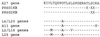Repertoire of human antibodies against the polysaccharide capsule of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 6B - PubMed (original) (raw)
Repertoire of human antibodies against the polysaccharide capsule of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 6B
Y Sun et al. Infect Immun. 1999 Mar.
Abstract
We examined the repertoire of antibodies to Streptococcus pneumoniae 6B capsular polysaccharide induced with the conventional polysaccharide vaccine in adults at the molecular level two ways. In the first, we purified from the sera of seven vaccinees antipneumococcal antibodies and determined their amino acid sequences. Their VH regions are mainly the products of VH3 family genes (candidate genes, 3-23, 3-07, 3-66, and 3-74), but the product of a VH1 family gene (candidate gene, 1-03) is occasionally used. All seven individuals have small amounts of polyclonal kappa+ antibodies (Vkappa1 to Vkappa4 families), although kappa+ antibodies are occasionally dominated by antibodies formed with the product of the A27 Vkappa gene. In contrast, lambda+ anti-6B antibodies are dominated by the antibodies derived from one of 3 very similar Vlambda2 family genes (candidate genes, 2c, 2e, and 2a2) and Clambda1 gene product. The Vlambda2(+) antibodies express the 8.12 idiotype, which is expressed on anti-double-stranded-DNA antibodies. In one case, Vlambda is derived from a rarely expressed Vlambda gene, 10a. In the second approach, we studied a human hybridoma (Dob1) producing anti-6B antibody. Its VH region sequence is closely related to those of the 3-15 VH gene (88% nucleotide homology) and JH4 (92% homology). Its VL region is homologous to the 2a2 Vlambda2 gene (91%) and Jlambda1/Clambda1. Taken together, the V region of human anti-6B antibodies is commonly formed by a VH3 and a Vlambda2 family gene product.
Figures
FIG. 1
Relationship between the amount of anti-6B antibodies (Ab) expressing the 8.12 idiotype and the amount of anti-6B antibodies expressing λ light chain for volunteers vaccinated with a PS vaccine (B), compared with the relationship between total anti-6B and anti-6B antibodies expressing either κ or λ chain (A). Donor P26, who was found to express antibody derived from a Vλ10 family gene, is indicated with an arrow. Panel A was reproduced with permission of the publisher (J. Infect. Dis. 174:75–82, 1996).
FIG. 2
Amino acid sequences of the V region of the light chain of anti-6B antibodies expressing the λ light chain. Dayhoff amino acid notation and the residue numbering system of Kabat et al. (17) are used. X indicates no residue identified; the X at position 22 of P26λ is likely an invariant cysteine not identifiable by our sequencing method. The lowercase letter denotes the recovery of a smaller than expected amount of amino acid during the Edman degradation cycle; the solid line denotes identity to the reference sequence at the top. Tryptophan at positions 38, 148, and 186 are inferred by the cleavage method.
FIG. 3
Amino acid sequences of the V region of the light chain of anti-6B antibodies expressing the κ light chain. Symbols are as in Fig. 2.
FIG. 4
Amino acid sequences of the V region of the heavy chain of anti-6B antibodies. Symbols are as in Fig. 2.
FIG. 5
cDNA sequences of VH (A) and VL (B) regions of Dob1. The first lines denote the VH and VL domains as assigned by Kabat et al. (17). The third lines denote the reference DNA sequences for the heavy and light chains, which were based on the sequences of VH gene 3-15 (DP-38) (GenBank accession no. Z12338), JH4 gene (Z14191), IgG2 gene (J00230), VL gene 2a2 (Z73664), and Jλ1 and Cλ1 genes (X51755). The second lines denote amino acids translated from the reference sequences. The fourth and fifth lines, respectively, denote cDNA sequences of Dob1 VH and VL regions and their amino acid translations. The fifth lines show only the translated amino acids of Dob1 cDNAs that are different from those of the reference sequences.
FIG. 5
cDNA sequences of VH (A) and VL (B) regions of Dob1. The first lines denote the VH and VL domains as assigned by Kabat et al. (17). The third lines denote the reference DNA sequences for the heavy and light chains, which were based on the sequences of VH gene 3-15 (DP-38) (GenBank accession no. Z12338), JH4 gene (Z14191), IgG2 gene (J00230), VL gene 2a2 (Z73664), and Jλ1 and Cλ1 genes (X51755). The second lines denote amino acids translated from the reference sequences. The fourth and fifth lines, respectively, denote cDNA sequences of Dob1 VH and VL regions and their amino acid translations. The fifth lines show only the translated amino acids of Dob1 cDNAs that are different from those of the reference sequences.
Similar articles
- Recurrent variable region gene usage and somatic mutation in the human antibody response to the capsular polysaccharide of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 23F.
Zhou J, Lottenbach KR, Barenkamp SJ, Lucas AH, Reason DC. Zhou J, et al. Infect Immun. 2002 Aug;70(8):4083-91. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4083-4091.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12117915 Free PMC article. - Somatic hypermutation and diverse immunoglobulin gene usage in the human antibody response to the capsular polysaccharide of Streptococcus pneumoniae Type 6B.
Zhou J, Lottenbach KR, Barenkamp SJ, Reason DC. Zhou J, et al. Infect Immun. 2004 Jun;72(6):3505-14. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.6.3505-3514.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15155658 Free PMC article. - The repertoire of human antibody to the Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide.
Insel RA, Adderson EE, Carroll WL. Insel RA, et al. Int Rev Immunol. 1992;9(1):25-43. doi: 10.3109/08830189209061781. Int Rev Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1484268 Review. - Characterization of the human IgG antibody VL repertoire to Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide.
Scott MG, Nahm MH. Scott MG, et al. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165 Suppl 1:S53-6. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165-supplement_1-s53. J Infect Dis. 1992. PMID: 1375255 Review.
Cited by
- Rapid multiplex assay for serotyping pneumococci with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies.
Yu J, Lin J, Benjamin WH Jr, Waites KB, Lee CH, Nahm MH. Yu J, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Jan;43(1):156-62. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.1.156-162.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15634965 Free PMC article. - A latex bead-based flow cytometric immunoassay capable of simultaneous typing of multiple pneumococcal serotypes (Multibead assay).
Park MK, Briles DE, Nahm MH. Park MK, et al. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2000 May;7(3):486-9. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.7.3.486-489.2000. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10799465 Free PMC article. - Germline V-genes sculpt the binding site of a family of antibodies neutralizing human cytomegalovirus.
Thomson CA, Bryson S, McLean GR, Creagh AL, Pai EF, Schrader JW. Thomson CA, et al. EMBO J. 2008 Oct 8;27(19):2592-602. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.179. Epub 2008 Sep 4. EMBO J. 2008. PMID: 18772881 Free PMC article. - Correlation of molecular characteristics, isotype, and in vitro functional activity of human antipneumococcal monoclonal antibodies.
Baxendale HE, Goldblatt D. Baxendale HE, et al. Infect Immun. 2006 Feb;74(2):1025-31. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.2.1025-1031.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16428749 Free PMC article. - VH3 gene usage in neutralizing human antibodies specific for the Entamoeba histolytica Gal/GalNAc lectin heavy subunit.
Tachibana H, Watanabe K, Cheng XJ, Tsukamoto H, Kaneda Y, Takeuchi T, Ihara S, Petri WA Jr. Tachibana H, et al. Infect Immun. 2003 Aug;71(8):4313-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.8.4313-4319.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12874307 Free PMC article.
References
- Adderson E E, Shackelford P G, Quinn A, Wilson P M, Cunningham M W, Insel R A, Carroll W L. Restricted immunoglobulin VH usage and VDJ combinations in the human response to Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide. Nucleotide sequences of monospecific anti-Haemophilus antibodies and polyspecific antibodies cross-reacting with self antigens. J Clin Investig. 1993;91:2734–2743. - PMC - PubMed
- Billadello J J, Roman D G, Grace A M, Sobel B E, Strauss A W. The nature of post-translational formation of MM creatine kinase isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:14988–14992. - PubMed
- Brauer A W, Oman C L, Margolies M N. Use of o-phthalaldehyde to reduce background during automated Edman degradation. Anal Biochem. 1984;137:134–142. - PubMed
- Breiman R F, Butler J C, Tenover F C, Elliott J A, Facklam R R. Emergence of drug-resistant pneumococcal infections in the United States. JAMA. 1994;271:1831–1835. - PubMed
- Carroll W L, Thielemans K, Dilley J, Levy R. Mouse X human heterohybridomas as fusion partners with human B cell tumors. J Immunol Methods. 1986;89:61–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01AI45248/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-31473/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI031473/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA010056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI 45248/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA10056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI031473/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous