Phosphatidylethanolamine and Cardiolipin Differentially Affect the Stability of Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Supercomplexes (original) (raw)
Abstract
The mitochondrial inner membrane contains two non-bilayer‐forming phospholipids, phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and cardiolipin (CL). Lack of CL leads to destabilization of respiratory chain supercomplexes, a reduced activity of cytochrome c oxidase, and a reduced inner membrane potential Δψ. Although PE is more abundant than CL in the mitochondrial inner membrane, its role in biogenesis and assembly of inner membrane complexes is unknown. We report that similar to the lack of CL, PE depletion resulted in a decrease of Δψ and thus in an impaired import of preproteins into and across the inner membrane. The respiratory capacity and in particular the activity of cytochrome c oxidase were impaired in PE-depleted mitochondria, leading to the decrease of Δψ. In contrast to depletion of CL, depletion of PE did not destabilize respiratory chain supercomplexes but favored the formation of larger supercomplexes (megacomplexes) between the cytochrome _bc_1 complex and the cytochrome c oxidase. We conclude that both PE and CL are required for a full activity of the mitochondrial respiratory chain and the efficient generation of the inner membrane potential. The mechanisms, however, are different since these non-bilayer‐forming phospholipids exert opposite effects on the stability of respiratory chain supercomplexes.
Abbreviations: AAC, ADP/ATP carrier; CL, cardiolipin; Crd1, cardiolipin synthase; F1β, β subunit of F1Fo-ATP synthase; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; Psd, phosphatidylserine decarboxylase; TIM22, carrier translocase of the inner mitochondrial membrane; TIM23, presequence translocase of the inner mitochondrial membrane
Keywords: membrane potential, Psd1, Psd2, protein import, Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
► PE required for full respiratory capacity of mitochondria. ► Membrane potential and protein import are impaired in PE-depleted mitochondria. ► PE depletion stabilizes respiratory chain supercomplexes (megacomplexes). ► PE and CL exert antagonistic effects on respiratory chain supercomplexes.
Mitochondria are crucial for the synthesis of the major non-bilayer‐forming phospholipids, phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and cardiolipin (CL).1–3 Non-bilayer lipids have a comparably small head group and a bulky fatty acid moiety, which results in a conical shape of the phospholipid. These phospholipids have the tendency to form hexagonal‐phase structures and thus to increase the tension within a bilayer, which is important for the function of membrane proteins.2 PE is an abundant phospholipid present in all cellular membranes and essential for cell survival,2,4–8 whereas CL is specific for mitochondria.2,4,8,9 The synthesis of CL takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where the CL synthase (Crd1) catalyzes the formation of CL from phosphatidylglycerol and CDP-diacylglycerol.2,3,10–12 In yeast, the majority of PE is generated by decarboxylation of phosphatidylserine catalyzed by phosphatidylserine decarboxylases (Psd). Two Psd enzymes have been described. Psd1 plays the major role in PE synthesis and is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane/intermembrane space.13–16 Smaller amounts of PE are generated by the Psd2 activity of the Golgi apparatus/vacuole membrane, as well as by the CDP-ethanolamine pathway and the acyltransferases Tgl3 and Ale1.1,4,13,17–26 Little is known of how PE synthesized in mitochondria is transported to other cellular membranes. The efficient transfer of phospholipids between the mitochondrial membranes and the endoplasmic reticulum might occur at contact sites between the membranes.2
CL and PE are of particular importance for mitochondrial functions. Lack of either Crd1 or Psd1 impairs growth of cells on non-fermentable carbon sources and leads to an altered mitochondrial morphology.6,27–29 CL and PE are required for mitochondrial fusion,30,31 and Crd1 as well as Psd1 show genetic interactions with prohibitins, which have been proposed to function as scaffolds that enrich CL and PE in membrane domains.2,15,32 Deletion of both genes, CRD1 and PSD1, is synthetically lethal for yeast cells.27 Based on these observations, it was proposed that CL and PE perform overlapping functions, which might be partially attributed to their non-bilayer‐forming character.33
The role of CL in the mitochondrial inner membrane has been analyzed on a molecular level. CL is required for function and stability of several protein complexes. It binds to the ADP/ATP carrier (AAC) and is crucial for the formation of AAC oligomers.34–41 CL also plays a central role for the activity and organization of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. It binds to the cytochrome _bc_1 complex (complex III) and cytochrome c oxidase (complex IV)40,42,43 that form high‐molecular‐weight supercomplexes.44–46 In the absence of CL, the III–IV supercomplexes are destabilized, the activity of the respiratory chain, particularly of cytochrome c oxidase, is decreased, and thus the inner membrane potential Δψ is reduced.38,47–49 CL-deficient mitochondria are impaired in the import and assembly of inner membrane proteins.35,39 Precursor proteins are transported to the inner membrane by two routes.50–56 In the presequence pathway, preproteins with a cleavable presequence are transported by the general translocase of the outer membrane and the presequence translocase of the inner membrane (TIM23 complex). Precursors of carrier proteins contain internal targeting signals and are integrated into the inner membrane by the carrier translocase (TIM22 complex). Since both import routes into the inner membrane depend on a Δψ, the decrease of Δψ in CL-deficient mitochondria is a main reason for disturbed protein import.35,39,57 In addition, the stability and function of protein translocases such as the TIM23 complex are affected when CL is absent, and also the assembly of AAC into oligomers depends on the presence of CL.39,57–61
PE is the most abundant non-bilayer‐forming phospholipid in the mitochondrial inner membrane.4,62,63 PE binds to respiratory chain complexes43,64 and in vivo data indicate an important role of PE for mitochondrial functions.6,29,31 Studies with lactose permease revealed a role of PE in folding and activity of membrane proteins in Escherichia coli.65–68 The effect of PE depletion on mitochondrial processes, however, has not been studied on a molecular level.
Here, we report that protein transport into and across the inner membrane is impaired in PE-depleted mitochondria. The protein translocases and inner membrane complexes are not dissociated upon lack of PE, but the activity of the respiratory chain, in particular of cytochrome c oxidase, is impaired, leading to a reduction of Δψ. Thus, the reduced Δψ leads to an impairment of protein import into the inner membrane. In contrast to the lack of CL, lack of PE stabilizes supercomplexes of the respiratory chain and does not block the formation of AAC oligomers. Though both PE and CL are required for respiratory activity and efficient generation of a Δψ by mitochondria, they play opposing roles in the stabilization of protein complexes.
PE-depleted mitochondria are impaired in preprotein transport to the inner membrane
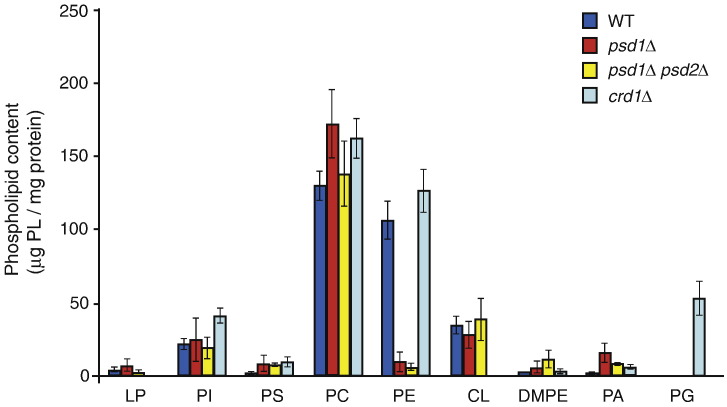
To study the role of PE in mitochondrial protein biogenesis, we used a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain lacking Psd1 and a double deletion strain lacking Psd1 and Psd2.69 Both yeast strains exhibited a poor growth on non-fermentable carbon sources and were sensitive to growth at high and low temperatures (Fig. S1a). For further analysis, we grew the cells at an intermediate temperature (30 °C, early logarithmic growth phase) on non-fermentable carbon sources and analyzed the phospholipid profiles of cell extracts from _psd1_Δ and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ strains.6 The level of PE (29 mol% of total phospholipids in wild-type cells) was considerably decreased in _psd1_Δ cells (7%) and strongly reduced in the double deletion mutant (1%) (Fig. S1b).6 We also determined the content of total phospholipids in purified inner membrane vesicles from these mutants and observed a moderate reduction of the phospholipid‐to‐protein ratio compared to wild type (Fig. S1c). Moreover, we determined the absolute amounts of individual phospholipid classes in inner membrane vesicles from wild-type, _psd1_Δ, and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ mitochondria. Figure 1 shows that only the PE content was strongly reduced in the mutants, whereas the amounts of other phospholipids remained largely unaffected. In comparison, the levels of PE in total cell extracts and mitochondrial inner membrane vesicles from _crd1_Δ mutants were similar to the wild-type levels, whereas the levels of phosphatidylglycerol were strongly increased (Fig. 1 and Fig. S1b).35,48,49
Fig. 1.
PE is selectively depleted in inner membrane vesicles from _psd1_Δ and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ mitochondria. The S. cerevisiae strains _crd1_Δ, _psd1_Δ, and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ in the BY4741 background69 were grown in YPLac medium39 at 30 °C to early logarithmic growth phase. Mitochondria were isolated by differential centrifugation, the protein concentrations were adjusted, and inner membrane vesicles were isolated by sucrose gradient centrifugation as previously described.4,70 Phospholipids were extracted, separated by thin-layer chromatography, and analyzed as reported previously.69,71,72 The amounts of individual phospholipid classes were determined using a phosphate solution with 1 mg/ml phosphor as standard.73 Shown are the mean values of two determinations with range. DMPE, dimethylphosphatidylethanolamine; LP, lysophospholipids; PA, phosphatidic acid; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PS, phosphatidylserine.
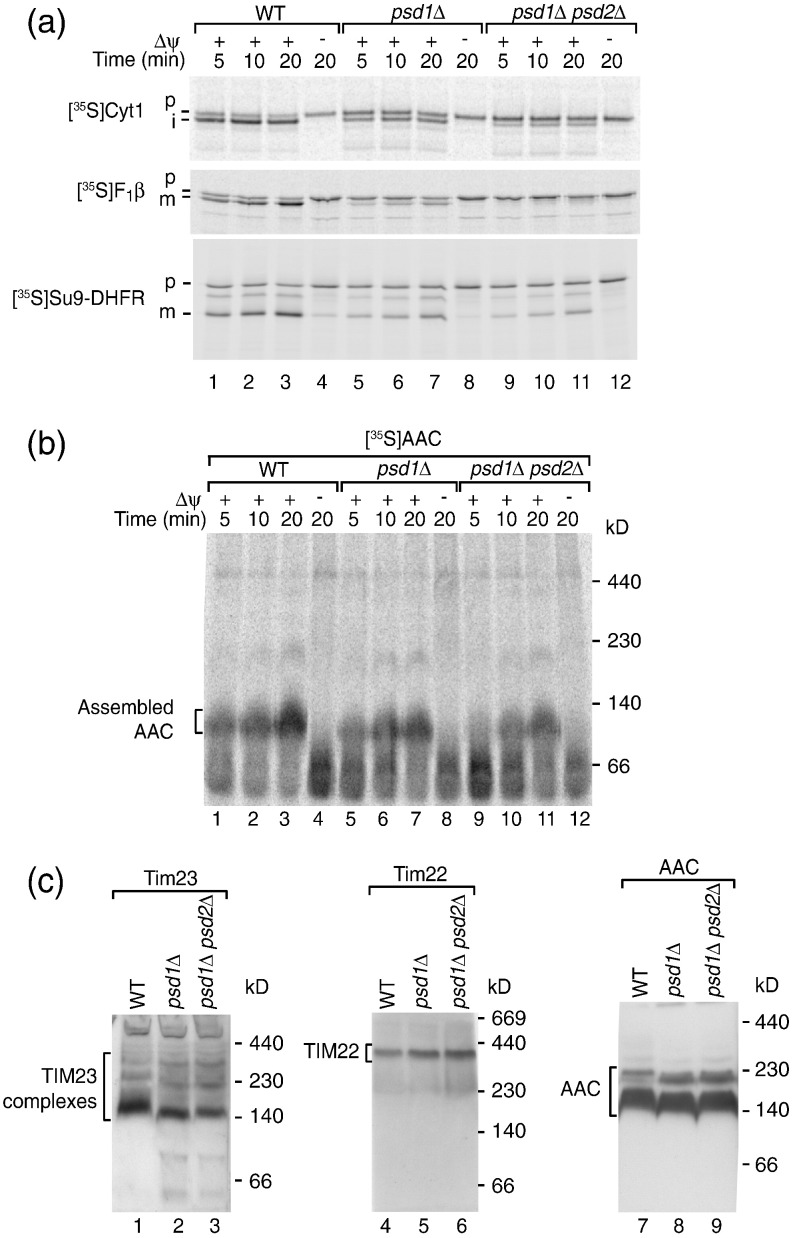
For protein import experiments, mitochondrial precursor proteins were synthesized in reticulocyte lysates and labeled with [35S]methionine. We used three presequence-containing preproteins and incubated them with mitochondria isolated from _psd1_Δ and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ strains: cytochrome _c_1 is inserted into the inner membrane, whereas subunit β of the F1Fo-ATP synthase (F1β) and the model preprotein Su9-DHFR are translocated across the inner membrane into the matrix.61,74–77 Each of these preproteins was imported in a Δψ-dependent manner and the presequences were proteolytically removed (Fig. 2a). Import of the three preproteins was reduced in _psd1_Δ mitochondria and strongly reduced in _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ mitochondria (Fig. 2a, lanes 5–7 and 9–11). The import of AAC via the carrier pathway was analyzed by monitoring assembly of AAC in the inner membrane.80,81 We imported AAC into isolated mitochondria, lysed the mitochondria with the non-ionic detergent digitonin, and studied AAC assembly by blue native electrophoresis (Fig. 2b). The biogenesis of AAC was moderately reduced in _psd1_Δ and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ mitochondria (Fig. 2b, lanes 5–7 and 9–11).
Fig. 2.
PE-depleted mitochondria are impaired in import of preproteins into and across the inner membrane. (a) Isolated mitochondria from wild-type, _psd1_Δ, and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ yeast strains were incubated with the 35S-labeled precursors of cytochrome _c_1 (Cyt1), F1β, and Su9-DHFR in import buffer [3% (w/v) bovine serum albumin, 250 mM sucrose, 80 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 5 mM methionine, 2 mM KH2PO4, 10 mM Mops/KOH, pH 7.2, 2 mM NADH, 5 mM creatine phosphate, 0.1 mg/ml creatine kinase, and 2 mM ATP] at 25 °C for the indicated periods. In control reactions, the membrane potential (Δψ) was dissipated prior to import by addition of 8 μM antimycin A, 1 μM valinomycin, and 20 μM oligomycin. The import reactions were stopped by adding 8 μM antimycin A, 1 μM valinomycin, and 20 μM oligomycin. After washing with SEM buffer (250 mM sucrose, 1 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and 10 mM Mops/KOH, pH 7.2), the mitochondria were lysed under denaturing conditions and subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by digital autoradiography. p, precursor; i, intermediate; m, mature. (b) Isolated mitochondria from wild-type, _psd1_Δ, and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ yeast strains were incubated with 35S-labeled AAC at 25 °C as indicated in the presence or absence of Δψ. The mitochondria were lysed with 1% (w/v) digitonin in digitonin buffer [20 mM Tris/HCl, pH 7.4, 50 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and 10% (v/v) glycerol] and protein complexes were separated by blue native electrophoresis.78,7935S-labeled proteins were detected by digital autoradiography. (c) Wild-type, _psd1_Δ, and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ mitochondria were lysed with 1% (w/v) digitonin in digitonin buffer and subjected to blue native electrophoresis. Protein complexes were detected by Western blotting using the indicated antisera.
It has been reported that in CL-deficient mitochondria, the stability of the TIM23 translocase is partially affected.39,58–60 We thus tested whether depletion of PE also affected the stability of the TIM23 or TIM22 complexes. The protein levels of subunits of the TIM23 complex (Tim17, Tim23) and the TIM22 complex (Tim22, Tim54) were comparable in psd mutant and wild-type mitochondria (Fig. S2). The stability of the translocases was analyzed by blue native electrophoresis of digitonin-lysed mitochondria (Fig. 2c). The TIM23 translocase forms several blue native-stable complexes,39,58,77 which were not dissociated but only slightly shifted to faster migrating forms in _psd1_Δ and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ mitochondria (Fig. 2c, lanes 2 and 3) (the slight mobility shifts may indicate that PE is bound to TIM23 in wild-type mitochondria but not critical for the stability of the translocase). The mobility of the TIM22 translocase was not affected in the mutant mitochondria (Fig. 2c, lanes 5 and 6). One hallmark of mitochondria lacking CL is the dissociation of AAC oligomers.35,39 In contrast, depletion of PE did not block the oligomerization of AAC but only led to a slight mobility shift of AAC oligomers (Fig. 2c, lanes 8 and 9).
In summary, the import of presequence-carrying preproteins and carrier proteins is impaired in PE-depleted mitochondria. The main import machineries TIM23 and TIM22, as well as the AAC oligomers, are not dissociated when PE is depleted, indicating that PE is not crucial for the stability of these complexes.
PE is required for the activity of the respiratory chain
We noticed that the mitochondrial import of the precursor of F1β was more severely affected by PE depletion than the import of Su9-DHFR (Fig. 2a). It was previously shown that the import of F1β requires a higher membrane potential and is thus more sensitive to a reduction of Δψ than the import of Su9-DHFR,74 raising the possibility that the preprotein import defects observed in PE-depleted mitochondria may be related to a reduction of Δψ in the mutant mitochondria.
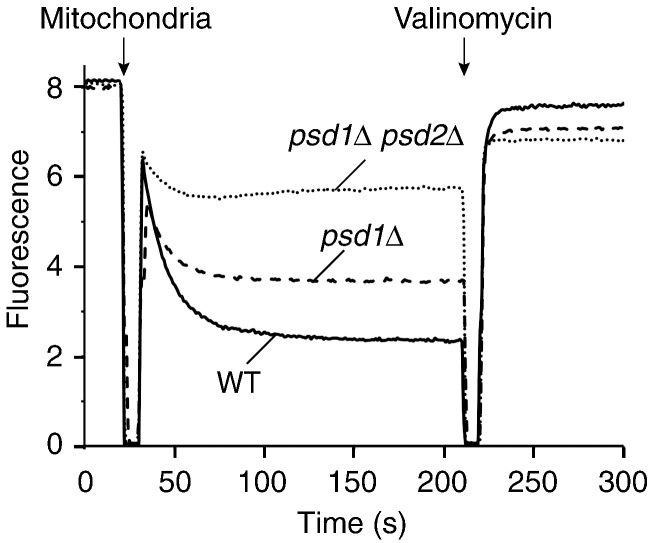
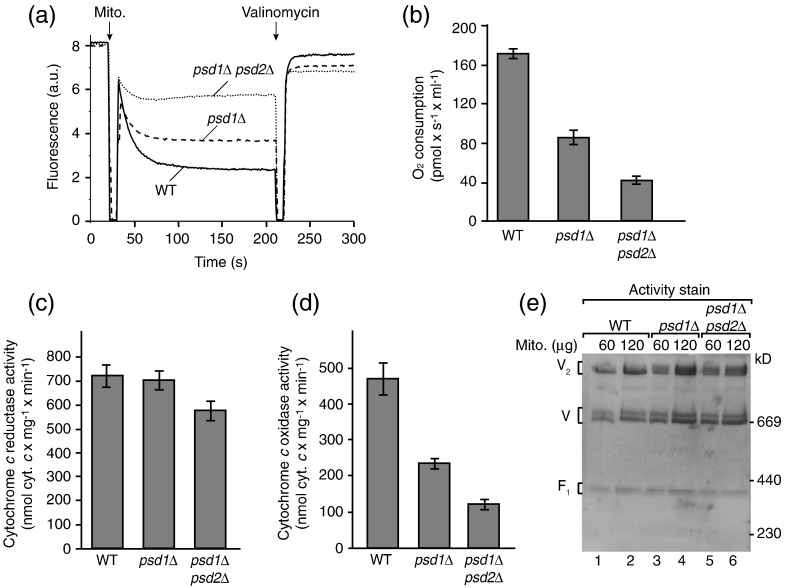
To assess the membrane potential of mitochondria, we used a Δψ‐sensitive fluorescent dye.39,76,82 Δψ was partially reduced in _psd1_Δ mitochondria and strongly decreased in _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ mitochondria (Fig. 3a). We determined the activity of the respiratory chain by oxygen consumption and observed that the rate of oxygen consumption was reduced in _psd1_Δ mitochondria and more severely decreased in _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ mitochondria (Fig. 3b). Budding yeast does not contain complex I of the respiratory chain. The cytochrome _bc_1 complex and cytochrome c oxidase are the two proton-pumping respiratory complexes and thus we analyzed their activities individually. The activity of the cytochrome _bc_1 complex was only marginally affected by the depletion of PE (Fig. 3c), whereas the activity of the cytochrome c oxidase was considerably reduced (Fig. 3d). The protein levels of several subunits of cytochrome c oxidase such as Cox1 were moderately reduced in the psd mutant mitochondria (Fig. S2), supporting the conclusion that cytochrome c oxidase was affected in the mutants. The F1Fo-ATP synthase was visualized in native gels by ATPase activity staining,86,87 revealing comparable activities in wild-type and psd mutant mitochondria (Fig. 3e).
Fig. 3.
PE is required for the activity of the respiratory chain. (a) The membrane potential (Δψ) of wild-type, _psd1_Δ, and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ yeast mitochondria was assessed at 25 °C by fluorescence quenching using the Δψ-sensitive dye DiSC3(5) (3,3′-dipropylthiadicarbocyanine iodide) in membrane potential buffer [0.6 M sorbitol, 0.1% (w/v) bovine serum albumin, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and 20 mM KPi, pH 7.2] as described previously.39,82 (b) The oxygen consumption of isolated wild-type, _psd1_Δ, and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ mitochondria was analyzed by oxygraph measurements at 25 °C. Isolated yeast mitochondria (100 μg protein) were added to 2 ml of buffer (10 mM Mops/KOH, pH 7.2, 250 mM sucrose, 5 mM MgCl2, 80 mM KCl, 5 mM KPi, 1 mM ADP, and 1 mM NADH) and oxygen consumption was measured. The oxygen flux (negative time derivative of oxygen concentration) corrected for instrumental background flux was expressed in picomoles per second per milliliter. Shown are the mean values with standard error of the mean (n = 3). (c and d) The activity of the cytochrome _bc_1 complex (c) and the cytochrome c oxidase (d) was determined in submitochondrial particles prepared from wild-type, _psd1_Δ, and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ yeast cells as described earlier.83,84 Ubiquinol-dependent cytochrome c reduction was measured as described by Palsdottir and Hunte84 using 3 μg protein (submitochondrial particles), 50 μM horse heart cytochrome c, and 80 μM decylubiquinol for 1 ml assay volume (40 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, 1 mM NaN3, and 0.05 % β-d-undecylmaltoside). Reduction of cytochrome c was monitored at 550 nm and the activity was calculated with an extinction coefficient of 19.4 mM− 1 cm− 1. The activity was fully sensitive to the specific inhibitor stigmatellin (1 μM). Cytochrome c oxidase activity was measured as described by Horvath et al.85 with 50 μM reduced horse heart cytochrome c and 3–50 μg of protein (submitochondrial particles) in 1 ml assay volume (75 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, 1 mM antimycin A, and 0.05% β-d-dodecylmaltoside). Oxidation of cytochrome c was monitored and quantified as for the cytochrome _bc_1 complex. The activity was fully sensitive to the specific inhibitor sodium azide (1 μM). Specific enzyme activities are based on total protein determined by bicinchoninic acid assay (Pierce). Three preparations per strain were used and the activity measurements were repeated five times for each sample. Mean values with standard error of the mean are shown. (e) The activity of the mitochondrial ATPase was assessed by in‐gel calcium phosphate precipitation upon ATP hydrolysis.86,87 Mitochondria isolated from wild-type, _psd1_Δ, or _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ strains were lysed with 1% (w/v) digitonin in digitonin buffer and protein complexes were separated by blue native electrophoresis. Subsequently, the gel was washed with water and incubated with ATP-containing buffer (50 mM glycine, pH 8.4, 5 mM MgCl2, and 20 mM ATP) for 20 min and transferred into 10% (w/v) CaCl2 solution. Incubation was performed until calcium phosphate precipitation became visible and the reaction was stopped by transfer into water. V2, ATP synthase dimer; V, ATP synthase monomer; F1, F1 part of the ATP synthase.
Taken together, the stepwise decrease of PE levels in _psd1_Δ and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ mutants correlates with the stepwise decrease of cytochrome c oxidase activity, oxygen consumption, membrane potential, and preprotein import into and across the inner membrane. Thus, both PE and CL are important for the activity of the respiratory chain and the generation of a membrane potential. A decreased Δψ results in an impaired protein import into and across the inner membrane.74,76
Lack of PE stabilizes respiratory chain supercomplexes
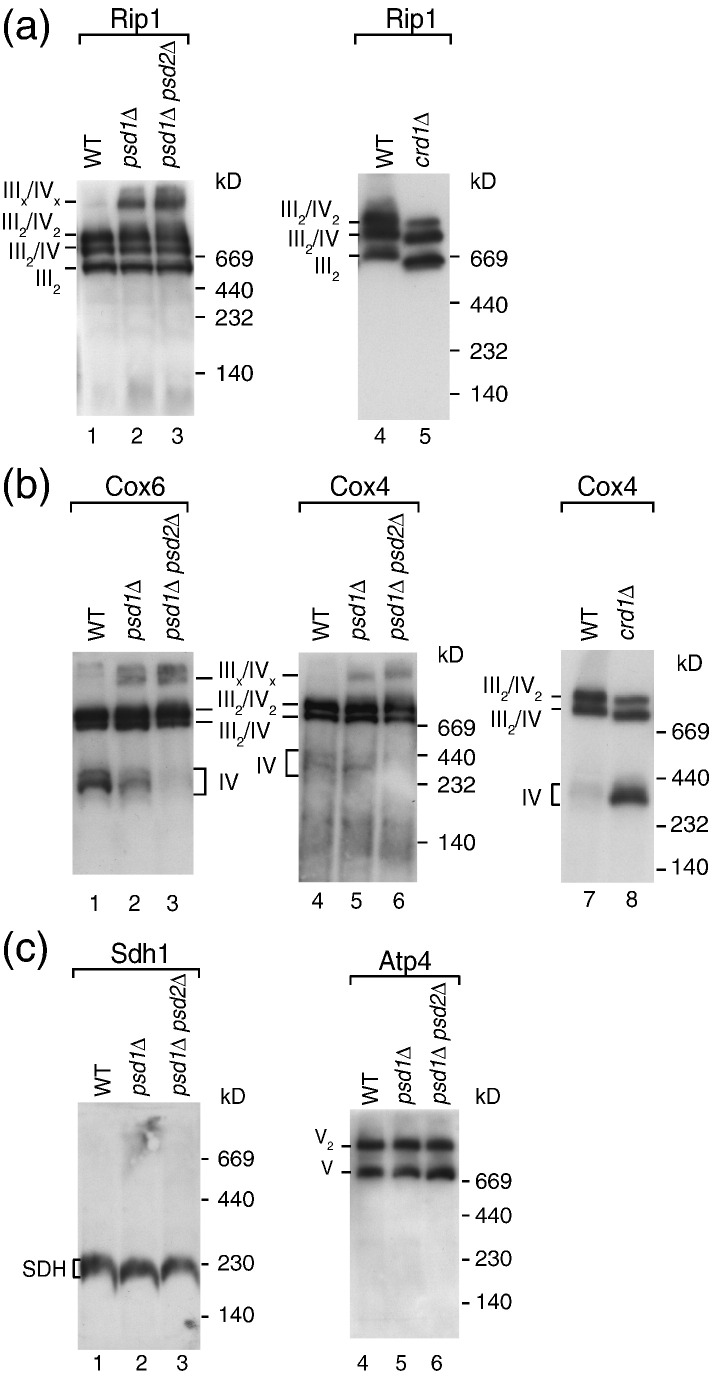
The cytochrome _bc_1 complex and cytochrome c oxidase form supercomplexes that can be resolved by blue native electrophoresis. The supercomplexes contain a dimer of the cytochrome _bc_1 complex (III2) and one (III2/IV) or two copies (III2/IV2) of cytochrome c oxidase (Fig. 4a and b).44,45 We lysed mitochondria with digitonin and analyzed the protein complexes by blue native electrophoresis and immunodecoration. Surprisingly, the supercomplexes were not dissociated in _psd1_Δ and _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ mitochondria, but rather formed a larger oligomeric assembly, containing both cytochrome _bc_1 complex and cytochrome c oxidase (Fig. 4a, lanes 2 and 3; Fig. 4b, lanes 2, 3, 5, and 6). The amount of free cytochrome c oxidase was decreased upon depletion of PE (Fig. 4b, lanes 2, 3, and 6), indicating that the lack of PE stabilizes the interaction of both complexes. For comparison, lack of CL in _crd1_Δ mitochondria has an opposing effect on the supercomplexes as the association of the cytochrome _bc_1 complex with cytochrome c oxidase is destabilized (Fig. 4a, lane 5; Fig. 4b, lane 8).38,39,47,48,82,88,89 Neither succinate dehydrogenase (complex II) nor the F1Fo-ATP synthase (complex V) altered their blue native mobility upon depletion of PE (Fig. 4c), indicating that these complexes were not present in the large oligomeric assembly of the respiratory chain.
Fig. 4.
Depletion of PE stabilizes respiratory chain supercomplexes. (a–c) Wild-type, _psd1_Δ, _psd1_Δ _psd2_Δ, and _crd1_Δ mitochondria were lysed with 1% (w/v) digitonin in digitonin buffer and subjected to blue native electrophoresis, followed by Western blotting using the indicated antisera. III, cytochrome _bc_1 complex; IV, cytochrome c oxidase; V2, ATP synthase dimer; V, ATP synthase monomer; Atp4, ATP synthase subunit 4 (subunit b); Cox4, cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4; Cox6, cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6; Rip1, Rieske iron–sulfur protein; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase (complex II).
In conclusion, PE and CL are both important for mitochondrial function. Like CL, PE is required for maintaining the membrane potential, which is crucial for the import of preproteins into and across the inner membrane. The activity of the respiratory chain, in particular of cytochrome c oxidase, is decreased when PE (this study) or CL48,49 is depleted. However, PE and CL showed different effects on the molecular level when the stability of mitochondrial protein complexes was analyzed. Lack of CL results in dissociation of AAC oligomers and destabilization of respiratory chain supercomplexes.35,38,39,48,49 In contrast, upon depletion of PE, the AAC oligomers remained stable and even higher forms of the respiratory chain supercomplexes were observed. CL and PE were shown to bind to the cytochrome _bc_1 complex and cytochrome c oxidase, likely including the interface of both complexes.42,43,48,64,90,91 CL and PE are both non-bilayer‐forming phospholipids. Their opposite effects on protein complex stability may provide an explanation why CL does not fully compensate for the loss of PE and vice versa.6,27 CL has a negatively charged head group, whereas PE is a zwitterionic phospholipid of neutral charge, suggesting that the differently charged head groups may contribute to the differential effects on protein complex stability. Wenz et al. indeed showed that the negative charge of CL is important for maintaining the structural integrity of respiratory supercomplexes.91 Wittig and Schägger92 and Bultema et al.93 proposed that the cytochrome _bc_1 complex and the cytochrome c oxidase can be organized into higher oligomeric structures that are larger than the known supercomplexes and called them respiratory strings or megacomplexes. Our results suggest that such structures are stabilized when PE is depleted and thus megacomplexes of the respiratory chain can be detected on blue native gels.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Natalia Gebert, Martin van der Laan, and Nora Vögtle for materials and discussion and Nicole Zufall for expert technical assistance. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Sonderforschungsbereich 746, Excellence Initiative of the German Federal and State Governments (EXC 294 BIOSS; GSC-4 Spemann Graduate School), Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung, the Austrian Science Fund FWF (project 21429), and DK Molecular Enzymology (W901-B05 to G.D.).
Edited by M. Yaniv
Footnotes
Contributor Information
Günther Daum, Email: guenther.daum@tugraz.at.
Nikolaus Pfanner, Email: nikolaus.pfanner@biochemie.uni-freiburg.de.
Appendix A. Supplementary Data
Supplementary data
References
- 1.Schuiki I., Daum G. Phosphatidylserine decarboxylase, key enzymes of lipid metabolism. IUBMB Life. 2009;61:151–162. doi: 10.1002/iub.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Osman C., Voelker D., Langer T. Making heads or tails of phospholipids in mitochondria. J. Cell Biol. 2011;192:7–16. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201006159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Claypool S.M., Koehler C.M. The complexity of cardiolipin in health and disease. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012;37:32–41. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2011.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zinser E., Sperka-Gottlieb C.D.M., Fasch E.V., Kohlwein S.D., Paltauf F., Daum G. Phospholipid synthesis and lipid composition of subcellular membranes in the unicellular eukaryote Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Bacteriol. 1991;173:2026–2034. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.2026-2034.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Storey M.K., Clay K.L., Kutateladze T., Murphy R.C., Overduin M., Voelker D.R. Phosphatidylethanolamine has an essential role in Saccharomyces cerevisiae that is independent of its ability to form hexagonal phase structures. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:48539–48548. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109043200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Birner R., Bürgermeister M., Schneiter R., Daum G. Roles of phosphatidylethanolamine and its several biosynthetic pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2001;12:997–1007. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.4.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Steenbergen R., Nanowski T.S., Beigneux A., Kulinski A., Young S.G., Vance J.E. Disruption of the phosphatidylserine decarboxylase gene in mice causes embryonic lethality and mitochondrial defects. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:40032–40040. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506510200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.van Meer G., Voelker D.R., Feigenson G.W. Membrane lipids: where they are and how they behave. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008;9:112–124. doi: 10.1038/nrm2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jiang F., Rizavi H.S., Greenberg M.L. Cardiolipin is not essential for the growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on fermentable or non-fermentable carbon sources. Mol. Microbiol. 1997;26:481–491. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.5841950.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tamai K.T., Greenberg M.L. Biochemical characterization and regulation of cardiolipin synthase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1990;1046:214–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90192-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tuller G., Hrastnik C., Achleitner G., Schiefthaler U., Klein F., Daum G. YDL142c encodes cariolipin synthase (Cls1p) and is non-essential for aerobic growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 1998;421:15–18. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(97)01525-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chang S.-C., Hecock P.N., Mileykovskaya E., Voelker D.R., Dowhan W. Isolation and characterization of the gene (CLS1) encoding cardiolipin synthase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:14933–14941. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.24.14933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Trotter P.J., Pedretti J., Voelker D.R. Phosphatidylserine decarboxylase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation of mutants, cloning of the gene, and creation of a null allele. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:21416–21424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Clancey C.J., Chang S.C., Dowhan W. Cloning of a Gene (PSD1) encoding phosphatidylserine decarboxylase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by complementation of an Escherichia coli mutant. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:24580–24590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Birner R., Nebauer R., Schneiter R., Daum G. Synthetic lethal interaction of the mitochondrial phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthetic machinery with the prohibitin complex of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2003;14:370–383. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E02-05-0263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bürgermeister M., Birner-Grünberger R., Nebauer R., Daum G. Contribution of different pathways to the supply of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine to mitochondrial membranes of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1686:161–168. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2004.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Trotter P.J., Pedretti J., Yates R., Voelker D.R. Phosphatidylserine decarboxylase 2 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: cloning and mapping of the gene, heterologous expression, and creation of the null allele. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:6071–6080. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.11.6071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Trotter P.J., Voelker D.R. Identification of a non-mitochondrial phosphatidylserine decarboxylase activity (PSD2) in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:6062–6070. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.11.6062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kennedy E.P., Weiss S.B. The function of cytidine coenzymes in the biosynthesis of phospholipids. J. Biol. Chem. 1956;222:193–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kuchler K., Daum G., Paltauf F. Subcellular and submitochondrial localization of phospholipid-synthesizing enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Bacteriol. 1986;165:901–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.901-910.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Saba J.D., Nara F., Bielawska A., Garrett S., Hannun Y.A. The BST1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is the sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:26087–26090. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.42.26087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Daum G., Lees N.D., Bard M., Dickson R. Biochemistry, cell biology and molecular biology of lipids of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1998;14:1471–1510. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(199812)14:16<1471::AID-YEA353>3.0.CO;2-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kim K., Kim K.H., Storey M.K., Voelker D.R., Carman G.M. Isolation and characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae EKI1 gene encoding ethanolamine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:14857–14866. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.21.14857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Riekhof W.R., Voelker D.R. Uptake and utilization of lyso-phosphatidylethanolamine by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:36588–36596. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608851200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Riekhof W.R., Wu J., Jones J.L., Voelker D.R. Identification and characterization of the major lysophosphatidylethanolamine acyltransferase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:28344–28352. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705256200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rajakumari S., Daum G. Janus-faced enzymes yeast Tgl3p and Tgl5p catalyze lipase and acyltransferase reactions. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2010;21:501–510. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E09-09-0775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gohil V.M., Thompson M.N., Greenberg M.L. Synthetic lethal interaction of the mitochondrial phosphatidylethanolamine and cardiolipin biosynthetic pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:35410–35416. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505478200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mileykovskaya E., Dowhan W. Cardiolipin membrane domains in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009;1788:2084–2091. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kuroda T., Tani M., Moriguchi A., Tokunaga S., Higuchi T., Kitada S., Kuge O. FMP30 is required for the maintenance of a normal cardiolipin level and mitochondrial morphology in the absence of mitochondrial phosphatidylethanolamine synthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2011;80:248–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Devay R.M., Dominguez-Ramirez L., Lackner L.L., Hoppins S., Stahlberg H., Nunnari J. Coassembly of Mgm1 isoforms requires cardiolipin and mediates mitochondrial inner membrane fusion. J. Cell Biol. 2009;186:793–803. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200906098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Joshi A.S., Thompson M.N., Fei N., Hüttemann M., Greenberg M.L. Cardiolipin and mitochondrial phosphatidylethanolamine have overlapping functions in mitochondrial fusion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2012;287:17589–17597. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.330167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Osman C., Haag M., Potting C., Rodenfels J., Dip P.V., Wieland F.T. The genetic interactome of prohibitins: coordinated control of cardiolipin and phosphatidylethanolamine by conserved regulators in mitochondria. J. Cell Biol. 2009;184:583–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200810189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gohil V.M., Greenberg M.L. Mitochondrial membrane biogenesis: phospholipids and proteins go hand in hand. J. Cell Biol. 2009;184:469–472. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200901127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Beyer K., Klingenberg M. ADP/ATP carrier protein from beef heart mitochondria has high amounts of tightly bound cardiolipin, as revealed by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1985;16:3821–3826. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jiang F., Ryan M.T., Schlame M., Zhao M., Gu Z., Klingenberg M. Absence of cardiolipin in the crd1 null mutant results in decreased mitochondrial membrane potential and reduced mitochondrial function. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:22387–22394. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M909868199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pebay-Peyroula E., Dahout-Gonzalez C., Kahn R., Trezeguet V., Lauguin G.J., Brandolin G. Structure of mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier in complex with carboxyatractyloside. Nature. 2003;426:39–44. doi: 10.1038/nature02056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nury H., Dahout-Gonzalez C., Trezeguet V., Lauguin G., Brandolin G., Pebay-Peyroula E. Structural basis for lipid-mediated interactions between mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier monomers. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:6031–6036. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.09.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Claypool S.M., Oktay Y., Boontheung P., Loo J.A., Koehler C.M. Cardiolipin defines the interactome of the major ADP/ATP carrier protein of the mitochondrial inner membrane. J. Cell Biol. 2008;182:937–950. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200801152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kutik S., Rissler M., Guan X.L., Guiard B., Shui G., Gebert N. The translocator maintenance protein Tam41 is required for mitochondrial cardiolipin biosynthesis. J. Cell Biol. 2008;183:1213–1221. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200806048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Gubbens J., de Kroon A.I. Proteome-wide detection of phospholipid–protein interactions in mitochondria by photocrosslinking and click chemistry. Mol. Biosyst. 2010;6:1751–1759. doi: 10.1039/c003064n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Palmieri F., Pierri C.L., De Grassi A., Nunes-Nesi A., Fernie A.R. Evolution, structure and function of mitochondrial carriers: a review with new insights. Plant J. 2011;66:161–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lange C., Nett J.H., Trumpower B.L., Hunte C. Specific roles of protein–phospholipid interactions in the yeast cytochrome bc1 complex structure. EMBO J. 2001;20:6591–6600. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.23.6591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Shinzawa-Itho K., Aoyama H., Muramoto K., Terada H., Kurauchi T., Tadehara Y. Structures and physiological roles of 13 integral lipids of bovine heart cytochrome c oxidase. EMBO J. 2007;26:1713–1725. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Schägger H., Pfeiffer K. Supercomplexes in the respiratory chains of yeast and mammalian mitochondria. EMBO J. 2000;19:1777–1783. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.8.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cruciat C.-M., Brunner S., Baumann F., Neupert W., Stuart R.A. The cytochrome bc1 and cytochrome c oxidase complexes associate to form a single supracomplex in yeast mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:18093–18098. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M001901200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zara V., Conte L., Trumpower B.L. Evidence that the assembly of the yeast cytochrome bc1 complex involves the formation of a large core structure in the inner mitochondrial membrane. FEBS J. 2009;276:1900–1914. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.06916.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zhang M., Mileykovskaya E., Dowhan W. Gluing the respiratory chain together: cardiolipin is required for supercomplex formation in the inner mitochondrial membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:43553–43556. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C200551200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Pfeiffer K., Gohil V., Stuart R.A., Hunte C., Brandt U., Greenberg M.L., Schägger H. Cardiolipin stabilizes respiratory chain supercomplexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:52873–52880. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308366200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhong Q., Gohil V.M., Ma L., Greenberg M.L. Absence of cardiolipin results in temperature sensitivity, respiratory defects, and mitochondrial DNA instability independent of pet56. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:32294–32300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403275200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Koehler C.M. New developments in mitochondrial assembly. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004;20:309–335. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.20.010403.105057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Dolezal P., Likic V., Tachezy J., Lithgow T. Evolution of the molecular machines for protein import into mitochondria. Science. 2006;313:314–318. doi: 10.1126/science.1127895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.de Marcos-Lousa C., Sideris D.P., Tokatlidis K. Translocation of mitochondrial inner-membrane proteins: conformation matters. Trends Biochem. 2006;31:259–267. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Neupert W., Herrmann J.M. Translocation of proteins into mitochondria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007;76:723–749. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.052705.163409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Chacinska A., Koehler C.M., Milenkovic D., Lithgow T., Pfanner N. Importing mitochondrial proteins: machineries and mechanisms. Cell. 2009;138:628–644. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Endo T., Yamano K. Multiple pathways for mitochondrial protein traffic. Biol. Chem. 2009;390:723–730. doi: 10.1515/BC.2009.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Becker T., Böttinger L., Pfanner N. Mitochondrial protein import: from transport pathways to an integrated network. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012;37:85–91. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2011.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gebert N., Joshi A.S., Kutik S., Becker T., McKenzie M., Guan X.L. Mitochondrial cardiolipin involved in outer-membrane protein biogenesis: implications for Barth syndrome. Curr. Biol. 2009;19:2133–2139. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.10.074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Tamura Y., Harada Y., Yamano K., Watanabe K., Ishikawa D., Ohshima C. Identification of Tam41 maintaining integrity of the TIM23 protein translocator complex in mitochondria. J. Cell Biol. 2006;174:631–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200603087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gallas M.R., Dienhart M.K., Stuart R.A., Long R.M. Characterization of Mmp37p, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondrial matrix protein with a role in mitochondrial protein import. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2006;17:4051–4062. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E06-04-0366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Tamura Y., Endo T., Iijima M., Sesaki H. Ups1p and Ups2p antagonistically regulate cardiolipin metabolism in mitochondria. J. Cell Biol. 2009;185:1029–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200812018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.van der Laan M., Meinecke M., Dudek J., Hutu D.P., Lind M., Perschil I. Motor-free mitochondrial presequence translocase drives membrane integration of preproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007;9:1152–1159. doi: 10.1038/ncb1635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bednarz-Prashad A.J., Mize C.E. Phospholipid, enzymatic, and polypeptide analyses of the mitochondrial membranes from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Biochemistry. 1978;17:4178–4186. doi: 10.1021/bi00613a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Simbeni R., Pon L., Zinser E., Paltauf F., Daum G. Mitochondrial membrane contact sites of yeast: characterization of lipid components and possible involvement in intramitochondrial translocation of phospholipids. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:10047–10049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Palsdottir H., Hunte C. Lipids in membrane protein structures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1666:2–18. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bogdanov M., Dowhan W. Phosphatidylethanolamine is required for in vivo function of the membrane-associated lactose permease of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:732–739. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Bogdanov M., Dowhan W. Phospholipid-assisted protein folding: phosphatidylethanolamine is required at a late step of the conformational maturation of the polytopic membrane protein lactose permease. EMBO J. 1998;17:5255–5264. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.18.5255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bogdanov M., Umeda M., Dowhan W. Phospholipid-assisted refolding of an integral membrane protein: minimum structural features for phosphatidylethanolamine to act as a molecular chaperone. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:12339–12345. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.18.12339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Dowhan W., Bogdanov M. Lipid-dependent membrane protein topogenesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009;78:515–540. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.060806.091251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Horvath S.E., Wagner A., Steyrer E., Daum G. Metabolic link between phosphatidylethanolamine and triacylglycerol metabolism in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011;1811:1030–1037. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zinser E., Daum G. Isolation and biochemical characterization of organelles from the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1995;11:493–536. doi: 10.1002/yea.320110602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Folch J., Lees M., Stanley G.H.S. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957;226:497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Broekhuyse R.M. Phospholipids in tissues of the eye. I. Isolation, characterization and quantitative analysis by two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography of diacyl and vinyl-ether phospholipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1968;152:307–315. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Schneiter R., Daum G. Analysis of yeast lipids. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006;313:75–84. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-958-3:075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Martin J., Mahlke K., Pfanner N. Role of an energized inner membrane in mitochondrial protein import: Δψ drives the movement of presequences. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:18051–18057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Glick B.S., Brandt A., Cunningham K., Müller S., Hallberg R.L., Schatz G. Cytochrome c1 and b2 are sorted to the intermembrane space of yeast mitochondria by a stop-transfer mechanism. Cell. 1992;69:809–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90292-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Geissler A., Krimmer T., Bömer U., Guiard B., Rassow J., Pfanner N. Membrane potential-driven protein import into mitochondria: the sorting sequence of cytochrome b2 modulates the Δψ-dependence of translocation of the matrix-targeting sequence. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2000;11:3977–3991. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.11.3977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Chacinska A., Lind M., Frazier A.E., Dudek J., Meisinger C., Geissler A. Mitochondrial presequence translocase: switching between TOM tethering and motor recruitment involves Tim21 and Tim17. Cell. 2005;120:817–829. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Schägger H., von Jagow G. Blue native electrophoresis for isolation of membrane protein complexes in enzymatically active form. Anal. Biochem. 1991;199:223–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90094-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Stojanovski D., Pfanner N., Wiedemann N. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Methods Cell Biol. 2007;80:783–806. doi: 10.1016/S0091-679X(06)80036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Ryan M.T., Müller H., Pfanner N. Functional staging of ADP/ATP carrier translocation across the outer mitochondrial membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:20619–20627. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.29.20619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Rehling P., Model K., Brandner K., Kovermann P., Sickmann A., Meyer H.E. Protein insertion into the mitochondrial inner membrane by a twin-pore translocase. Science. 2003;299:1747–1751. doi: 10.1126/science.1080945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Brandner K., Mick D.U., Frazier A.E., Taylor R.D., Meisinger C., Rehling P. Taz1, an outer mitochondrial membrane protein, affects stability and assembly of inner membrane protein complexes: implications for Barth syndrome. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2005;16:5202–5214. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E05-03-0256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Hunte C., Köpke J., Lange C., Roßmanith T., Michel H. Structure at 2.3 Å resolution of the cytochrome bc1 complex from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae co-crystallized with an antibody Fv fragment. Structure. 2000;8:669–684. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Palsdottir H., Hunte C. Purification of the cytochrome bc1 complex from yeast. In: Hunte C., von Jagow G., Schägger H., editors. Membrane Protein Purification and Crystallization, 2nd Edition, A Practical Guide. Academic Press; London, UK: 2003. pp. 191–203. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Horvath A., Berry E.A., Huang L.S., Maslov D.A. Leishmania tarentolae: a parallel isolation of cytochrome bc1 and cytochrome c oxidase. Exp. Parasitol. 2000;96:160–167. doi: 10.1006/expr.2000.4564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Bornhövd C., Vogel F., Neupert W., Reichert A.S. Mitochondrial membrane potential is dependent on the oligomeric state of the F1Fo–ATP synthase supracomplexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:13990–13998. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512334200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Wagner K., Perschil I., Fichter C.D., van der Laan M. Stepwise assembly of dimeric F1Fo–ATP synthase in mitochondria involves the small Fo-subunits k and i. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2010;21:1494–1504. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E09-12-1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Zhang M., Mileykovskaya, Dowhan W. Cardiolipin is essential for organization of complexes III and IV into a supercomplex in intact yeast mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:29403–29408. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M504955200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.McKenzie M., Lazarou M., Thorburn D.R., Ryan M.T. Mitochondrial respiratory chain supercomplexes are destabilized in Barth syndrome patients. J. Mol. Biol. 2006;361:462–469. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.06.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Qin L., Hiser C., Mulichak A., Garavito R.M., Ferguson-Miller S. Identification of conserved lipid/detergent-binding sites in a high-resolution structure of the membrane protein cytochrome c oxidase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2006;103:16117–16122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606149103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Wenz T., Hielscher R., Hellwig P., Schägger H., Richers S., Hunte C. Role of phospholipids in respiratory cytochrome bc1 complex catalysis and supercomplex formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009;1787:609–616. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2009.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Wittig I., Schägger H. Supramolecular organization of ATP synthase and respiratory chain in mitochondrial membranes. Biophys. Biochim. Acta. 2009;1787:672–680. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Bultema J.B., Braun H.-P., Boekema E.J., Kouril R. Megacomplex organization of the oxidative phosphorylation system by structural analysis of respiratory chain supercomplexes from tomato. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009;1787:60–67. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary data