Host–pathogen interactions: the seduction of molecular cross talk (original) (raw)
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (249.3 KB).
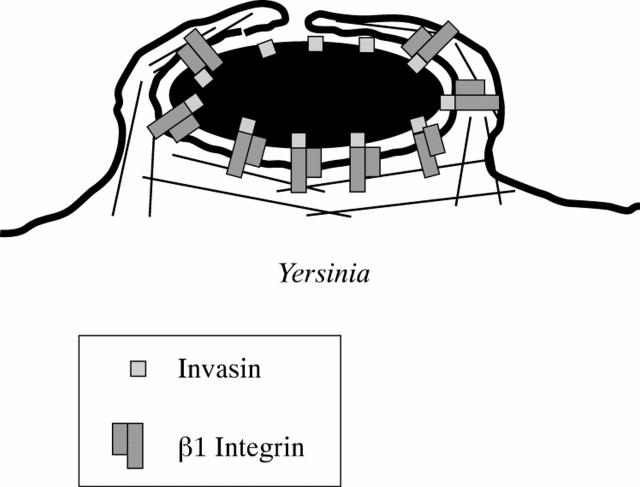
Figure 1 .
A paradigm of "zippering" entry of a bacterial pathogen into epithelial cells. Invasin mediated binding of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis to ß1 integrins and internalisation.
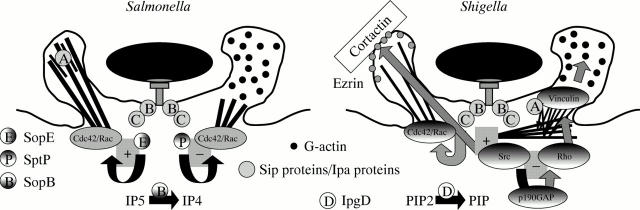
Figure 2 .
A paradigm or "triggering" entry of pathogens into epithelial cells: TTSS mediated translocation of Salmonella and Shigella effectors of entry inducing the formation of a macropinocytic vacuole.
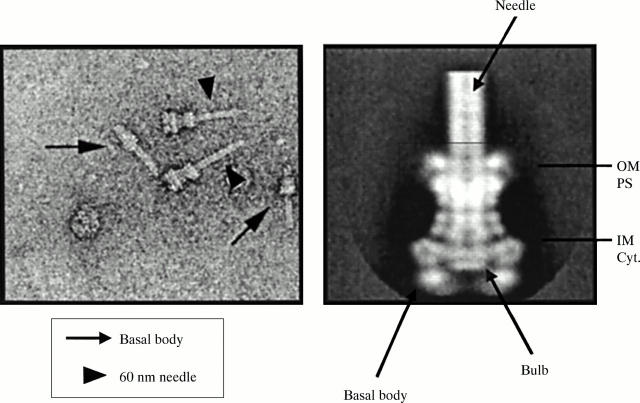
Figure 3 .
Structure of the TTSS of Shigella flexneri. OM, outer membrane; PS, periplasmic space; IM, inner membrane; Cyt, cytoplasm.
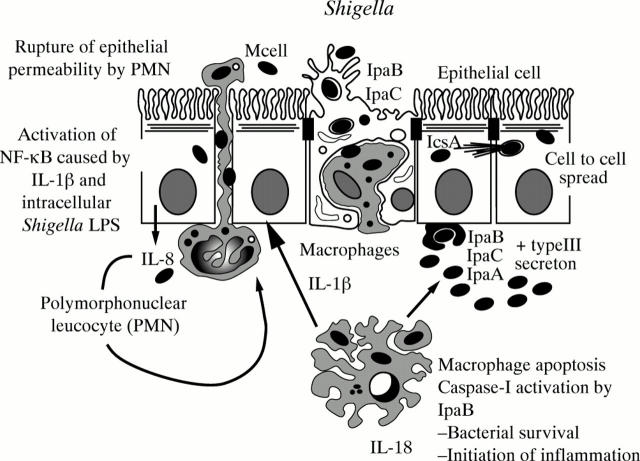
Figure 4 .
Physiopathological scheme of Shigella infection.
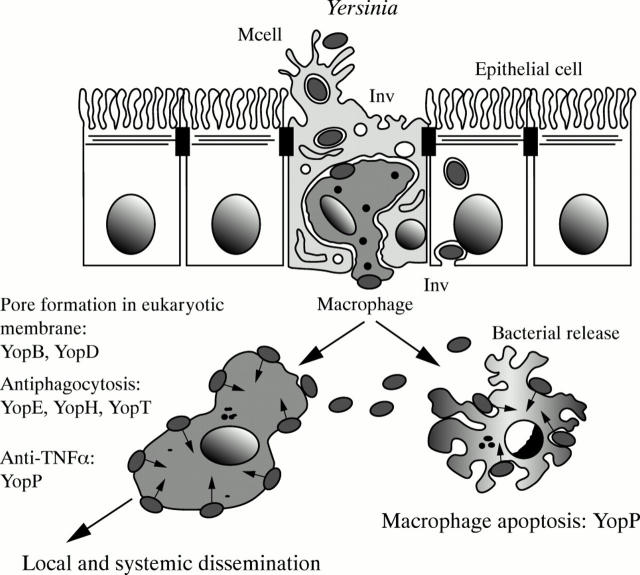
Figure 5 .
Physiopathological scheme of Yersinia infection.
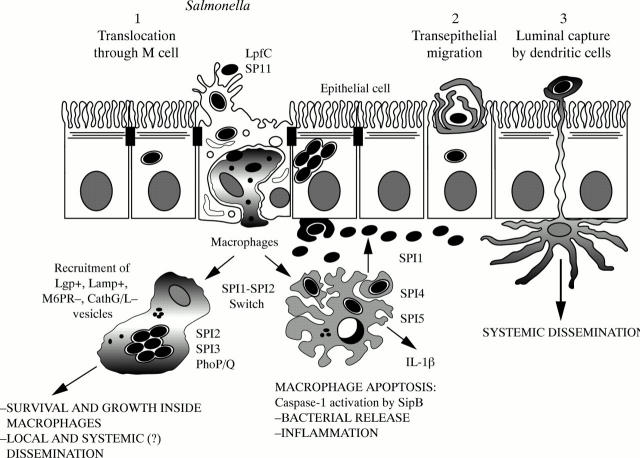
Figure 6 .
Salmonella routes for crossing the intestinal barrier and physiopathological scheme of infection.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alrutz M. A., Isberg R. R. Involvement of focal adhesion kinase in invasin-mediated uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Nov 10;95(23):13658–13663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.23.13658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Mounier J., d'Hauteville H., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of icsA, a plasmid locus of Shigella flexneri that governs bacterial intra- and intercellular spread through interaction with F-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3867–3871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. S., Bliska J. B. The RhoGAP activity of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis cytotoxin YopE is required for antiphagocytic function and virulence. Mol Microbiol. 2000 Aug;37(3):515–527. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blocker A., Gounon P., Larquet E., Niebuhr K., Cabiaux V., Parsot C., Sansonetti P. The tripartite type III secreton of Shigella flexneri inserts IpaB and IpaC into host membranes. J Cell Biol. 1999 Nov 1;147(3):683–693. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blocker A., Jouihri N., Larquet E., Gounon P., Ebel F., Parsot C., Sansonetti P., Allaoui A. Structure and composition of the Shigella flexneri "needle complex", a part of its type III secreton. Mol Microbiol. 2001 Feb;39(3):652–663. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdet-Sicard R., Egile C., Sansonetti P. J., Tran Van Nhieu G. Diversion of cytoskeletal processes by Shigella during invasion of epithelial cells. Microbes Infect. 2000 Jun;2(7):813–819. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(00)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdet-Sicard R., Rüdiger M., Jockusch B. M., Gounon P., Sansonetti P. J., Nhieu G. T. Binding of the Shigella protein IpaA to vinculin induces F-actin depolymerization. EMBO J. 1999 Nov 1;18(21):5853–5862. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.21.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäumler A. J., Tsolis R. M., Heffron F. The lpf fimbrial operon mediates adhesion of Salmonella typhimurium to murine Peyer's patches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jan 9;93(1):279–283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.1.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Smith M. R., Thirumalai K., Zychlinsky A. A bacterial invasin induces macrophage apoptosis by binding directly to ICE. EMBO J. 1996 Aug 1;15(15):3853–3860. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. A., Hirst B. H., Jepson M. A. M-cell surface beta1 integrin expression and invasin-mediated targeting of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis to mouse Peyer's patch M cells. Infect Immun. 1998 Mar;66(3):1237–1243. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.3.1237-1243.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. A., Jepson M. A., Simmons N. L., Hirst B. H. Preferential interaction of Salmonella typhimurium with mouse Peyer's patch M cells. Res Microbiol. 1994 Sep;145(7):543–552. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(94)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G. R. The Yersinia deadly kiss. J Bacteriol. 1998 Nov;180(21):5495–5504. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.21.5495-5504.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Geyter C., Wattiez R., Sansonetti P., Falmagne P., Ruysschaert J. M., Parsot C., Cabiaux V. Characterization of the interaction of IpaB and IpaD, proteins required for entry of Shigella flexneri into epithelial cells, with a lipid membrane. Eur J Biochem. 2000 Sep;267(18):5769–5776. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVinney R., Knoechel D. G., Finlay B. B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: cellular harassment. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999 Feb;2(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(99)80014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duménil G., Sansonetti P., Tran Van Nhieu G. Src tyrosine kinase activity down-regulates Rho-dependent responses during Shigella entry into epithelial cells and stress fibre formation. J Cell Sci. 2000 Jan;113(Pt 1):71–80. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everest P., Ketley J., Hardy S., Douce G., Khan S., Shea J., Holden D., Maskell D., Dougan G. Evaluation of Salmonella typhimurium mutants in a model of experimental gastroenteritis. Infect Immun. 1999 Jun;67(6):2815–2821. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.6.2815-2821.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Cossart P. Exploitation of mammalian host cell functions by bacterial pathogens. Science. 1997 May 2;276(5313):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5313.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Salmonella interactions with polarized human intestinal Caco-2 epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1096–1106. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y., Galán J. E. A salmonella protein antagonizes Rac-1 and Cdc42 to mediate host-cell recovery after bacterial invasion. Nature. 1999 Sep 16;401(6750):293–297. doi: 10.1038/45829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fällman M., Persson C., Wolf-Watz H. Yersinia proteins that target host cell signaling pathways. J Clin Invest. 1997 Mar 15;99(6):1153–1157. doi: 10.1172/JCI119270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galan J. E., Zhou D. Striking a balance: modulation of the actin cytoskeleton by Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Aug 1;97(16):8754–8761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.16.8754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-del Portillo F., Finlay B. B. Targeting of Salmonella typhimurium to vesicles containing lysosomal membrane glycoproteins bypasses compartments with mannose 6-phosphate receptors. J Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;129(1):81–97. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-del Portillo F., Zwick M. B., Leung K. Y., Finlay B. B. Salmonella induces the formation of filamentous structures containing lysosomal membrane glycoproteins in epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10544–10548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirtz A. T., Siber A. M., Madara J. L., McCormick B. A. Orchestration of neutrophil movement by intestinal epithelial cells in response to Salmonella typhimurium can be uncoupled from bacterial internalization. Infect Immun. 1999 Feb;67(2):608–617. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.2.608-617.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannasca K. T., Giannasca P. J., Neutra M. R. Adherence of Salmonella typhimurium to Caco-2 cells: identification of a glycoconjugate receptor. Infect Immun. 1996 Jan;64(1):135–145. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.1.135-145.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grützkau A., Hanski C., Hahn H., Riecken E. O. Involvement of M cells in the bacterial invasion of Peyer's patches: a common mechanism shared by Yersinia enterocolitica and other enteroinvasive bacteria. Gut. 1990 Sep;31(9):1011–1015. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.9.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A. Reprogramming the phagocytic pathway--intracellular pathogens and their vacuoles (review). Mol Membr Biol. 1998 Jul-Sep;15(3):103–121. doi: 10.3109/09687689809074522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science. 1998 Jan 23;279(5350):509–514. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5350.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward R. D., Koronakis V. Direct nucleation and bundling of actin by the SipC protein of invasive Salmonella. EMBO J. 1999 Sep 15;18(18):4926–4934. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.18.4926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh D., Monack D. M., Smith M. R., Ghori N., Falkow S., Zychlinsky A. The Salmonella invasin SipB induces macrophage apoptosis by binding to caspase-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Mar 2;96(5):2396–2401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.5.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilbi H., Moss J. E., Hersh D., Chen Y., Arondel J., Banerjee S., Flavell R. A., Yuan J., Sansonetti P. J., Zychlinsky A. Shigella-induced apoptosis is dependent on caspase-1 which binds to IpaB. J Biol Chem. 1998 Dec 4;273(49):32895–32900. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.49.32895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins S. A., Niedergang F., Corthesy-Theulaz I. E., Kraehenbuhl J. P. A recombinant Salmonella typhimurium vaccine strain is taken up and survives within murine Peyer's patch dendritic cells. Cell Microbiol. 2000 Feb;2(1):59–68. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2000.00035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Barnes P. Subversion of integrins by enteropathogenic Yersinia. J Cell Sci. 2001 Jan;114(Pt 1):21–28. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Discrimination between intracellular uptake and surface adhesion of bacterial pathogens. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):934–938. doi: 10.1126/science.1674624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Uptake of enteropathogenic Yersinia by mammalian cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996;209:1–24. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-85216-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Ghori N., Falkow S. Salmonella typhimurium initiates murine infection by penetrating and destroying the specialized epithelial M cells of the Peyer's patches. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):15–23. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung H. C., Eckmann L., Yang S. K., Panja A., Fierer J., Morzycka-Wroblewska E., Kagnoff M. F. A distinct array of proinflammatory cytokines is expressed in human colon epithelial cells in response to bacterial invasion. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jan;95(1):55–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI117676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernéis S., Bogdanova A., Kraehenbuhl J. P., Pringault E. Conversion by Peyer's patch lymphocytes of human enterocytes into M cells that transport bacteria. Science. 1997 Aug 15;277(5328):949–952. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5328.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohbata S., Yokoyama H., Yabuuchi E. Cytopathogenic effect of Salmonella typhi GIFU 10007 on M cells of murine ileal Peyer's patches in ligated ileal loops: an ultrastructural study. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(12):1225–1237. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb03055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubori T., Matsushima Y., Nakamura D., Uralil J., Lara-Tejero M., Sukhan A., Galán J. E., Aizawa S. I. Supramolecular structure of the Salmonella typhimurium type III protein secretion system. Science. 1998 Apr 24;280(5363):602–605. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5363.602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Nash S., Moore R., Atisook K. Structure and function of the intestinal epithelial barrier in health and disease. Monogr Pathol. 1990;(31):306–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Kurata T., Yoshikawa M. A genetic determinant required for continuous reinfection of adjacent cells on large plasmid in S. flexneri 2a. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90880-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra A., Isberg R. R. Invasin-dependent and invasin-independent pathways for translocation of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis across the Peyer's patch intestinal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1997 Aug;65(8):3412–3421. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.8.3412-3421.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathan M. M., Mathan V. I. Morphology of rectal mucosa of patients with shigellosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Mar-Apr;13 (Suppl 4):S314–S318. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.supplement_4.s314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maury J., Nicoletti C., Guzzo-Chambraud L., Maroux S. The filamentous brush border glycocalyx, a mucin-like marker of enterocyte hyper-polarization. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Mar 1;228(2):323–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick B. A., Miller S. I., Carnes D., Madara J. L. Transepithelial signaling to neutrophils by salmonellae: a novel virulence mechanism for gastroenteritis. Infect Immun. 1995 Jun;63(6):2302–2309. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.6.2302-2309.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki H., Suetsugu S., Takenawa T. WAVE, a novel WASP-family protein involved in actin reorganization induced by Rac. EMBO J. 1998 Dec 1;17(23):6932–6941. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.23.6932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I. PhoP/PhoQ: macrophage-specific modulators of Salmonella virulence? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2073–2078. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Vasselon T., Hellio R., Lesourd M., Sansonetti P. J. Shigella flexneri enters human colonic Caco-2 epithelial cells through the basolateral pole. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):237–248. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.237-248.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méresse S., Steele-Mortimer O., Finlay B. B., Gorvel J. P. The rab7 GTPase controls the maturation of Salmonella typhimurium-containing vacuoles in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1999 Aug 16;18(16):4394–4403. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.16.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy A., Szoke B., Schally A. V. Selective coupling of methotrexate to peptide hormone carriers through a gamma-carboxamide linkage of its glutamic acid moiety: benzotriazol-1-yloxytris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate activation in salt coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6373–6376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neutra M. R. M cells in antigen sampling in mucosal tissues. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1999;236:17–32. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-59951-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niebuhr K., Jouihri N., Allaoui A., Gounon P., Sansonetti P. J., Parsot C. IpgD, a protein secreted by the type III secretion machinery of Shigella flexneri, is chaperoned by IpgE and implicated in entry focus formation. Mol Microbiol. 2000 Oct;38(1):8–19. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L. Uptake and transport of intestinal macromolecules and microorganisms by M cells in Peyer's patches--a personal and historical perspective. Semin Immunol. 1999 Jun;11(3):157–163. doi: 10.1006/smim.1999.0171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page A. L., Ohayon H., Sansonetti P. J., Parsot C. The secreted IpaB and IpaC invasins and their cytoplasmic chaperone IpgC are required for intercellular dissemination of Shigella flexneri. Cell Microbiol. 1999 Sep;1(2):183–193. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.1999.00019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penheiter K. L., Mathur N., Giles D., Fahlen T., Jones B. D. Non-invasive Salmonella typhimurium mutants are avirulent because of an inability to enter and destroy M cells of ileal Peyer's patches. Mol Microbiol. 1997 May;24(4):697–709. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.3741745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdomo J. J., Gounon P., Sansonetti P. J. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte transmigration promotes invasion of colonic epithelial monolayer by Shigella flexneri. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):633–643. doi: 10.1172/JCI117015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdomo O. J., Cavaillon J. M., Huerre M., Ohayon H., Gounon P., Sansonetti P. J. Acute inflammation causes epithelial invasion and mucosal destruction in experimental shigellosis. J Exp Med. 1994 Oct 1;180(4):1307–1319. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson C., Carballeira N., Wolf-Watz H., Fällman M. The PTPase YopH inhibits uptake of Yersinia, tyrosine phosphorylation of p130Cas and FAK, and the associated accumulation of these proteins in peripheral focal adhesions. EMBO J. 1997 May 1;16(9):2307–2318. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.9.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathman M., Jouirhi N., Allaoui A., Sansonetti P., Parsot C., Tran Van Nhieu G. The development of a FACS-based strategy for the isolation of Shigella flexneri mutants that are deficient in intercellular spread. Mol Microbiol. 2000 Mar;35(5):974–990. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathman M., de Lanerolle P., Ohayon H., Gounon P., Sansonetti P. Myosin light chain kinase plays an essential role in S. flexneri dissemination. J Cell Sci. 2000 Oct;113(Pt 19):3375–3386. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.19.3375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rescigno M., Urbano M., Valzasina B., Francolini M., Rotta G., Bonasio R., Granucci F., Kraehenbuhl J. P., Ricciardi-Castagnoli P. Dendritic cells express tight junction proteins and penetrate gut epithelial monolayers to sample bacteria. Nat Immunol. 2001 Apr;2(4):361–367. doi: 10.1038/86373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Arondel J., Cantey J. R., Prévost M. C., Huerre M. Infection of rabbit Peyer's patches by Shigella flexneri: effect of adhesive or invasive bacterial phenotypes on follicle-associated epithelium. Infect Immun. 1996 Jul;64(7):2752–2764. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.7.2752-2764.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Arondel J., Cavaillon J. M., Huerre M. Role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of experimental shigellosis. J Clin Invest. 1995 Aug;96(2):884–892. doi: 10.1172/JCI118135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Arondel J., Fontaine A., d'Hauteville H., Bernardini M. L. OmpB (osmo-regulation) and icsA (cell-to-cell spread) mutants of Shigella flexneri: vaccine candidates and probes to study the pathogenesis of shigellosis. Vaccine. 1991 Jun;9(6):416–422. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90128-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Mounier J., Prévost M. C., Mège R. M. Cadherin expression is required for the spread of Shigella flexneri between epithelial cells. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):829–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Phalipon A., Arondel J., Thirumalai K., Banerjee S., Akira S., Takeda K., Zychlinsky A. Caspase-1 activation of IL-1beta and IL-18 are essential for Shigella flexneri-induced inflammation. Immunity. 2000 May;12(5):581–590. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Phalipon A. M cells as ports of entry for enteroinvasive pathogens: mechanisms of interaction, consequences for the disease process. Semin Immunol. 1999 Jun;11(3):193–203. doi: 10.1006/smim.1999.0175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuch R., Sandlin R. C., Maurelli A. T. A system for identifying post-invasion functions of invasion genes: requirements for the Mxi-Spa type III secretion pathway of Shigella flexneri in intercellular dissemination. Mol Microbiol. 1999 Nov;34(4):675–689. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea J. E., Hensel M., Gleeson C., Holden D. W. Identification of a virulence locus encoding a second type III secretion system in Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Mar 19;93(6):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A. Electron microscope studies of experimental Salmonella infection. I. Penetration into the intestinal epithelium by Salmonella typhimurium. Am J Pathol. 1967 Jan;50(1):109–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamano K., Aizawa S., Katayama E., Nonaka T., Imajoh-Ohmi S., Kuwae A., Nagai S., Sasakawa C. Supramolecular structure of the Shigella type III secretion machinery: the needle part is changeable in length and essential for delivery of effectors. EMBO J. 2000 Aug 1;19(15):3876–3887. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.15.3876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran Van Nhieu G., Ben-Ze'ev A., Sansonetti P. J. Modulation of bacterial entry into epithelial cells by association between vinculin and the Shigella IpaA invasin. EMBO J. 1997 May 15;16(10):2717–2729. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.10.2717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran Van Nhieu G., Bourdet-Sicard R., Duménil G., Blocker A., Sansonetti P. J. Bacterial signals and cell responses during Shigella entry into epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 2000 Jun;2(3):187–193. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2000.00046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran Van Nhieu G., Caron E., Hall A., Sansonetti P. J. IpaC induces actin polymerization and filopodia formation during Shigella entry into epithelial cells. EMBO J. 1999 Jun 15;18(12):3249–3262. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.12.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nhieu G. T., Isberg R. R. The Yersinia pseudotuberculosis invasin protein and human fibronectin bind to mutually exclusive sites on the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24367–24375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Torres A., Fang F. C. Cellular routes of invasion by enteropathogens. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2000 Feb;3(1):54–59. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(99)00051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Torres A., Jones-Carson J., Bäumler A. J., Falkow S., Valdivia R., Brown W., Le M., Berggren R., Parks W. T., Fang F. C. Extraintestinal dissemination of Salmonella by CD18-expressing phagocytes. Nature. 1999 Oct 21;401(6755):804–808. doi: 10.1038/44593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassef J. S., Keren D. F., Mailloux J. L. Role of M cells in initial antigen uptake and in ulcer formation in the rabbit intestinal loop model of shigellosis. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):858–863. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.858-863.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M. D. The world according to Arp: regulation of actin nucleation by the Arp2/3 complex. Trends Cell Biol. 1999 Nov;9(11):423–427. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(99)01651-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarmolinsky M. B. A pot-pourri of plasmid paradoxes: effects of a second copy. Mol Microbiol. 2000 Oct;38(1):1–7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D., Chen L. M., Hernandez L., Shears S. B., Galán J. E. A Salmonella inositol polyphosphatase acts in conjunction with other bacterial effectors to promote host cell actin cytoskeleton rearrangements and bacterial internalization. Mol Microbiol. 2001 Jan;39(2):248–259. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D., Mooseker M. S., Galán J. E. Role of the S. typhimurium actin-binding protein SipA in bacterial internalization. Science. 1999 Mar 26;283(5410):2092–2095. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5410.2092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumbihl R., Aepfelbacher M., Andor A., Jacobi C. A., Ruckdeschel K., Rouot B., Heesemann J. The cytotoxin YopT of Yersinia enterocolitica induces modification and cellular redistribution of the small GTP-binding protein RhoA. J Biol Chem. 1999 Oct 8;274(41):29289–29293. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.41.29289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zychlinsky A., Prevost M. C., Sansonetti P. J. Shigella flexneri induces apoptosis in infected macrophages. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):167–169. doi: 10.1038/358167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]