THE ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THE TRANSFUSION OF OLDER BLOOD AND OUTCOMES AFTER TRAUMA (original) (raw)
. Author manuscript; available in PMC: 2012 Jan 1.
Abstract
Allogeneic red blood cells (PRBCs) suppress immunity and influence outcomes. The influence of blood on the risk of infection and death may be related to the duration of storage. We sought to determine whether blood storage duration was associated with infection or death in a large cohort of injury victims.
We reviewed a cohort of trauma patients transfused at least one unit of PRBCs within 24 hours of admission to a level 1 trauma center. The outcomes of interest were complicated sepsis and mortality. We compared the amount of older blood (>14 days storage) given to patients who did or did not develop the outcomes of interest using univariate and multivariate methods.
A total of 820 patients were included. Patients who died (n = 117) received more units of older blood than those who lived (5 units [IQR 2–9] versus 3 units [IQR 2–6], p < 0.001). Patients with complicated sepsis (n = 244) received a greater volume of older blood than those without complicated sepsis (6 units [IQR 2–10] versus 3 units [IQR 1–5], p < 0.001). After adjusting for clinical factors including the total amount of blood transfused, patients receiving ≥7 units of older blood had a higher risk of complicated sepsis than patients receiving 1 or fewer units (OR = 1.9, p-value = 0.03).
The risk for complicated sepsis and death in trauma victims who are transfused blood is high. The amount of older blood transfused is associated with complicated sepsis. While the best strategy to minimize the effects of allogeneic blood is to avoid unnecessary transfusions, it may be particularly important to avoid transfusing multiple units of older blood.
Keywords: Allogenic, blood transfusion, trauma, sepsis, infection, immune suppression
Introduction
Transfusion of red blood cells and other blood products are life saving in severely injured patients. However, allogeneic blood transfusion, most notably packed red blood cells (PRBCs), may contribute to sepsis and organ failure in a variety of ways that are only partially understood. A number of investigators have demonstrated that blood transfusions are a consistent risk factor for post-injury multiple organ failure (MOF) independent of other shock indices (such as base deficit and lactate concentrations). The risk of post-injury organ failure and infection increases with an increasing number of units of PRBCs transfused in the initial 24 hours.(1;2) Taken together, the existing data indicate that allogeneic blood transfusions contribute to organ failure and infection and are not just markers for other indices of injury or illness severity.(3)
Although allogeneic blood likely affects innate and adaptive immunity in a variety of ways, the exact mechanisms responsible for transfusion-related immune suppression in trauma are unknown. During preservation under standard blood bank conditions, the red blood cell undergoes a series of reversible and irreversible changes that could be implicated in post-transfusion complications.(4–6) Both plasma and cellular factors may contribute. For example, plasma from stored PRBCs primes cultured neutrophils for superoxide production.(7) Moreover, stored plasma activates endothelial cells in an apparent age-dependent manner.(8) Experimental evidence also suggests that several lipids and micro-particles derived from cells in stored blood can cause pulmonary endothelial injury.(9) Despite the evidence supporting a relationship between PRBC transfusion and infectious outcomes, not all are consistent with this notion.(10)
In addition to the amount of blood transfused, the age or duration of PRBC storage has been considered a factor contributing to organ failure. Although investigators have concluded that there is a relationship, they have not convincingly separated the effects of storage duration of individual units from the number of units transfused. Furthermore, in the case of transfusion for traumatic hemorrhage, attention has primarily been directed towards the blood transfused in the first 12 or 24 hours, perhaps underestimating whether blood received after the initial 24 hours may be important. Suggestive clinical evidence of an adverse effect of the duration blood storage comes from a review of patients who underwent coronary artery bypass graft surgery and received allogeneic blood transfusions.(11) Patients who were given exclusively older blood had poorer outcomes than those given exclusively newer blood. The transfusion requirements of these cardiac surgery patients were relatively small (50% received 1 or 2 units) and the observations, while important may not apply to severely injured patients. Furthermore, concern was raised regarding important characteristics of this study that limit its validity.(12) In light of the limitations in the existing literature, we conducted this study to determine whether the storage age of transfused PRBCs was associated with the development of complicated sepsis and mortality in a large cohort of critically injured trauma patients.
Patients and Methods
Study Subject Enrollment
This is a retrospective review of a subgroup of a previously described prospective cohort of severely injured trauma victims. (13) Inclusion and exclusion criteria were derived from the parent study and are summarized here. We included victims of blunt and penetrating trauma who were admitted to the intensive care unit at Harborview Medical Center (Seattle, WA) between August 2003 and December 2005 who received at least 1 unit of allogeneic PRBCs during the first 24 hours after arrival to hospital. We excluded patients who died within 24 hours of injury, were transferred out of the ICU within 24 hours of injury or received blood prior to transfer to our hospital. The Institutional Review Board of the University of Washington approved the study. We collected demographic information (i.e., age, gender), injury characteristics (i.e., mechanism, anatomic injury severity), and information pertaining to hospital course (i.e. length of stay, complications such as sepsis and organ failure), and discharge disposition. Detailed data regarding all transfused blood products were obtained from the Puget Sound Blood Center (Seattle, WA). These data included the date of transfusion and the duration of storage prior to transfusion (days).
Transfusion Practice during Study Period
The approach to the transfusion of packed red blood cells and other blood products has remained relatively stable over the study period. During acute resuscitation, PRBC and other blood products are transfused early in patients with hemorrhagic shock. Our hospital also has a massive transfusion protocol (MTP) which is instituted in all patients who are in shock and considered by the trauma surgeon likely to require > 6 of PRBC during resuscitation. The objective of the MTP is to obtain measures of coagulation status early (PT, PTT, platelet count and fibrinogen concentration) and to ensure that additional blood products (platelets, plasma and cryoprecipitate when indicated) are rapidly available for patients at high risk for or who have a coagulopathy. Following resuscitation and once the patient is stabilized and admitted to the ICU or hospital ward, our practice is to follow a more restrictive practice of PRBC transfusion. We adhere to published guidelines for the transfusion of critically ill patients.(14;15)
Primary Outcomes
We focused on two end-points of primary importance: complicated sepsis and death. Sepsis was defined by the presence of a positive bacterial culture from a normally sterile site combined with the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS).(16) Complicated sepsis includes patients who developed severe sepsis (sepsis with organ failure) or septic shock, the two most severe manifestations of infection.(17) The clinical criteria for SIRS, organ failure or shock must have been met within a 48 hour period of the index positive culture. The day of sepsis onset was assigned based upon when the first evidence for sepsis (clinical or microbiological) was present. Therefore, if a culture was positive on day “5” and the associated SIRS criteria were met on day “3”, the date of onset was recorded as day “3”.
Statistical Analyses
Studies suggest that deleterious effects of allogeneic red blood cell transfusion are evident after a storage age beyond 14 days. For the purpose of our primary analyses, each unit of blood was categorized as “younger” (≤ 14 days storage) or “older” (>14 days storage).(6;18) Our analyses include all the PRBC transfusions that patients received during their hospitalization. Continuous data are presented as medians and interquartile ranges (IQR). Categorical data are presented as numbers and percentages. Excel 7.0 for Windows (Redmond, WA) and SPSS 16.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc, Chicago, Ill) were used for data management and analysis. Our primary comparisons concerned the two main end points of mortality and complicated sepsis. We chose these endpoints as they were frequent, are clearly adverse outcomes and may be directly influenced by the amount and possibly age of allogeneic PRBCs. We used the Mann-Whitney – U and chi-square tests to compare continuous and categorical variables, respectively. Actual _p_-values from each analysis are reported. Forward stepwise logistic regression was used to determine whether the age of transfused PRBCs was associated with mortality or complicated sepsis, controlling for important covariates and potential confounders. These covariates included: age, sex, race, injury severity score, body region AIS scores, arterial base deficit, co-morbid conditions and injury mechanism. Adjusted odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) as well as the associated p-values are presented. We included continuous variables (age, base deficit, ISS, total number of units transfused and number of older units of blood transfused) in a variety of ways in our logistic regression models. The form in which these variables were included (continuous, categorized into quartiles or binary) in each of the final models was based upon which format resulted in the best predictive model (lowest Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit statistic). For example we included age in various ways in our multivariate models (continuous, quartiles and dichotomized as < 55 or ≥ 55 years). Age was dichotomized as < 55 or ≥ 55 years for our final analyses because this resulted in the best predictive models for both mortality and complicated sepsis.
Results
Details of study cohort
From August 1, 2003 to December 31, 2005, 1958 trauma patients were prospectively enrolled and included in our database. Of these, 820 received at least one unit of PRBCs within 24 hours of admission and are included in our analyses. Figure 1 summarizes the study subject inclusion and exclusion. Demographic and clinical characteristics are included in Table 1 and are summarized here. Patients were initially transfused for hemorrhagic shock or anemia. In all cases either the initial hemoglobin or lowest hemoglobin in the first 24 hours was ≤ 11 g/dl. The median number of units transfused was 6 (IQR 4–11) of which 4 units (IQR 2–7) were administered during the first 24 hours (Table 2). The median age of all transfused blood was 17 days (IQR 11–23). The median number of units of older blood transfused was 3 (IQR 2–7). A total of 471 patients (57% of the transfused patients) developed sepsis. The median day of onset of the first evidence of sepsis was day 5. Figure 2 illustrates the day of transfusion of all PRBC units received as well as the first evidence of sepsis for the 471 patients who developed any infection. A total of 6,626 units (87% of all units) were transfused within the first 3 days after injury.
Figure 1. Study subject inclusion.
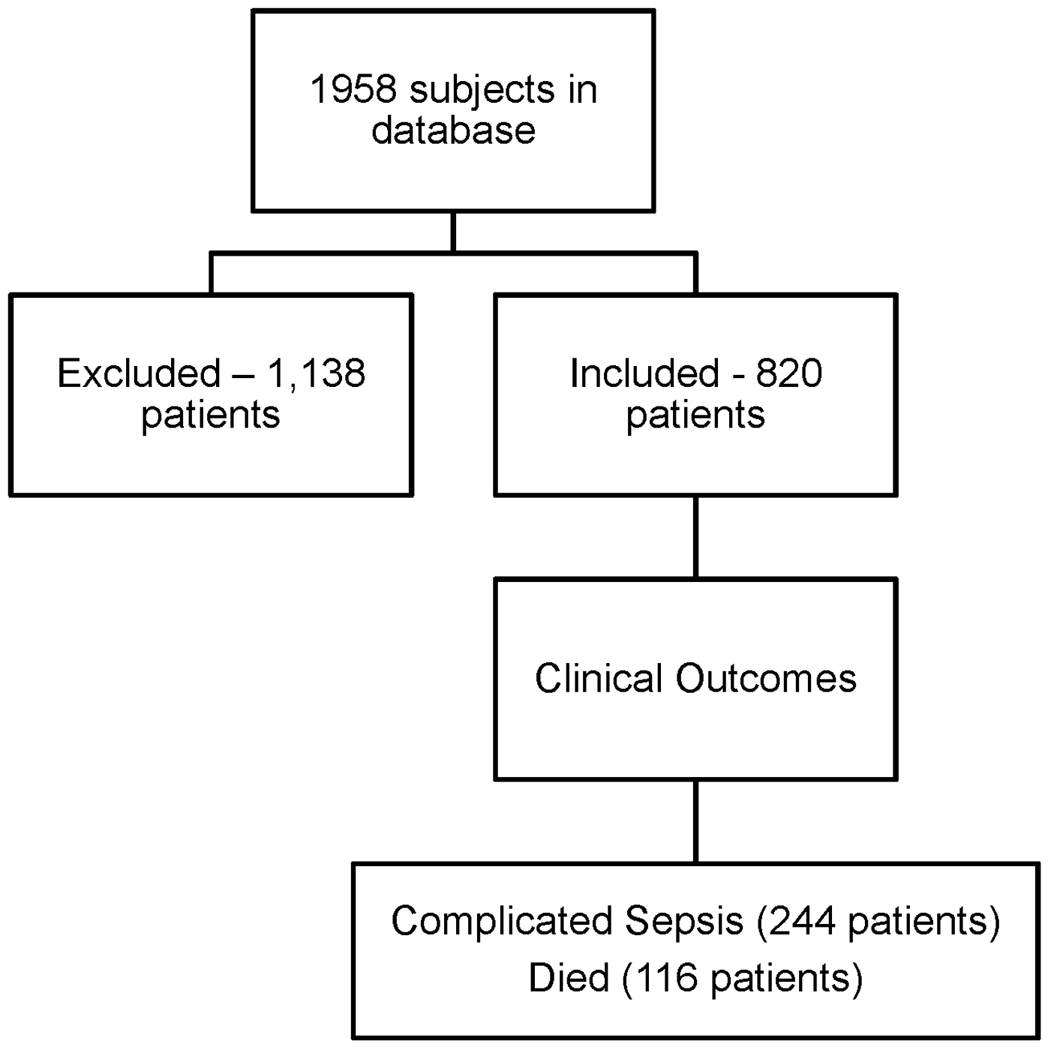
1,958 patients were enrolled and of those, 820 received at least one unit of PRBCs during the 1st 24 hours of admission. These patients were then analyzed for outcomes of interest – complicated sepsis and death. All blood transfused during the hospitalization was analyzed.
Table 1.
Demographic, Injury and Outcome Characteristics
| Age (years) | 40 (24–52) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 553 (67%) |
| Female | 267 (33%) |
| Race/Ethnicity | |
| Caucasian | 622 (76%) |
| African-American | 62 (8%) |
| Hispanic | 56 (7%) |
| Asian | 45 (6%) |
| Injury Severity Score | 27 (18–34) |
| Severe Traumatic Brain Injury | 359 (44%) |
| Severe Thoracic Injury | 418 (51%) |
| Severe Abdominal Injury | 256 (31%) |
| Severe Extremity Injury | 374 (46%) |
| Injury Mechanism | |
| Blunt | 726 (89%) |
| Penetrating | 94 (12%) |
| Interventions | |
| Laparotomy | 212 (26%) |
| Thoracotomy/Thoracoscopy | 101 (12%) |
| Fracture Fixation | 415 (51%) |
| Outcomes | |
| Complicated Sepsis | 244 (30%) |
| Died | 117 (14%) |
| ICU length of stay (days) | 7 (3–14) |
| Hospital length of stay (days) | 16 (9–25) |
Table 2.
Transfusion Characteristics
| Pre-transfusion hematocrit (%) | 20 (19–22) |
|---|---|
| Total units transfused | 6 (4–11) |
| Units transfused in 1st 24 hrs | 4 (2–7) |
| Units transfused after 24 hrs | 2 (0–4) |
| Age of all blood transfused (days) | 17 (11–23) |
| Units of older blood | 3 (2–7) |
Figure 2. Units of blood transfused and day of sepsis onset.
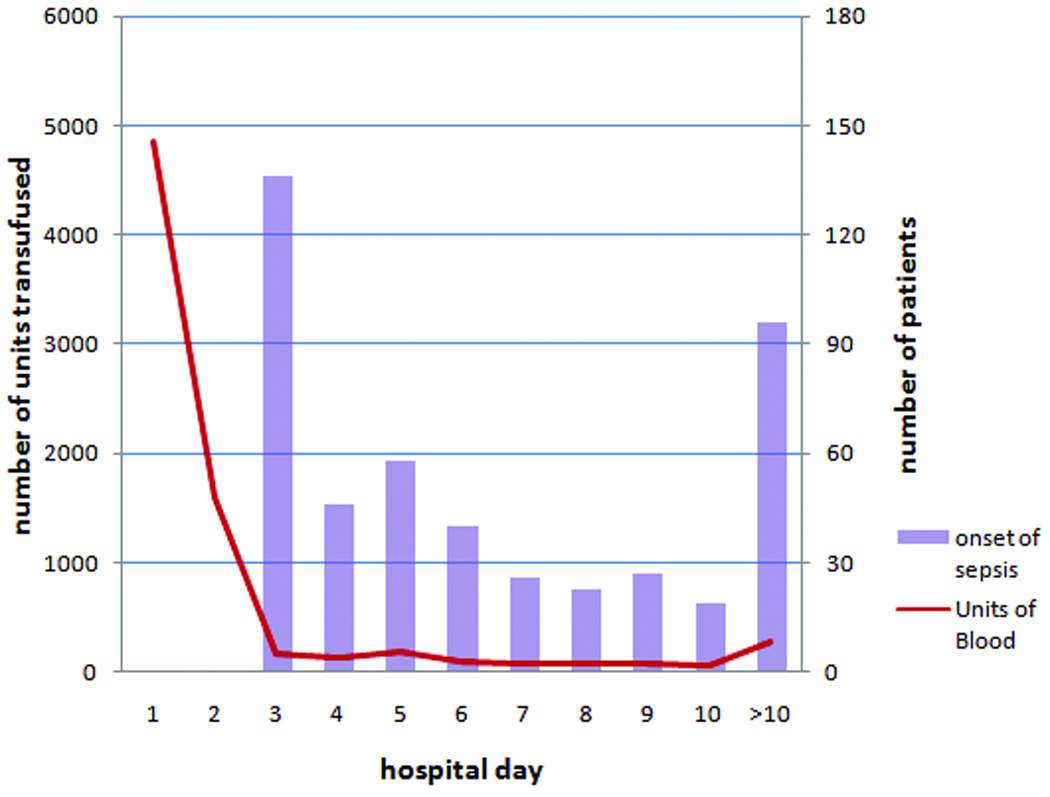
Shown in this figure are the total number of units of PRBCs transfused (left y-axis) and the number of patients diagnosed with sepsis (right y-axis) on each post-injury day (x-axis).
Ventilator associated pneumonia was the most common site of infection, occurring in 340 (42%) patients. Urinary tract infections occurred in 169 (20%) patients but were rarely the only site of infection in patients with complicated sepsis. Bloodstream (n = 125 [15%]) and wound infections (n = 121 [15%]) were the next most frequent sites of infection. Many patients developed multiple infections over the course of their hospital stay.
The number of units of PRBCs transfused but not the number of older units is associated with death
The 117 (14%) patients who died received more blood when compared to those who lived (9 units [QR 5–19] versus 6 units [QR 6–10]). Patients who died also received more units of older blood (5 units [IQR 2–9] versus 3 units [IQR 2–6]) in survivors. The data are shown in Figure 2 and Table 3. Also shown Table 3 are the important injury and demographic factors that were different between the survivors and non-survivors by unadjusted analyses.
Table 3.
Unadjusted Analysis of Factors Associated with Mortality
| Variable | Lived (n = 703) | Died (n = 117) | p – value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient age (years) | 38 (23 – 50) | 49 (26 – 73) | <0.001 |
| Traumatic brain injury AIS ≥ 3 | 283 (40%) | 76 (65%) | <0.001 |
| Injury severity score | 26 (17 – 34) | 29 (22 – 38) | <0.001 |
| Base deficit | 5 (3 – 8) | 8 (4 – 12) | <0.001 |
| Number of older units | 3 (2 – 6) | 5 (2 – 9) | 0.004 |
| Total number of units | 6 (3 – 10) | 9 (5 – 19) | <0.001 |
The results of the multivariate analysis are also in Table 4. Multivariate analysis indicated that the total number of units transfused but not the number of units of older blood was an independent risk factor for mortality after controlling for patient age, ISS, sex and severity of traumatic brain injury.
Table 4.
Risk Factors for Death
| Variable | Odds Ratio(95% Confidence Interval) | p – value |
|---|---|---|
| Patient age ≥ 55 years | 3.7 (2.4 – 5.9) | < 0.001 |
| Traumatic brain injury AIS ≥ 3 | 3.4 (2.2 – 5.4) | < 0.001 |
| Base deficit | 1.5 (1.2 – 1.8) | < 0.001 |
| Number of older units | 0.9 (0.7 – 1.2) | 0.69 |
| Total number of units | 1.4 (1.1 – 1.9) | 0.007 |
The number of older units transfused is associated with the development of complicated sepsis
Patients who developed complicated sepsis received more blood in total and more units of older blood. The 244 patients who developed complicated sepsis received a median of 9 units (IQR 6–17) in comparison to the 576 patients without complicated sepsis who received 5 units (IQR 2–6). The patients with complicated sepsis received 6 units (IQR 2–10) of older blood compared to patients without complicated sepsis, who received 3 units (IQR 1–5) of older blood (Figure 3 and Table 5). The differences were statistically significant for both the total number of units and the number of units of older blood transfused.
Figure 3. Mortality and infection outcome for entire cohort.
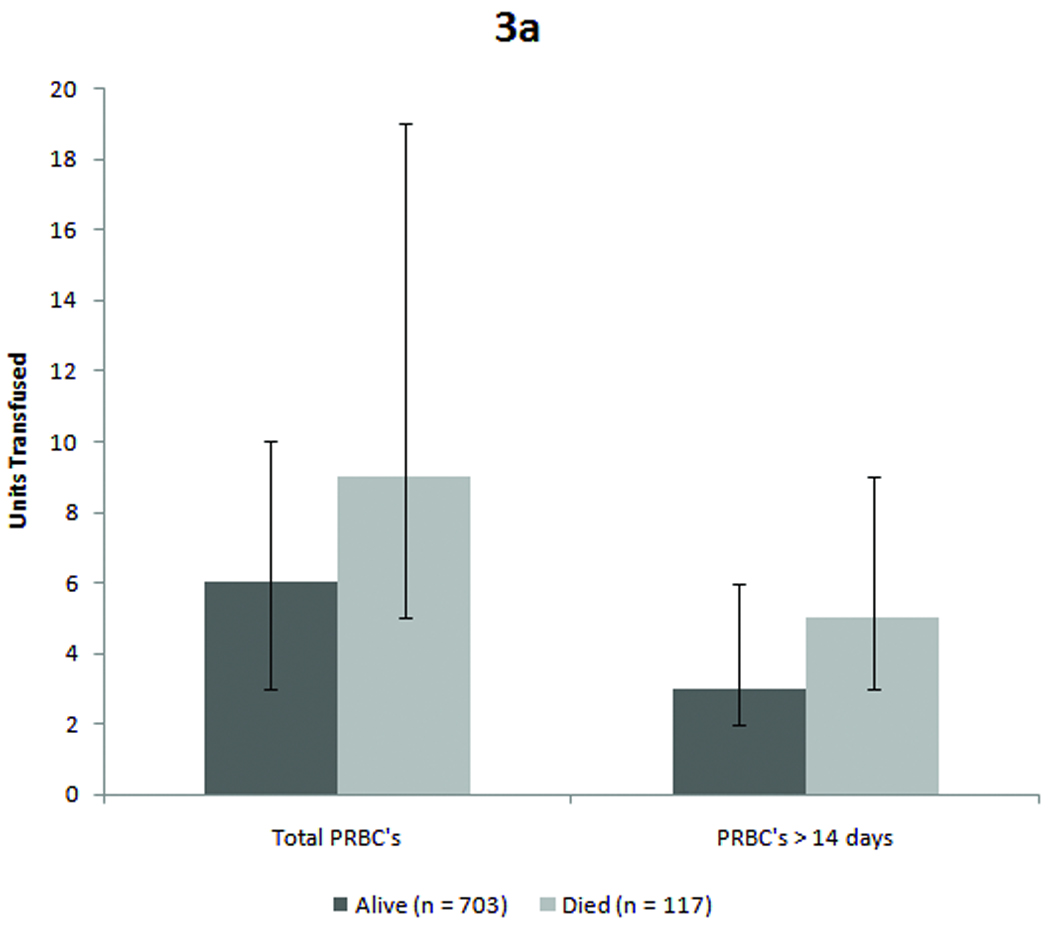
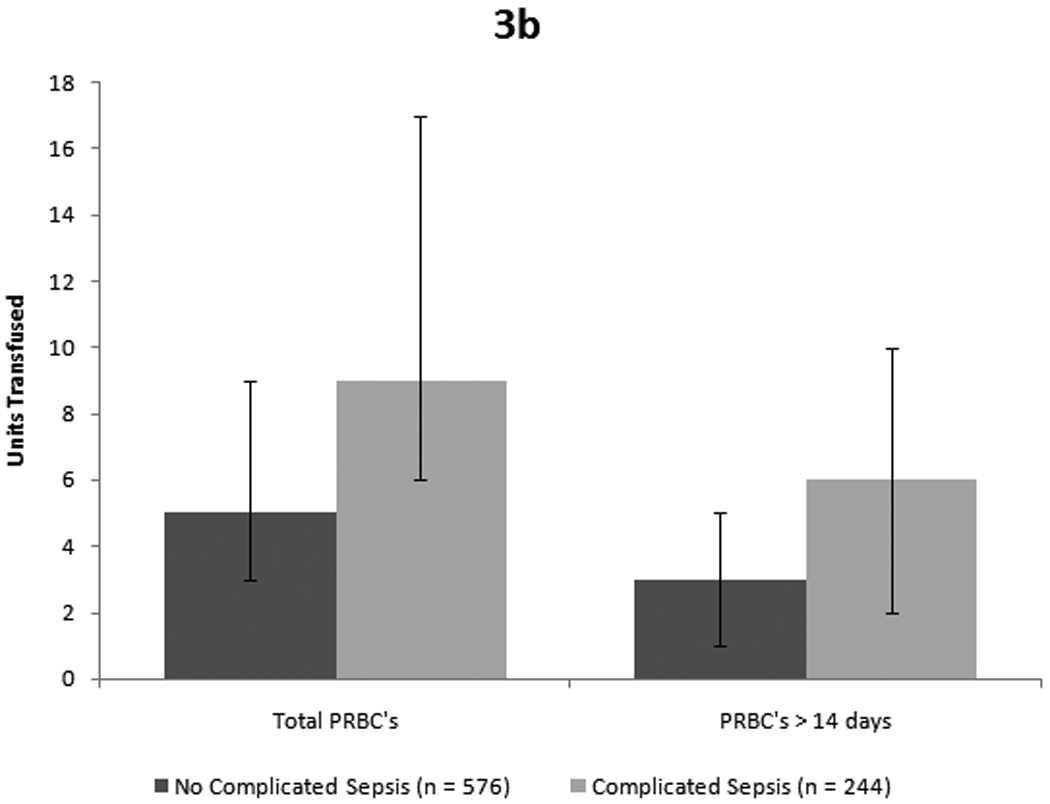
Figure 3a: Patients who died received significantly more units overall as well as a greater number of units of older blood. (p < 0.001 for total transfusions and p = 0.004 for older blood, both by Mann-Whitney-U test). Figure 3b: Similarly, patients who developed complicated sepsis received more blood overall and more units of older blood. (p < 0.001 for total PRBCs and p = 0.004 for older blood by Mann-Whitney-U test)
Table 5.
Unadjusted Analysis of Factors Associated with Complicated Sepsis
| Variable | No complicatedsepsis (n = 576) | Complicatedsepsis (n = 244) | p – value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient age (years) | 37 (22 – 49) | 45 (27 – 61) | <0.001 |
| Traumatic brain injury AIS ≥ 3 | 255 (44%) | 104 (43%) | 0.68 |
| Chest AIS ≥ 3 | 272 (47%) | 147 (60%) | 0.001 |
| Injury severity score | 25 (17 – 34) | 27 (22 – 34) | <0.001 |
| Base deficit | 5 (3 – 8) | 6 (3 – 10) | 0.003 |
| Number of older units | 3 (1 – 5) | 6 (2 – 10) | <0.001 |
| Total number of units | 5 (3 – 9) | 9 (6 – 17) | <0.001 |
Unlike the case with mortality, the number of units of older blood remained associated with complicated sepsis after controlling for age, sex, total amount of PRBCs transfused and injury severity score (Table 5). The association was primarily determined by patients who received 7 or more units of older blood (OR 1.9, 95% CI 1.1 – 3.4).
Not all blood was transfused prior to patients demonstrating any evidence of sepsis. However, it is also difficult to determine the exact onset of sepsis. Understanding this, we also compared the amount of old blood received prior to any evidence of sepsis. Even by this conservative estimate, patients with complicated sepsis received more old blood (4 units, IQR 2–7) than patients with uncomplicated sepsis (3 units, IQR 1–4. P-value = 0.001).
Discussion
Allogeneic blood transfusions are potentially harmful. Hemolytic transfusion reactions are rare and can be avoided by careful attention to patient and unit identification throughout the process of obtaining and administering blood.(19) However, it is evident that blood transfusions have other immunological effects with important clinical implications. Of these, transfusion-related acute lung injury has received the most attention and is perhaps the best understood.(20) However, there is evidence suggesting a broader range of clinical effects of blood transfusions in trauma and other critically ill patients.(21;22) We observed two important associations in our study.
First, the volume of blood transfused is associated with death. While hemorrhage is clearly an important cause of death after injury, these patients did not simply bleed to death as the majority died days, and often weeks, after injury and after transfusion. Our study design excluded patients who died less than 24 hours after admission, resulting in non-survivors who died after a median of 7 days in the ICU. Nevertheless, we recognize that the volume of blood transfused, particularly during the initial resuscitation, reflects the severity of injury and amount of hemorrhage. Both of which are important risk factors for mortality and complications such as organ failure and infection. Our observations are similar to what other investigators have found.(23;24) Although patients who died did receive a greater volume of older blood, after adjusting for other mortality risk factors, including the total amount of blood transfused, the amount of older blood was not associated with death. This observation differs from other reports. Our data, in conjunction with previous reports, demonstrates that the total volume of blood is the primary transfusion-related mortality risk factor.(24;25) While older blood may have an impact, it is not discernable from the effects of severe injuries and the relatively large volume of blood transfused in our study.
Our second finding is notable and is the focus of our study. We observed that the amount of older transfused blood was associated with complicated sepsis. In contradistinction to the situation with mortality, the amount of older blood, rather than simply the total amount of blood, is an important transfusion related factor that is associated with more serious infections. The association between the transfusion of older blood and complicated sepsis that we observed is consistent with the existing literature and suggests that the immunomodulatory effect of the allogeneic blood is influenced by the duration of storage.(11;22) Trauma patients are at high risk for nosocomial infection. They are often colonized with a broad range of potentially pathogenic organisms and their normal defense mechanisms are breeched by intravascular catheters, endotracheal tubes and other monitoring devices. Suppression of innate immune responses by allogeneic blood may contribute to the development of nosocomial infection and their severity. Our observations suggest that older blood may contribute to this risk to a greater degree than younger blood and that the risk is not linearly related to the number of older units. It appears that the risk is primarily limited to when the cumulative amount of older blood is ≥ 7 units of PRBCs (the highest quartile of older units transfused in our study). This observation was not based upon a pre-defined hypothesis, but was a function of our categorization of the amount of older blood transfused. Our data suggest that repeated exposure to older units may render patients more susceptible to severe infections. Sepsis accompanied by organ failure or shock is a relevant complication after trauma and is related to other objective outcomes. First, patients in our study who developed complicated sepsis had approximately twice the case-fatality rate as those without complicated sepsis (21% versus 11%). In addition, patients with complicated sepsis spent longer in the ICU than patients without complicated sepsis (a median of 18 days versus 5 days).
Reducing the amount of older blood that a patient receives can be achieved first by reducing the total amount of blood transfused. It is clear that accepting a lower hemoglobin threshold (7g/dl) in critically ill patients without active hemorrhage reduces the amount of blood transfused and improves outcomes.(14;25) Our study subjects were generally managed according to this approach once they had been resuscitated and were hemodynamically stable. In fact, a very small proportion of the blood transfused in this study was given after the initial 48 hours of injury. Our data therefore reinforce the notion that the potential benefit of each transfusion must be carefully assessed. Beyond reducing amount of blood transfused overall, specifically limiting the amount of older blood may be important. Perhaps blood banks should consider limiting the amount of older blood that is given to individual trauma patients over the course of their hospitalization. Such a recommendation has broad implications and we recognize that such a change in blood banking practice would have a considerable impact on blood availability. The results of a recent review of this topic are consistent with our observations.(26) These authors reviewed 27 publications that reported on associations between the age of transfused blood and outcomes in adults. They felt that there was too much heterogeneity among the studies to allow for a formal meta-analysis. They concluded that in most of the clinical settings examined there was no relationship between the storage duration of blood and morbidity or mortality. They did note that trauma patients undergoing large volume transfusions may be negatively affected by receiving older blood.
Our observations must be interpreted in the context of the limitations of our data. The patients at the highest risk of mortality and complicated sepsis received a combination of older and younger blood. A total of 166 patients received exclusively younger blood and only 54 of these received more than 3 units in total. The small number of patients receiving exclusively older or exclusively younger blood do not allow us to conduct an analysis comparable to Koch et al. who were able to compare patients who received exclusively older blood with those receiving exclusively younger blood.(11) That most of our patients received a combination of younger and older blood may explain why we did not observe a measurable association between older blood and mortality. Ultimately, determining whether longer periods of blood storage lead to observable complications is challenging and perhaps can only be definitively addressed by a randomized clinical trial.
In the absence of a clinical trial, our data indicates that the risk of complicated sepsis is related to the amount of older blood that a patient receives. We believe that strategies limiting the amount of older blood that an individual patient receives to fewer than 7 units should be considered.
Table 6.
Risk Factors for Complicated Sepsis
| Variable | Odds Ratio(95% Confidence Interval) | p – value |
|---|---|---|
| Patient age ≥ 55 years | 2.2 (1.5 – 3.2) | < 0.001 |
| Male | 1.5 (1.1 – 2.2) | 0.02 |
| Injury severity score | 1.3 (1.1 – 1.4) | 0.002 |
| Total units transfused | 1.5 (1.2 – 1.8) | < 0.001 |
| Number of older units transfused | 0.01 | |
| 2 – 3 units | 0.9 (0.5 – 1.4) | 0.52 |
| 4 – 6 units | 1.0 (0.6 – 1.6) | 0.87 |
| ≥ 7 units | 1.9 (1.1 – 3.4) | 0.03 |
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grants 5P50GM021681-370013 and 1R01GM066946.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Reference List
- 1.Moore FA, Moore EE, Sauaia A. Blood Transfusion. An Independent Risk Factor for Postinjury Multiple Organ Failure. Arch.Surg. 1997;132(6):620–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Croce MA, Tolley EA, Claridge JA, Fabian TC. Transfusions Result in Pulmonary Morbidity and Death After a Moderate Degree of Injury. J.Trauma. 2005;59(1):19–23. doi: 10.1097/01.ta.0000171459.21450.dc. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hensler T, Heinemann B, Sauerland S, Lefering R, Bouillon B, Andermahr J, Neugebauer EA. Immunologic Alterations Associated With High Blood Transfusion Volume After Multiple Injury: Effects on Plasmatic Cytokine and Cytokine Receptor Concentrations. Shock. 2003;20(6):497–502. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000095058.62263.1f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stadler I, Toumbis CA, Ambrus JL. Influence of Cold Storage Altered Red Cell Surface on the Function of Platelets. J.Med. 1994;25(6):353–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Berezina TL, Zaets SB, Morgan C, Spillert CR, Kamiyama M, Spolarics Z, Deitch EA, Machiedo GW. Influence of Storage on Red Blood Cell Rheological Properties. J.Surg.Res. 2002;102(1):6–12. doi: 10.1006/jsre.2001.6306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kirkpatrick UJ, Adams RA, Lardi A, McCollum CN. Rheological Properties and Function of Blood Cells in Stored Bank Blood and Salvaged Blood. Br.J.Haematol. 1998;101(2):364–368. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1998.00689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Silliman CC, Thurman GW, Ambruso DR. Stored Blood Components Contain Agents That Prime the Neutrophil NADPH Oxidase Through the Platelet-Activating-Factor Receptor. Vox Sang. 1992;63(2):133–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1992.tb02500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Silliman CC, Voelkel NF, Allard JD, Elzi DJ, Tuder RM, Johnson JL, Ambruso DR. Plasma and Lipids From Stored Packed Red Blood Cells Cause Acute Lung Injury in an Animal Model. J.Clin.Invest. 1998;101(7):1458–1467. doi: 10.1172/JCI1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Silliman CC, Paterson AJ, Dickey WO, Stroneck DF, Popovsky MA, Caldwell SA, Ambruso DR. The Association of Biologically Active Lipids With the Development of Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury: a Retrospective Study. Transfusion. 1997;37(7):719–726. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1997.37797369448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ruttinger D, Wolf H, Kuchenhoff H, Jauch KW, Hartl WH. Red Cell Transfusion: an Essential Factor for Patient Prognosis in Surgical Critical Illness? Shock. 2007;28(2):165–171. doi: 10.1097/shk.0b013e31803df84d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Koch CG, Li L, Sessler DI, Figueroa P, Hoeltge GA, Mihaljevic T, Blackstone EH. Duration of Red-Cell Storage and Complications After Cardiac Surgery. N.Engl.J.Med. 2008;358(12):1229–1239. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa070403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dzik W. Fresh Blood for Everyone? Balancing Availability and Quality of Stored RBCs. Transfus.Med. 2008;18(4):260–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3148.2008.00870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shalhub S, Junker CE, Imahara SD, Mindrinos MN, Dissanaike S, O'Keefe GE. Variation in the TLR4 Gene Influences the Risk of Organ Failure and Shock Posttrauma: a Cohort Study. J.Trauma. 2009;66(1):115–122. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e3181938d50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hebert PC, Wells G, Blajchman MA, Marshall J, Martin C, Pagliarello G, Tweeddale M, Schweitzer I, Yetisir E. A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial of Transfusion Requirements in Critical Care. Transfusion Requirements in Critical Care Investigators, Canadian Critical Care Trials Group. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1999;340(6):409–417. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199902113400601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.West MA, Shapiro MB, Nathens AB, Johnson JL, Moore EE, Minei JP, Bankey PE, Freeman B, Harbrecht BG, McKinley BA, Moore FA, Maier RV. Inflammation and the Host Response to Injury, a Large-Scale Collaborative Project: Patient-Oriented Research Core-Standard Operating Procedures for Clinical Care. IV. Guidelines for Transfusion in the Trauma Patient. J.Trauma. 2006;61(2):436–439. doi: 10.1097/01.ta.0000232517.83039.c4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RM, Sibbald WJ. Definitions for Sepsis and Organ Failure and Guidelines for the Use of Innovative Therapies in Sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992;101(6):1644–1655. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.6.1644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.O'Keefe GE, Hybki DL, Munford RS. The G-->A Single Nucleotide Polymorphism at the −308 Position in the Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Promoter Increases the Risk for Severe Sepsis After Trauma. J Trauma. 2002;52(5):817–826. doi: 10.1097/00005373-200205000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chin-Yee I, Arya N, d'Almeida MS. The Red Cell Storage Lesion and Its Implication for Transfusion. Transfus.Sci. 1997;18(3):447–458. doi: 10.1016/S0955-3886(97)00043-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Eder AF, Chambers LA. Noninfectious Complications of Blood Transfusion. Arch.Pathol.Lab Med. 2007;131(5):708–718. doi: 10.5858/2007-131-708-NCOBT. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Eder AF, Herron R, Strupp A, Dy B, Notari EP, Chambers LA, Dodd RY, Benjamin RJ. Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury Surveillance (2003–2005) and the Potential Impact of the Selective Use of Plasma From Male Donors in the American Red Cross. Transfusion. 2007;47(4):599–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2007.01102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sauaia A, Moore FA, Moore EE, Haenel JB, Read RA, Lezotte DC. Early Predictors of Postinjury Multiple Organ Failure. Arch.Surg. 1994;129(1):39–45. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1994.01420250051006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Offner PJ, Moore EE, Biffl WL, Johnson JL, Silliman CC. Increased Rate of Infection Associated With Transfusion of Old Blood After Severe Injury. Arch.Surg. 2002;137(6):711–716. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.137.6.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.O'Keefe GE, Hybki DL, Munford RS. The G-->A Single Nucleotide Polymorphism at the −308 Position in the Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Promoter Increases the Risk for Severe Sepsis After Trauma. J Trauma. 2002;52(5):817–826. doi: 10.1097/00005373-200205000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Weinberg JA, McGwin G, Jr, Griffin RL, Huynh VQ, Cherry SA, III, Marques MB, Reiff DA, Kerby JD, Rue LW., III Age of Transfused Blood: an Independent Predictor of Mortality Despite Universal Leukoreduction. J.Trauma. 2008;65(2):279–282. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e31817c9687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Corwin HL, Gettinger A, Pearl RG, Fink MP, Levy MM, Abraham E, MacIntyre NR, Shabot MM, Duh MS, Shapiro MJ. The CRIT Study: Anemia and Blood Transfusion in the Critically Ill--Current Clinical Practice in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(1):39–52. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000104112.34142.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lelubre C, Piagnerelli M, Vincent JL. Association Between Duration of Storage of Transfused Red Blood Cells and Morbidity and Mortality in Adult Patients: Myth or Reality? Transfusion. 2009;49(7):1384–1394. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2009.02211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]