insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling. Exp Cell Res. 2003;291:289–298. doi: 10.1016/S0014-4827(03)00406-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Kitabayashi C, Fukada T, Kanamoto M, et al. Zinc suppresses Th17 development via inhibition of STAT3 activation. Int Immunol. 2010;22:375–386. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxq017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Mathews WR, Ong D, Milutinovich AB, Van Doren M. Zinc transport activity of fear of intimacy is essential for proper gonad morphogenesis and DE-cadherin expression. Dev Camb Engl. 2006;133:1143–1153. doi: 10.1242/dev.02256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Hojyo S, Miyai T, Fujishiro H, et al. Zinc transporter SLC39A10/ZIP10 controls humoral immunity by modulating B-cell receptor signal strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:11786–11791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323557111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Fukada T, Civic N, Furuichi T, et al. The zinc transporter SLC39A13/ZIP13 is required for connective tissue development; its involvement in BMP/TGF-beta signaling pathways. PLoS One. 2008;3:e3642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Aydemir TB, Sitren HS, Cousins RJ. The zinc transporter Zip14 influences c-Met phosphorylation and hepatocyte proliferation during liver regeneration in mice. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(1536–1546):e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.02.046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Andrews GK, Wang H, Dey SK, Palmiter RD. Mouse zinc transporter 1 gene provides an essential function during early embryonic development. Genesis (N.Y. : 2000) 2004;40:74–81. doi: 10.1002/gene.20067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Chowanadisai W, Lönnerdal B, Kelleher SL. Identification of a mutation in SLC30A2 (ZnT-2) in women with low milk zinc concentration that results in transient neonatal zinc deficiency. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:39699–39707. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605821200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Itsumura N, Inamo Y, Okazaki F, et al. Compound heterozygous mutations in SLC30A2/ZnT2 results in low milk zinc concentrations: a novel mechanism for zinc deficiency in a breast-fed infant. PLoS One. 2013;8:e64045. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Lee S, Hennigar SR, Alam S, et al. Essential role for Zinc transporter 2 (ZnT2)-mediated zinc transport in mammary gland development and function during lactation. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:13064–13078. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.637439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Itsumura N, Kibihara Y, Fukue K, et al. Novel mutations in SLC30A2 involved in the pathogenesis of transient neonatal zinc deficiency. Pediatr Res. 2016;80:586–594. doi: 10.1038/pr.2016.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Adlard PA, Parncutt JM, Finkelstein DI, Bush AI. Cognitive loss in zinc transporter-3 knock-out mice: a phenocopy for the synaptic and memory deficits of Alzheimer’s disease? J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci. 2010;30:1631–1636. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5255-09.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Hildebrand MS, Phillips AM, Mullen SA, et al. Loss of synaptic Zn2+ transporter function increases risk of febrile seizures. Sci Rep. 2015 doi: 10.1038/srep17816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Huang L, Gitschier J. A novel gene involved in zinc transport is deficient in the lethal milk mouse. Nat Genet. 1997;17:292–297. doi: 10.1038/ng1197-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Nishida K, Hasegawa A, Nakae S, et al. Zinc transporter Znt5/Slc30a5 is required for the mast cell-mediated delayed-type allergic reaction but not the immediate-type reaction. J Exp Med. 2009;206:1351–1364. doi: 10.1084/jem.20082533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Inoue K, Matsuda K, Itoh M, et al. Osteopenia and male-specific sudden cardiac death in mice lacking a zinc transporter gene, Znt5. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:1775–1784. doi: 10.1093/hmg/11.15.1775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Huang L, Yu YY, Kirschke CP, et al. Znt7 (Slc30a7)-deficient mice display reduced body zinc status and body fat accumulation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:37053–37063. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706631200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Huang L, Kirschke CP, Lay Y-AE, et al. Znt7-null mice are more susceptible to diet-induced glucose intolerance and insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:33883–33896. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.309666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2007;445:881–885. doi: 10.1038/nature05616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Wenzlau JM, Juhl K, Yu L, et al. The cation efflux transporter ZnT8 (Slc30A8) is a major autoantigen in human type 1 diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:17040–17045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705894104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Lemaire K, Ravier MA, Schraenen A, et al. Insulin crystallization depends on zinc transporter ZnT8 expression, but is not required for normal glucose homeostasis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:14872–14877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906587106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Nicolson TJ, Bellomo EA, Wijesekara N, et al. Insulin storage and glucose homeostasis in mice null for the granule zinc transporter ZnT8 and studies of the type 2 diabetes-associated variants. Diabetes. 2009;58:2070–2083. doi: 10.2337/db09-0551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Wijesekara N, Dai FF, Hardy AB, et al. Beta cell-specific Znt8 deletion in mice causes marked defects in insulin processing, crystallisation and secretion. Diabetologia. 2010;53:1656–1668. doi: 10.1007/s00125-010-1733-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Tamaki M, Fujitani Y, Hara A, et al. The diabetes-susceptible gene SLC30A8/ZnT8 regulates hepatic insulin clearance. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:4513–4524. doi: 10.1172/JCI68807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Bosomworth HJ, Thornton JK, Coneyworth LJ, et al. Efflux function, tissue-specific expression and intracellular trafficking of the Zn transporter ZnT10 indicate roles in adult Zn homeostasis. Met Integr Biometal Sci. 2012;4:771–779. doi: 10.1039/c2mt20088k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Quadri M, Federico A, Zhao T, et al. Mutations in SLC30A10 cause parkinsonism and dystonia with hypermanganesemia, polycythemia, and chronic liver disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90:467–477. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.01.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Stamelou M, Tuschl K, Chong WK, et al. Dystonia with brain manganese accumulation resulting from SLC30A10 mutations: a new treatable disorder. Mov Disord Off J Mov Disord Soc. 2012;27:1317–1322. doi: 10.1002/mds.25138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Dufner-Beattie J, Huang ZL, Geiser J, et al. Generation and characterization of mice lacking the zinc uptake transporter ZIP3. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:5607–5615. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.13.5607-5615.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Dufner-Beattie J, Huang ZL, Geiser J, et al. Mouse ZIP1 and ZIP3 genes together are essential for adaptation to dietary zinc deficiency during pregnancy. Genesis (N.Y. : 2000) 2006;44:239–251. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Peters JL, Dufner-Beattie J, Xu W, et al. Targeting of the mouse Slc39a2 (Zip2) gene reveals highly cell-specific patterns of expression, and unique functions in zinc, iron, and calcium homeostasis. Genesis (N.Y. : 2000) 2007;45:339–352. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Kambe T, Geiser J, Lahner B, et al. Slc39a1 to 3 (subfamily II) Zip genes in mice have unique cell-specific functions during adaptation to zinc deficiency. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008;294:R1474–R1481. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00130.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Andrews GK. Regulation and function of Zip4, the acrodermatitis enteropathica gene. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36:1242–1246. doi: 10.1042/BST0361242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Küry S, Dréno B, Bézieau S, et al. Identification of SLC39A4, a gene involved in acrodermatitis enteropathica. Nat Genet. 2002;31:239–240. doi: 10.1038/ng913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Wang K, Zhou B, Kuo Y-M, et al. A novel member of a zinc transporter family is defective in acrodermatitis enteropathica. Am J Hum Genet. 2002;71:66–73. doi: 10.1086/341125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Dufner-Beattie J, Weaver BP, Geiser J, et al. The mouse acrodermatitis enteropathica gene Slc39a4 (Zip4) is essential for early development and heterozygosity causes hypersensitivity to zinc deficiency. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:1391–1399. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Guo H, Jin X, Zhu T, et al. SLC39A5 mutations interfering with the BMP/TGF-β pathway in non-syndromic high myopia. J Med Genet. 2014;51:518–525. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Ohashi W, Kimura S, Iwanaga T, et al. Zinc transporter SLC39A7/ZIP7 promotes intestinal epithelial self-renewal by resolving ER stress. PLoS Genet. 2016;12:e1006349. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Gálvez-Peralta M, He L, Jorge-Nebert LF, et al. ZIP8 zinc transporter: indispensable role for both multiple-organ organogenesis and hematopoiesis in utero. PLoS One. 2012;7:e36055. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Pickrell JK, Berisa T, Liu JZ, et al. Detection and interpretation of shared genetic influences on 42 human traits. Nat Genet. 2016;48:709–717. doi: 10.1038/ng.3570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Li D, Achkar J-P, Haritunians T, et al. A pleiotropic missense variant in SLC39A8 is associated with Crohn’s disease and human gut microbiome composition. Gastroenterology. 2016;151:724–732. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.06.051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Thomas P, Pang Y, Dong J, Berg AH. Identification and characterization of membrane androgen receptors in the ZIP9 zinc transporter subfamily: II. Role of human ZIP9 in testosterone-induced prostate and breast cancer cell apoptosis. Endocrinology. 2014;155:4250–4265. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Pal D, Sharma U, Singh SK, Prasad R. Association between ZIP10 gene expression and tumor aggressiveness in renal cell carcinoma. Gene. 2014;552:195–198. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Kagara N, Tanaka N, Noguchi S, Hirano T. Zinc and its transporter ZIP10 are involved in invasive behavior of breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2007;98:692–697. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Hojyo S, Fukada T, Shimoda S, et al. The zinc transporter SLC39A14/ZIP14 controls G-protein coupled receptor-mediated signaling required for systemic growth. PLoS One. 2011;6:e18059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Troche C, Aydemir TB, Cousins RJ. Zinc transporter Slc39a14 regulates inflammatory signaling associated with hypertrophic adiposity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016;310:E258–E268. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00421.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Van der Flier LG, Clevers H. Stem cells, self-renewal, and differentiation in the intestinal epithelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:241–260. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Heazlewood CK, Cook MC, Eri R, et al. Aberrant mucin assembly in mice causes endoplasmic reticulum stress and spontaneous inflammation resembling ulcerative colitis. PLoS Med. 2008;5:e54. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Heijmans J, van Lidth de Jeude JF, Koo B-K, et al. ER stress causes rapid loss of intestinal epithelial stemness through activation of the unfolded protein response. Cell Rep. 2013;3:1128–1139. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.02.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Kaser A, Lee A-H, Franke A, et al. XBP1 links ER stress to intestinal inflammation and confers genetic risk for human inflammatory bowel disease. Cell. 2008;134:743–756. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Zhao F, Edwards R, Dizon D, et al. Disruption of Paneth and goblet cell homeostasis and increased endoplasmic reticulum stress in Agr2–/– mice. Dev Biol. 2010;338:270–279. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.12.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Fukada T, Asada Y, Mishima K, et al. Slc39a13/Zip13: a crucial zinc transporter involved in tooth development and inherited disorders. J Oral Biosci. 2011;53:1–12. doi: 10.1016/S1349-0079(11)80030-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Fukada T, Hojyo S, Furuichi T. Zinc signal: a new player in osteobiology. J Bone Miner Metab. 2013;31:129–135. doi: 10.1007/s00774-012-0409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Giunta C, Elçioglu NH, Albrecht B, et al. Spondylocheiro dysplastic form of the Ehlers–Danlos syndrome–an autosomal-recessive entity caused by mutations in the zinc transporter gene SLC39A13. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;82:1290–1305. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Bin B-H, Hojyo S, Ryong Lee T, Fukada T. Spondylocheirodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (SCD-EDS) and the mutant zinc transporter ZIP13. Rare Dis Austin Tex. 2014;2:e974982. doi: 10.4161/21675511.2014.974982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Taylor KM, Morgan HE, Johnson A, Nicholson RI. Structure-function analysis of a novel member of the LIV-1 subfamily of zinc transporters, ZIP14. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:427–432. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Karsenty G, Kronenberg HM, Settembre C. Genetic control of bone formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2009;25:629–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.042308.113308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Mayo KE, Godfrey PA, Suhr ST, et al. Growth hormone-releasing hormone: synthesis and signaling. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1995;50:35–73. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571150-0.50007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Kronenberg HM. PTHrP and skeletal development. Ann N.Y. Acad Sci. 2006;1068:1–13. doi: 10.1196/annals.1346.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Datta NS, Abou-Samra AB. PTH and PTHrP signaling in osteoblasts. Cell Signal. 2009;21:1245–1254. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Nilsson O, Marino R, De Luca F, et al. Endocrine regulation of the growth plate. Horm Res. 2005;64:157–165. doi: 10.1159/000088791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Procter AM, Phillips JA, Cooper DN. The molecular genetics of growth hormone deficiency. Hum Genet. 1998;103:255–272. doi: 10.1007/s004390050815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Stathakis DG, Burton DY, McIvor WE, et al. The catecholamines up (Catsup) protein of Drosophila melanogaster functions as a negative regulator of tyrosine hydroxylase activity. Genetics. 1999;153:361–382. doi: 10.1093/genetics/153.1.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Groth C, Sasamura T, Khanna MR, et al. Protein trafficking abnormalities in Drosophila tissues with impaired activity of the ZIP7 zinc transporter Catsup. Development. 2013;140(14):3018–3027. doi: 10.1242/dev.088336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]