Vascular Permeability Factor/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Induces Lymphangiogenesis as well as Angiogenesis (original) (raw)
Abstract
Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor (VPF/VEGF, VEGF-A) is a multifunctional cytokine with important roles in pathological angiogenesis. Using an adenoviral vector engineered to express murine VEGF-A164, we previously investigated the steps and mechanisms by which this cytokine induced the formation of new blood vessels in adult immunodeficient mice and demonstrated that the newly formed blood vessels closely resembled those found in VEGF-A–expressing tumors. We now report that, in addition to inducing angiogenesis, VEGF-A164 also induces a strong lymphangiogenic response. This finding was unanticipated because lymphangiogenesis has been thought to be mediated by other members of the VPF/VEGF family, namely, VEGF-C and VEGF-D. The new “giant” lymphatics generated by VEGF-A164 were structurally and functionally abnormal: greatly enlarged with incompetent valves, sluggish flow, and delayed lymph clearance. They closely resembled the large lymphatics found in lymphangiomas/lymphatic malformations, perhaps implicating VEGF-A in the pathogenesis of these lesions. Whereas the angiogenic response was maintained only as long as VEGF-A was expressed, giant lymphatics, once formed, became VEGF-A independent and persisted indefinitely, long after VEGF-A expression ceased. These findings raise the possibility that similar, abnormal lymphatics develop in other pathologies in which VEGF-A is overexpressed, e.g., malignant tumors and chronic inflammation.
Keywords: VEGF-C, VEGF-D, PlGF, VPF/VEGF, VEGF-A
Introduction
Most mammalian tissues are supplied by two interconnected but largely independent vascular systems, the one carrying blood and the other lymph. Much has been learned in recent years about the generation of the blood vasculature and the two distinct but overlapping processes that are responsible: vasculogenesis (de novo generation of blood vessels from primitive precursor cells as occurs in development) and angiogenesis (generation of new blood vessels from preexisting blood vessels; references 1–4). Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor (VPF/VEGF, VEGF-A)* is a multifunctional cytokine that has essential roles in both processes (5–8). It mediates its several activities primarily through interaction with two receptor tyrosine kinases, VEGF receptor (VEGFR)-1 and VEGFR-2, that are selectively, though not exclusively, expressed on vascular endothelium. Another member of the VPF/VEGF family, placenta growth factor (PlGF), also has a role in pathological angiogenesis, interacting with VEGFR-1 but not VEGFR-2 (9).
Less is known about the cytokines responsible for generating the lymphatic vascular system. Recent work from several laboratories has identified critical roles for two members of the VPF/VEGF cytokine family, VEGF-C and VEGF-D (10–16). Mutation or loss of these cytokines or their receptor (VEGFR-3) leads to impaired lymphatic development and human disease whereas overexpression of VEGF-C or VEGF-D induces increased lymphangiogenesis in animal systems. Both VEGF-C and VEGF-D induce angiogenesis as well as lymphangiogenesis under appropriate circumstances (10, 15, 16) but VEGF-A is thought not to induce lymphangiogenesis (14, 17–19).
When murine VEGF-A164 was introduced into adult mouse tissues by means of an adenoviral vector, angiogenesis developed according to a characteristic series of steps (20, 21). Within a matter of hours, infected host cells expressed VEGF-A164, inducing microvascular hyperpermeability, extravasation of plasma and plasma proteins, deposition of extravascular fibrin gel and edema. Within the same time frame, preexisting capillaries and venules enlarged greatly to form thin-walled, hyperpermeable, pericyte-poor “mother” vessels; over the course of the next 2 wk, mother vessels evolved along several independent lines to form daughter capillaries, glomeruloid bodies, and arterio-venous malformations. Subsequently, as VEGF-A expression waned, the angiogenic response resolved with a return to near normal microvascular density by ∼8 wk.
We here report the unanticipated finding that, in addition to angiogenesis, VEGF-A also induces proliferation of lymphatic endothelium, resulting in the formation of greatly enlarged and poorly functioning lymphatic channels. Unlike angiogenesis, the lymphangiogenic response became VEGF-A independent, as, once formed, the newly formed “giant” lymphatics persisted indefinitely, long after VEGF-A expression and tissue edema had ceased. These findings raise the possibility that abnormal lymphangiogenesis may also be expected in other circumstances that are characterized by VEGF-A overexpression such as chronic inflammation and malignant tumors (5).
Materials and Methods
Adenoviral Vectors and Animals.
A nonreplicating adenoviral vector was engineered to express the predominant (164 amino acid) murine isoform of VEGF-A as described previously (20). An adenoviral vector expressing placenta growth factor (murine PlGF-2) was provided by Dr. Peter Carmeliet, Leuven, Belgium. Vectors were grown to titers of ∼1012 PFU/ml and purified using a double cesium chloride banding procedure by Qbiogene. Immediately before use, vectors were desalted using Quick Spin, High Capacity G-50 Sephadex columns (Boehringer) and diluted in PBS–3% glycerol. 5 μl of vectors containing 0.5–1.0 × 108 PFU were injected into the ears of 4–6-wk-old female athymic Nu/Nu mice (National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD) as described previously (20, 21). More than 200 mice participated in this study. Animal protocols were approved by the BIDMC Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Microscopic Studies.
Mice were killed by CO2 narcosis. For preparation of Giemsa-stained 1 μm Epon sections and for electron microscopy, ears were fixed in paraformaldehyde-glutaraldehyde and processed as described previously (20, 21). For quantifying lymphatic endothelial cell proliferation, mice were anesthetized with Avertin (200 mg/kg tribromoethanol IP) and injected intravenously with 50 μCi of [3H]thymidine. 1 h later, mice were killed and ears were fixed and processed for autoradiography on 1 μm Giemsa-stained Epon sections (22).
Rabbit antibodies to the extracellular soluble domain of murine VEGFR-2 (flk-1) were the kind gift of Drs. Rolf Brekken and Philip Thorpe, University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, TX (23). For immunohistochemical staining, mouse ears were immersed in freshly prepared 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.02 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.4. After 4 h at room temperature, tissues were transferred to 30% sucrose in PBS, pH 7.4, and incubated overnight at 4°C before embedding in OCT compound (Miles Diagnostics). Frozen 5–10 μm cryostat sections were collected on microscopic slides for immunostaining (23).
For immunofluorescence, 6-μm frozen sections were fixed in ice-cold acetone and 80% methanol, rehydrated in PBS, and double stained with a primary rabbit antibody to the murine hyaluronan receptor LYVE-1 (provided by Dr. D. Jackson, Institute of Molecular Medicine, John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, UK [24]) and with a rat monoclonal antibody to mouse CD31 (BD Biosciences). Corresponding secondary anti–rabbit IgG or anti–rat IgG antibodies were labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 or 594, respectively (Molecular Probes). Sections were examined in a Nikon E-600 fluorescent microscope.
For in situ hybridization, tissues were fixed and frozen in OCT compound as for immunohistochemistry but with RNase free reagents. Cryostat sections were hybridized with antisense and sense (control), single stranded, 35S-labeled RNA probes to murine VEGF-A, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, PlGF, VEGFR-1, and VEGFR-2 as described previously (25).
Intravital Perfusion of Lymphatics.
These experiments were slightly modified after Hudack and McMaster (26). Mice were anesthetized with sodium pentobarbital (75 mg/kg) and cradled in a transparent acrylic resin mold (Syndicate Sales, Inc.). Ears were mounted flat on the resin support and held in place by silicone vacuum grease and viewed in a Wild M400 Photomacroscope. Colloidal carbon (Higgins nonwaterproof drawing ink; Sanford) was diluted 1:1 in Tyrode's buffer and injected through a 10-μm prepulled borosilicate glass micropipette attached to a 500-μl Hamilton syringe. The micropipette was repeatedly injected into the dorsal surface of the peripheral ear until a lymphatic capillary was entered. Additional carbon (5–20 μl) was then slowly injected under the control of a threaded plunger to avoid overfilling and vessel damage. For photography, ears were flooded with immersion oil, coverslipped, and photographed with a SPOT Insight Digital camera.
Confocal Scanning Fluorescence Microscopy.
For simultaneous visualization of blood and lymphatic vessels, mice were anesthetized as above and injected intravenously with 2 × 106 MW lysine-fixable fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled dextran (FITC-dextran, 6 mg in 0.2 ml saline; Molecular Probes). Immediately thereafter, peripheral ear lymphatics were injected with 2 × 106 MW tetramethyl-rhodamine–dextran (TMR-dextran, 30 mg/ml in saline; Molecular Probes) as for colloidal carbon. 30 min later, ears were fixed in 4% formaldehyde in PBS for 4 h, washed in PBS-2% sucrose, mounted with Vectashield (Vector Laboratories) in imaging chambers (Sigma-Aldrich), and visualized with a 1024 MRC Bio-RAD confocal microscope equipped with a Krypton Argon laser. Five to seven fields from the same region of each ear were visualized. Data were collected with confocal setting in the sequential mode, exciting and collecting one channel (fluorophore) at a time to allow optimal separation of green and red fluorescence. Stacks of optical sections were collected by optical z sectioning (z step = 4 μm). Individual optical sections or vertical projections were processed using the Bio-Rad Laboratories LaserSharp Software version 3.2 and saved as TIFF files in Adobe Photoshop 6.0.
Results
Lymphangiogenic Response to Ad-VEGF-A164.
Lymphatic capillaries are normally collapsed and their initial response (1–3 d) to VEGF-A164 was, as expected, that of homeostatic distension (Fig. 1 , a and b). VEGF-A164 is a potent vascular permeabilizing factor that induces extravasation of blood plasma and consequent tissue edema (5, 7). In response to interstitial fluid accumulation, lymphatics distend in response to tension applied to the anchoring filaments connecting them to the surrounding connective tissues (27, 28).
Figure 1.
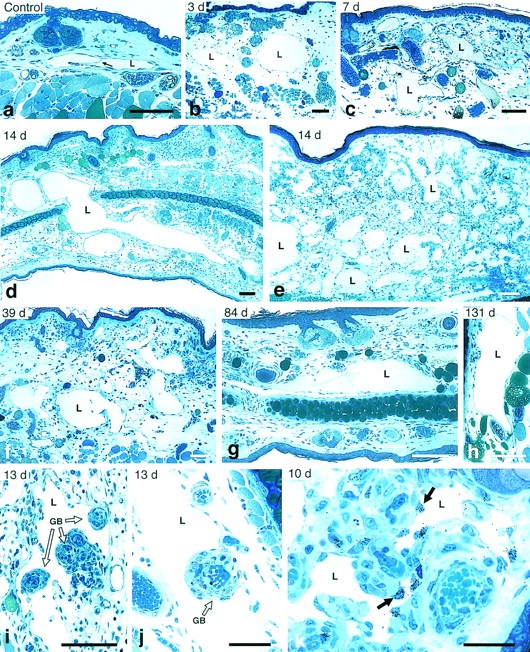
Lymphangiogenic response induced by Ad-VEGF-A164 in nude mouse ears. (a) Normal lymphatic in control ear skin (arrow indicates a valve). (b) Lymphatics at 3 d after Ad-VEGF-A164 are distended from dermal edema but have already enlarged further as the result of endothelial cell division and are transitioning into giant lymphatics. (c–h) Giant lymphatics occupy large portions of the dermis at 7–131 d after Ad-VEGF-A164. Panel c illustrates giant lymphatics that contain colloidal carbon injected as described in Materials and Methods and illustrated macroscopically in Fig. 5. Lymphatic (L) in g contains fibrin clot whereas three unlabeled lymphatics (top right) are filled with colloidal carbon. (i and j) Giant lymphatics wrap around glomeruloid bodies (GB) 13 d after Ad-VEGF-A164. (k) Autoradiograph showing [3H]thymidine incorporation by lymphatic endothelial cells (arrows) at 10 d after Ad-VEGF-A164. L, lymphatics. Giemsa stained 1 μm Epon sections. Bars: a–h, 100 μm; i and j, 50 μm; k, 25 μm.
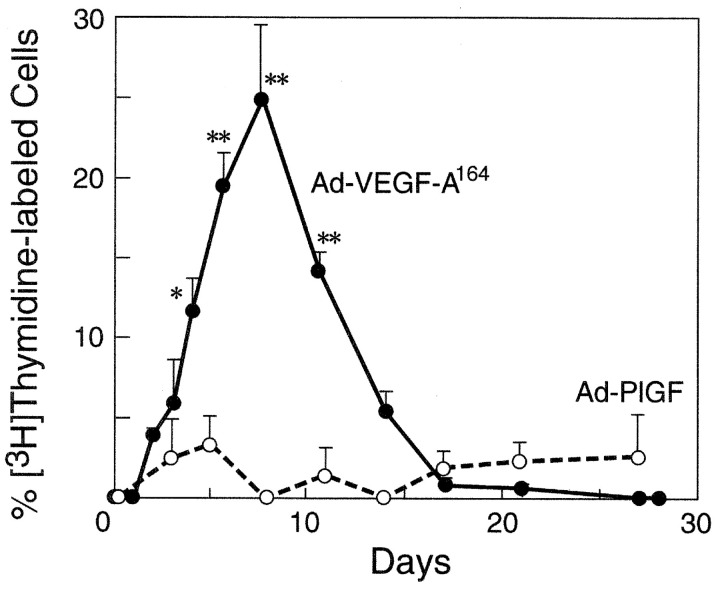
Incorporation of [3H]thymidine was not observed in lymphatic capillary endothelial cells of normal mouse ears or of ears injected 1 d prior with Ad-VEGF-A164 (Fig. 2) . Low level labeling was first detected on day 2, and, thereafter, lymphatic capillary endothelium incorporated increasing amounts of thymidine until by 8 d nearly 25% of cells were labeled (Figs. 1 k and 2). In parallel with lymphatic endothelial cell proliferation, lymphatic capillaries enlarged progressively and, by 2–3 wk had attained cross-sectional areas many times larger than the homeostatic response to tissue edema (Fig. 1, c–e). These “giant” lymphatics formed a meshwork of large, irregularly shaped vessels that occupied substantial portions of the dermis and persisted indefinitely, wrapping around blood vascular structures such as glomeruloid bodies (Fig. 1, f–j). After 8 d, the labeling index decreased steadily but as late as 3 wk nearly 1% of lymphatic endothelial cells continued to incorporate [3H]thymidine (Fig. 2).
Figure 2.
Percent of lymphatic endothelial cells labeled by [3H]thymidine (mean ± std error) at intervals after ear injection with Ad-VEGF-A164 or Ad-PlGF. Values at successive times (based on 3–6 animals per time point) were compared with those at time zero using Dunn's multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.
The lymphatic endothelium lining giant lymphatics stained strongly and consistently with antibodies to VEGFR-2 (23, 29) and to LYVE-1 (24), not differing in this respect from normal lymphatics (Fig. 3) . In accord with earlier work (20), infected host cells expressed VEGF-A164 mRNA steadily for ∼2 wk as determined by in situ hybridization, after which expression progressively declined and became undetectable by ∼4 wk (20, 21). mRNAs encoding both VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 were similarly overexpressed in the endothelium of newly formed blood vessels (reference 20, and unpublished data). We did not detect expression of either VEGF-C or VEGF-D mRNA at any time point. Ears injected with Ad-PlGF developed a characteristic angiogenic response (9) but neither edema nor lymphangiogenesis (Fig. 2).
Figure 3.
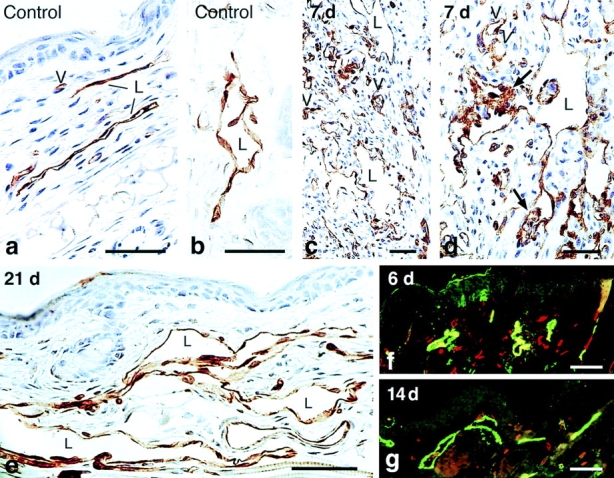
Immunostaining of lymphatics for VEGFR-2 (a–e) and for the hyaluronan receptor LYVE-1 (f and g). Immunoperoxidase staining of control lymphatics (a and b) or giant lymphatics (c–e) at indicated times after Ad-VEGF-A164. Note bridging of lymphatics by VEGFR-2–positive endothelium (d, arrows). L, lymphatics; v, micro blood vessels whose endothelial cells also stain. (f and g) Immunofluorescence staining of lymphatics with anti-LYVE antibody (green) and micro-blood vessels with CD31 (red), 6 and 14 d after Ad-VEGF-A164. Bars: a, b, and e, 10 μm; c and d, 20 μm; f and g, 200 μm.
Function of Giant Lymphatics.
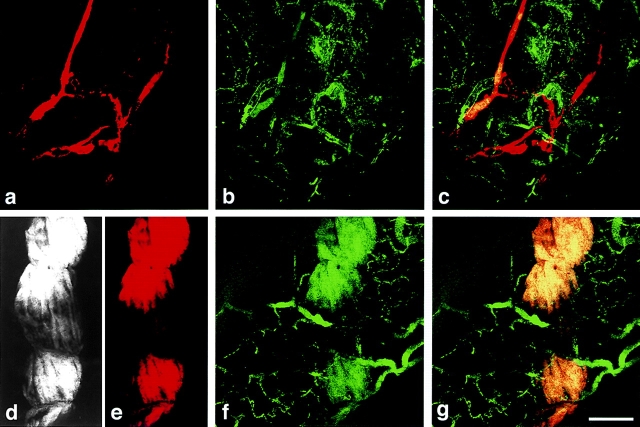
An important function of lymphatics is to take up and return to the blood extravasated plasma and plasma proteins in excess of that reabsorbed by capillaries. To determine whether giant lymphatics were able to take up macromolecules that had extravasated from leaky blood vessels, we injected tracer FITC-dextran (green) intravenously into mice that had had one ear injected 4 d previously with Ad-VEGF-A164, leaving the other ear uninjected. Giant lymphatics were labeled by injecting macromolecular TMR-dextran (red) directly into small lymphatics peripheral to the zone of VEGF-A164-induced edema, angiogenesis, and lymphangiogenesis. As expected, FITC-dextran was almost completely retained within the blood vessels of control ears and therefore was not available in the interstitium for uptake by lymphatics (Fig. 4 , a–c). By contrast, FITC-dextran leaked extensively from microvessels rendered hyperpermeable by Ad-VEGF164 and was taken up by giant lymphatics (Fig. 4, d–g). Some giant lymphatics exhibited zones of incomplete filling as the result of segmental intraluminal clotting and thrombosis (see below); such zones of interrupted filling were often traversed by narrow open channels that allowed passage of tracer (Fig. 4, d–g).
Figure 4.
Confocal microscopy of lymphatic and microvascular plexuses in ears of a control mouse (a–c) and a mouse injected 4 d previously with Ad-VEGF-A164 (d–g). FITC-dextran (green) was injected intravenously into the tail vein and TMR-dextran (red) was microinjected into the peripheral ear lymphatics. (a) Normal ear lymphatic plexus delineated by TMR-dextran. (b) Normal ear blood microvasculature delineated by FITC-dextran. (c) Composite retains distinct green and red compartments for the most part, indicating little or no lymphatic uptake of FITC-dextran. (d and e) TMR-dextran, reproduced in both black and white and in red, within a giant lymphatic. Centrally the channel is partially obstructed (presumably by fibrin clot, see text and Figs. 6 and 7), such that the upper and lower portions are connected only through narrow channels that allow tracer flow (best illustrated in d). (f) FITC-dextran fills leaky micro-blood vessels and has entered the lymphatic illustrated in d and e. (g) Merged image. Yellow color indicates FITC-dextran extravasated from leaky blood vessels has been taken up by the giant lymphatic infused with TMR-dextran. Bars, 50 μM.
The function of the Ad-VEGF-A164-induced giant lymphatics was further tested by assessing tracer flow and clearance. For these studies, colloidal carbon was injected into the peripheral lymphatics as above for TMR-dextran. In normal control ears, carbon entered fine, distinct, lymphatics that extended radially from the periphery to the base of the ear; these were punctuated by periodic bulbous swellings that marked valves (Fig. 5 a). Though joined at intervals by interconnecting side branches, there was minimal sideways filling. Therefore, multiple injection sites were required to fill the majority of lymphatics in normal ears (Fig. 5 a). Carbon injected at individual sites remained largely within one or two radially oriented lymphatics and drained rapidly and completely into postauricular and cervical lymph nodes within 20 min (Fig. 5, m and n). Similar results were obtained in mice whose ears had been injected with Ad-PlGF (Fig. 5, b–d), a finding consistent with the minimal proliferation of lymphatic endothelium induced by PlGF (Fig. 2).
Figure 5.
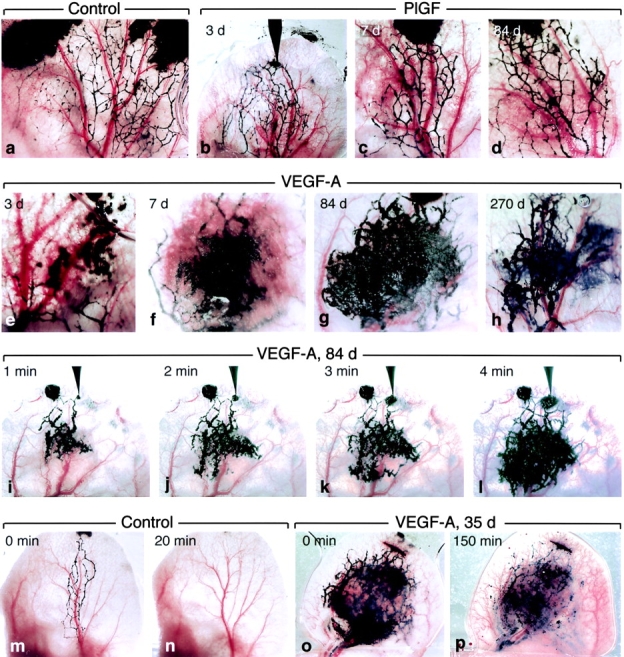
Ear lymphatics after intravital infusion of colloidal carbon in a control mouse and in mice injected at indicated intervals with Ad-PlGF or Ad-VEGF-A164. (a) Control ear. Multiple injection sites (black blotches at top) were required to fill the lymphatic network. Note periodic bulbous swellings that identify valves. (b–d) Lymphatic filling in ears of mice injected at indicated times with Ad-PlGF. Injecting micropipette is shown in place in b. Lymphatics retain bulbous valve markings. (e–h) Pattern of lymphatic filling in ears of mice injected previously, as indicated, with Ad-VEGF-A164. Giant lymphatics are apparent as early as 3 d (e) and persist through day 270. Bulbous valve markings are lost. (i–l) Kinetics of lymphatic filling in ear of a mouse 84 d after injection with Ad-VEGF-A164. Note widespread filling of lymphatic network by 4 min from a single injection site (that with the micropipette in place). An earlier injection site (to left of pipette) failed to engage the terminal lymphatics. (m–p) Clearance of carbon from control ear lymphatics (m and n) is complete by 20 min but at 35 d after Ad-VEGF-A164 ear lymphatics still retain abundant tracer after 150 min (o and p).
Very different results were obtained when colloidal carbon was injected into the terminal ear lymphatics of mice previously injected with Ad-VEGF-A164 (Fig. 5, e–h). In such mice, both radial and interconnecting lymphatics enlarged greatly to form giant lymphatics and no longer exhibited the bulbous swellings that marked the location of valves in normal lymphatics. As the result of cross-sectional enlargement, the valves in giant lymphatics were unable to close to prevent backward and sideways flow. Upon entering giant lymphatics, therefore, carbon from a single injection site was diverted into interconnecting side channels and, within a few minutes, filled lymphatics spread over a large portion of the ear surface (Fig. 5, i–l). However, lymph flow in giant lymphatics was sluggish and clearance of colloidal carbon was greatly delayed; substantial amounts of tracer persisted within giant lymphatics for long periods of time after cessation of tracer injection (Fig. 5, o and p), often for more than 24 h. Giant lymphatics with these properties were evident as early as 3 d in ears injected with Ad-VEGF-A164 and persisted indefinitely (Fig. 5, e–h). That the carbon injected was actually present in and confined to giant lymphatics is illustrated in Fig. 1, c and g.
Intravascular Clotting and Remodeling of Giant Lymphatics.
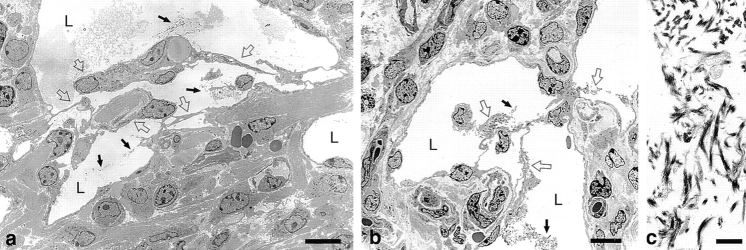
Whereas many giant lymphatics persisted as large, patent structures, others underwent intravascular clotting with consequent partial or complete obstruction to flow by fibrin clot (Figs. 6 and 7) . Although occasional red blood cells leaked from blood vessels and entered lymphatics (Fig. 6, d–f, and h), platelets were not recognized by either light or electron microscopy. Lymphatic endothelial cells, identified by their staining for VEGFR-2 (Fig. 3) and by ultrastructural features (Fig. 7), used fibrin as a substrate for intraluminal migration, forming a fishnet-like meshwork of interconnecting cells that bridged the lymphatic lumens and divided them into a multiplicity of smaller channels (Figs. 6 and 7). Fibrin bridges were subsequently replaced by thin bundles of collagen.
Figure 6.
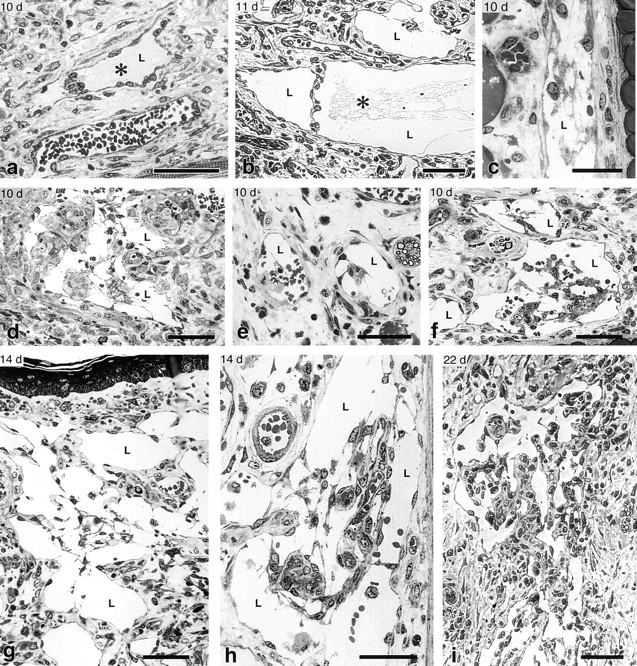
Intraluminal fibrin clot formation and transluminal bridging of giant lymphatics at indicated times after Ad-VEGF-A164 injection. None of the lymphatics illustrated had been injected with carbon or other agents. (a and b) Fibrin clot (*) within giant lymphatics at 10–11 d; note transluminal bridging by lymphatic endothelium. (c–i) Migrating lymphatic endothelial cells formed transluminal bridges across giant lymphatics, dividing their lumens into multiple smaller, endothelium-lined channels. Initially fibrin formed a substrate for endothelial cell migration but was subsequently digested and replaced by collagen. By 22 d (i) bridges had become quite cellular. Note red blood cells within lymphatics (d–f, h). L, giant lymphatics. Giemsa stained 1 μm Epon sections. Bars: a, b, and d–i, 50 μm; c, 25 μm.
Figure 7.
Electron micrographs of giant lymphatics at 21 d (a) and 14 d (b) after Ad-VEGF-A164 injection, illustrating intraluminal fibrin deposits and transluminal bridging by lymphatic endothelial cells. Black arrows indicate intralymphatic fibrin and open arrows the endothelial cell bridging that followed. (c) Intraluminal fibrin is more clearly demonstrated at higher magnification. L, lymphatic lumens. Bars: a and b, 5 μm; c, 1 μm.
Discussion
The data presented here indicate that murine VEGF-A164 induces lymphangiogenesis in addition to angiogenesis. This finding was unanticipated in that lymphangiogenesis has been thought to be the purview of two other members of the VPF/VEGF family, VEGF-C and VEGF-D, neither of which was detectably expressed in these experiments. The initial response of lymphatic capillaries to VEGF-A164 was distension, attributable to interstitial edema; this was followed by proliferation of lymphatic endothelium, leading to gross enlargement and the formation of “giant” lymphatics that exhibited sluggish flow and delayed tracer clearance. The angiogenic response induced by VEGF-A164 continued only as long as VEGF-A164 was expressed and completely resolved by ∼2 mo. On the other hand, giant lymphatics persisted indefinitely, for at least a year, long after VEGF-A164 expression had ceased and edema had resolved. Thus, whereas VEGF-A is a well known survival factor for newly formed blood vessels, it is apparently not required for the sustenance of newly formed giant lymphatics. Giant lymphatics also formed in peritoneal lining tissues in response to VEGF-A164 (unpublished data); therefore the lymphangiogenic response was not unique to ear skin. In contrast to Ad-VEGF-A164, an adenoviral vector expressing murine PlGF induced angiogenesis (9) but not lymphangiogenesis.
There are similarities and differences in the steps and mechanisms by which VEGF-A164 induced the formation of mother blood vessels and giant lymphatics. Mother blood vessels formed as the result of two temporally distinct processes (20): (a) degradation of venule endothelial cell basement membranes, detachment of pericytes, and transfer of stored intraendothelial cell membrane to the plasma membrane; together these events allowed vessel enlargement within 18 h, entirely independent of cell division. (b) Proliferation of vascular endothelial cells and pericytes, beginning on day 2 and reaching a peak on days 7–8.
Giant lymphatics also formed in two steps but these overlapped temporally. The second step in giant lymphatic formation, proliferation of lymphatic endothelial cells, paralleled the proliferation of vascular endothelial cells in enlarging mother blood vessels and followed nearly identical kinetics (illustrated for lymphatics in Fig. 2). However, the first step in the development of giant lymphatics was distinctly different from that leading to the formation of mother blood vessels. Unlike venules, lymphatic capillaries for the most part lack pericytes, have poorly developed basement membranes, and are flattened cells with limited internal membrane stores (28, 30); therefore, changes in these elements, characteristic of the first stage of mother blood vessel formation, had no role in initiating lymphatic enlargement. Instead, lymphatics, which are collapsed in normal tissues, became distended by 1 d in response to VEGF-A164-induced microvascular hyperpermeability, tissue edema, and the consequent outward pull of anchoring filaments (27, 28). Apart from this homeostatic distension, lymphatics did not increase in size until their lining endothelium began to proliferate (Figs. 1 and 2).
VEGF-A164–induced giant lymphatics were functional in that they took up macromolecules extravasated from hyperpermeable microvessels and transported them to draining lymph nodes (Fig. 4). However, flow in giant lymphatics was sluggish and tracer clearance was markedly delayed (Fig. 5), as compared with normal lymphatics, for at least two reasons. First, the valves of giant lymphatics were unable to close properly and were thus unable to prevent lateral lymph flow into side channels. Flow in giant lymphatics was also impeded by intralymphatic clotting and thrombosis (Figs. 6 and 7). Fibrinogen, like other plasma proteins, extravasated in response to VEGF-A–induced changes in venular permeability, and substantial amounts clotted in the extravascular space (20). However, extravasated fibrinogen was also taken up by giant lymphatics and underwent intraluminal clotting, forming a partial or in some cases a complete barrier to lymphatic flow (Figs. 6 and 7). The precise mechanisms responsible for triggering intralymphatic clotting are not known. Platelets were not observed within giant lymphatics by light or electron microscopy. However, clotting was favored by the high intraluminal concentration of fibrinogen and sluggish flow.
Fibrin deposited within giant lymphatics provided a substrate for intraluminal migration of lymphatic endothelial cells. These cells remodeled the fibrin clot, replacing it over time with a fishnet-like meshwork of cellular bridges that divided the original large lumens into multiple smaller channels (Figs. 6 and 7). This process has a parallel in the evolution of mother blood vessels that are induced by Ad-VEGF-A164 and also in VEGF-A–expressing tumors; in both cases endothelial cells lining blood vessels and giant lymphatics extended into and across the lumen, forming bridges that divided larger structures into smaller channels of capillary size (20, 22). It also has a parallel in the well-known recanalization of thrombosed blood vessels.
Several recent papers (14, 18, 19) have reported that human Ad-VEGF-A165 induces angiogenesis but not lymphangiogenesis in rodents, though one of these (19) did report lymphatic dilatation. In part these negative findings may reflect the selection of limited or nonoptimal time points (19); in one report, lymphangiogenesis may have been obscured by the use of immunocompetent animals that developed a strong inflammatory response against the adenoviral vector (18). Use of human rather than murine VEGF-A may also have influenced the results in that the amounts of vector injected to induce angiogenesis were substantially higher than those used here (19).
The mechanisms by which VEGF-A induced the abnormal lymphangiogenesis observed here have not yet been worked out. Skobe and Detmar reported that VEGF-A stimulates expression of VEGF-C in cultured vascular endothelium (31). It was possible, therefore, that VEGF-A induced lymphangiogenesis by up-regulating the expression of VEGF-C, a member of the VEGF family that has been previously implicated in lymphangiogenesis (10, 14). However, neither VEGF-C nor VEGF-D expression was detected at any time by in situ hybridization in ears injected with Ad-VEGF-A164. Another possibility is that VEGF-A acted directly to induce lymphatic endothelial cell proliferation through VEGFR-2. Although the literature is not in perfect agreement (32), we have consistently found VEGFR-2 to be expressed strongly on normal lymphatic endothelium (23), and, as shown here, on giant lymphatics. In further support of this possibility, VEGFR-2 is the receptor thought to mediate VEGF-A–induced proliferation of blood vascular endothelium (8, 33). Finally, PlGF, which induces angiogenesis but not lymphangiogenesis, does not interact with VEGFR-2 (9). Other possibilities, for example, that lymphangiogenesis results from a secondary effect of VEGF-A, such as prolonged interstitial edema, must also be considered.
The giant lymphatics we have described here appear identical to those found in lymphangiomas (34), suggesting that VEGF-A may have a role in the genesis of lymphatic tumors and malformations. To our knowledge, VEGF-A expression has not been investigated in lymphangiomas, though VEGF-C and VEGFR-2 and -3 are reportedly expressed (35, 36). Abnormally large lymphatics resembling giant lymphatics are also a feature of Crohn's disease (37, 38), a chronic inflammatory condition in which VEGF-A is overexpressed (39, 40); therefore, VEGF-A may have a role in the development of these abnormal lymphatics. Finally, there has been much debate about the existence of lymphatics in various malignant tumors and the possible role that lymphangiogenesis may play in tumor metastasis (15, 16, 32). Some human and animal tumors do overexpress VEGF-C and/or VEGF-D, and mouse tumor cells engineered to overexpress either induce angiogenesis and facilitate tumor metastasis (15, 32). It remains to be determined whether VEGF-A, a cytokine expressed by the vast majority of malignant human tumors (5, 7), does likewise.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance of Susan H. Bliss and Isabelle A. Eckelhoefer.
Supported in part by U.S. Public Health Service grants CA-50453 and HL-59316 (H.F. Dvorak); AI-33372 and AI-44066 (A.M. Dvorak); CA-69184, CA-86410, and CA-91861 (M.J. Detmar); P01 CA92644; and by a contract from the National Foundation for Cancer Research (H.F. Dvorak).
An abstract of this work was presented at the 41st annual meeting of the American Society for Cell Biology, Washington, DC, Dec. 12, 2001.
C. Sundberg's present address is Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala University, BMC, Box 575, SE-751 23 Uppsala, Sweden.
Footnotes
*
Abbreviations used in this paper: VPF/VEGF, VEGF-A, vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; PlGF, placenta growth factor; TMR, tetramethyl-rhodamine.
References
- 1.Hanahan, D. 1997. Signaling vascular morphogenesis and maintenance. Science. 277:48–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Folkman, J. 1997. Angiogenesis and angiogenesis inhibition: an overview. EXS. 79:1–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Beck, L., Jr., and P.A. D'Amore. 1997. Vascular development: cellular and molecular regulation. FASEB J. 11:365–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gale, N.W., and G.D. Yancopoulos. 1999. Growth factors acting via endothelial cell-specific receptor tyrosine kinases: VEGFs, angiopoietins, and ephrins in vascular development. Genes Dev. 13:1055–1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brown, L.F., M. Detmar, K. Claffey, J.A. Nagy, D. Feng, A.M. Dvorak, and H.F. Dvorak. 1997. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a multifunctional angiogenic cytokine. EXS. 79:233–269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Carmeliet, P., and D. Collen. 1999. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in vascular development. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 237:133–158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dvorak, H.F., J.A. Nagy, D. Feng, L.F. Brown, and A.M. Dvorak. 1999. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor and the significance of microvascular hyperpermeability in angiogenesis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 237:97–132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ferrara, N. 1999. Vascular endothelial growth factor: molecular and biological aspects. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 237:1–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Luttun, A., M. Tjwa, L. Moons, Y. Wu, A. Angelillo-Scherrer, F. Liao, J.A. Nagy, A. Hooper, J. Priller, B. De Klerck, et al. 2002. Revascularization of ischemic tissues by PlGF treatment, and inhibition of tumor angiogenesis, arthritis and atherosclerosis by anti-Flt1. Nat. Med. 8:831–840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cao, Y., P. Linden, J. Farnebo, R. Cao, A. Eriksson, V. Kumar, J.H. Qi, L. Claesson-Welsh, and K. Alitalo. 1998. Vascular endothelial growth factor C induces angiogenesis in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95:14389–14394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Achen, M.G., M. Jeltsch, E. Kukk, T. Makinen, A. Vitali, A.F. Wilks, K. Alitalo, and S.A. Stacker. 1998. Vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D) is a ligand for the tyrosine kinases VEGF receptor 2 (Flk1) and VEGF receptor 3 (Flt4). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95:548–553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Karkkainen, M.J., R.E. Ferrell, E.C. Lawrence, M.A. Kimak, K.L. Levinson, M.A. McTigue, K. Alitalo, and D.N. Finegold. 2000. Missense mutations interfere with VEGFR-3 signalling in primary lymphoedema. Nat. Genet. 25:153–159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Skobe, M., T. Hawighorst, D.G. Jackson, R. Prevo, L. Janes, P. Velasco, L. Riccardi, K. Alitalo, K. Claffey, and M. Detmar. 2001. Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Med. 7:192–198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Enholm, B., T. Karpanen, M. Jeltsch, H. Kubo, F. Stenback, R. Prevo, D.G. Jackson, S. Yla-Herttuala, and K. Alitalo. 2001. Adenoviral expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C induces lymphangiogenesis in the skin. Circ. Res. 88:623–629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jussila, L., and K. Alitalo. 2002. Vascular growth factors and lymphangiogenesis. Physiol. Rev. 82:673–700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Oliver, G., and M. Detmar. 2002. The rediscovery of the lymphatic system: old and new insights into the development and biological function of the lymphatic vasculature. Genes Dev. 16:773–783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Oh, S.J., M.M. Jeltsch, R. Birkenhager, J.E. McCarthy, H.A. Weich, B. Christ, K. Alitalo, and J. Wilting. 1997. VEGF and VEGF-C: specific induction of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in the differentiated avian chorioallantoic membrane. Dev. Biol. 188:96–109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Byzova, T.V., C.K. Goldman, J. Jankau, J. Chen, G. Cabrera, M.G. Achen, S.A. Stacker, K.A. Carnevale, M. Siemionow, S.R. Deitcher, and P.E. DiCorleto. 2002. Adenovirus encoding vascular endothelial growth factor-D induces tissue-specific vascular patterns in vivo. Blood. 99:4434–4442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Saaristo, A., T. Veikkola, B. Enholm, M. Hytonen, J. Arola, K. Pajusola, P. Turunen, M. Jeltsch, M.J. Karkkainen, D. Kerjaschki, et al. 2002. Adenoviral VEGF-C overexpression induces blood vessel enlargement, tortuosity, and leakiness but no sprouting angiogenesis in the skin or mucous membranes. FASEB J. 16:1041–1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pettersson, A., J.A. Nagy, L.F. Brown, C. Sundberg, E. Morgan, S. Jungles, R. Carter, J.E. Krieger, E.J. Manseau, V.S. Harvey, et al. 2000. Heterogeneity of the angiogenic response induced in different normal adult tissues by vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor. Lab. Invest. 80:99–115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sundberg, C., J.A. Nagy, L.F. Brown, D. Feng, I.A. Eckelhoefer, E.J. Manseau, A.M. Dvorak, and H.F. Dvorak. 2001. Glomeruloid microvascular proliferation follows adenoviral vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor-164 gene delivery. Am. J. Pathol. 158:1145–1160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nagy, J.A., E.S. Morgan, K.T. Herzberg, E.J. Manseau, A.M. Dvorak, and H.F. Dvorak. 1995. Pathogenesis of ascites tumor growth: angiogenesis, vascular remodeling, and stroma formation in the peritoneal lining. Cancer Res. 55:376–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Feng, D., J.A. Nagy, R.A. Brekken, A. Pettersson, E.J. Manseau, K. Pyne, R. Mulligan, P.E. Thorpe, H.F. Dvorak, and A.M. Dvorak. 2000. Ultrastructural localization of the vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor (VPF/VEGF) receptor-2 (FLK-1, KDR) in normal mouse kidney and in the hyperpermeable vessels induced by VPF/VEGF-expressing tumors and adenoviral vectors. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 48:545–556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Prevo, R., S. Banerji, D.J. Ferguson, S. Clasper, and D.G. Jackson. 2001. Mouse LYVE-1 is an endocytic receptor for hyaluronan in lymphatic endothelium. J. Biol. Chem. 276:19420–19430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Brown, L.F., B.J. Dezube, K. Tognazzi, H.F. Dvorak, and G.D. Yancopoulos. 2000. Expression of Tie1, Tie2, and angiopoietins 1, 2, and 4 in Kaposi's sarcoma and cutaneous angiosarcoma. Am. J. Pathol. 156:2179–2183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hudack, S., and P.D. McMaster. 1932. I. The permeability of the wall of the lymphatic capillary. J. Exp. Med. 56:223–238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pullinger, B.D., and H.W. Florey. 1935. Some observations on the structure and functions of lymphatics: their behavior in local edema. J. Exp. Pathol. 16:49–61. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Leak, L.V. 1970. Electron microscopic observations on lymphatic capillaries and the structural components of the connective tissue-lymph interface. Microvasc. Res. 2:361–391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Partanen, T.A., T. Makinen, J. Arola, T. Suda, H.A. Weich, and K. Alitalo. 1999. Endothelial growth factor receptors in human fetal heart. Circulation. 100:583–586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Feng, D., J. Nagy, H. Dvorak, and A. Dvorak. 2002. Ultrastructural studies define soluble macromolecular, particulate, and cellular transendothelial cell pathways in venules, lymphatic vessels, and tumor-associated microvessels in man and animals. Microsc. Res. Tech. 57:289–326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Skobe, M., and M. Detmar. 2000. Structure, function, and molecular control of the skin lymphatic system. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 5:14–19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Stacker, S.A., M.E. Baldwin, and M.G. Achen. 2002. The role of tumor lymphangiogenesis in metastatic spread. FASEB J. 16:922–934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zeng, H., H.F. Dvorak, and D. Mukhopadhyay. 2001. Vascular permeability factor (VPF)/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor-1 down-modulates VPF/VEGF receptor-2-mediated endothelial cell proliferation, but not migration, through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 276:26969–26979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.McKee, P. 1996. Pathology of the Skin with Clinical Correlations. Mosby International, London. 16.74.
- 35.Lymboussaki, A., T.A. Partanen, B. Olofsson, J. Thomas-Crusells, C.D. Fletcher, R.M. de Waal, A. Kaipainen, and K. Alitalo. 1998. Expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor C receptor VEGFR-3 in lymphatic endothelium of the skin and in vascular tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 153:395–403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Huang, H.Y., C.C. Ho, P.H. Huang, and S.M. Hsu. 2001. Co-expression of VEGF-C and its receptors, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3, in endothelial cells of lymphangioma. Implication in autocrine or paracrine regulation of lymphangioma. Lab. Invest. 81:1729–1734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dvorak, A.M., R.A. Monahan, J.E. Osage, and G.R. Dickersin. 1980. Crohn's disease: transmission electron microscopic studies. II. Immunologic inflammatory response. Alterations of mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, and the microvasculature. Hum. Pathol. 11:606–619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Goldman, H. 1998. Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Pathology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. S.-C. Ming and H. Goldman, editors. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, MD. 673–717.
- 39.Kanazawa, S., T. Tsunoda, E. Onuma, T. Majima, M. Kagiyama, and K. Kikuchi. 2001. VEGF, basic-FGF, and TGF-beta in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: a novel mechanism of chronic intestinal inflammation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 96:822–828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Griga, T., S. Werner, M. Koller, A. Tromm, and B. May. 1999. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in Crohn's disease: increased production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells and decreased VEGF165 labeling of peripheral CD14+ monocytes. Dig. Dis. Sci. 44:1196–1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]