Cell surface-associated lipoteichoic acid acts as an adhesion factor for attachment of Lactobacillus johnsonii La1 to human enterocyte-like Caco-2 cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Cell surface-associated lipoteichoic acid acts as an adhesion factor for attachment of Lactobacillus johnsonii La1 to human enterocyte-like Caco-2 cells
D Granato et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999 Mar.
Abstract
The influence of pH on the adhesion of two Lactobacillus strains to Caco-2 human intestinal cells was investigated. One strain, Lactobacillus johnsonii La1, was adherent at any pH between 4 and 7. The other one, L. acidophilus La10, did not attach to this cell line under the same experimental conditions. On the basis of these results, we used the monoclonal antibody technique as a tool to determine differences on the surface of these bacteria and to identify a factor for adhesion. Mice were immunized with live La1, and the hybridomas produced by fusion of spleen cells with ONS1 cells were screened for the production of antibodies specific for L. johnsonii La1. A set of these monoclonal antibodies was directed against a nonproteinaceous component of the L. johnsonii La1 surface. It was identified as lipoteichoic acid (LTA). This molecule was isolated, chemically characterized, and tested in adhesion experiments in the same system. The adhesion of L. johnsonii La1 to Caco-2 cells was inhibited in a concentration-dependent way by purified LTA as well as by L. johnsonii La1 culture supernatant that contained LTA. These results showed that the mechanism of adhesion of L. johnsonii La1 to human Caco-2 cells involves LTA.
Figures
FIG. 1
Immunogold staining of thin sections. (a) L. johnsonii La1 treated with monoclonal antibodies from the 113D2b3 clone supernatant. (b) L. acidophilus La10 incubated with the same antibodies. (c and e) L. johnsonii Lj1 incubated with the 113D2b3 clone supernatant before embedding. (d) L. johnsonii La1 incubated with hybridoma culture medium.
FIG. 1
Immunogold staining of thin sections. (a) L. johnsonii La1 treated with monoclonal antibodies from the 113D2b3 clone supernatant. (b) L. acidophilus La10 incubated with the same antibodies. (c and e) L. johnsonii Lj1 incubated with the 113D2b3 clone supernatant before embedding. (d) L. johnsonii La1 incubated with hybridoma culture medium.
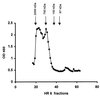
FIG. 2
Detection of antigenic activity of L. johnsonii La1 Triton X-100 extract by chromatography on Superose HR 6. Molecular mass markers: 2,000 kDa, fraction 20; 750 kDa, fraction 30; 150 kDa, fraction 38; 67 kDa, fraction 43. OD 450, optical density at 450 nm.
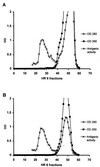
FIG. 3
Detection of antigenic activity of the aqueous fraction of delipidated L. johnsonii La1 after phenol extraction and nucleic acid digestion (A) or La1 culture supernatant (B) by chromatography on Superose HR 6. OD, optical density (numbers with OD are nanometers).
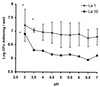
FIG. 4
Influence of pH on the adhesion of L. johnsonii La1 and L. acidophilus La10 to Caco-2 cells. Results are the mean ± standard deviations for five experiments done in triplicate. The asterisk indicates a P value of <0.05 when data were compared to pH 7 data for each strain by a t test. For La10, standard deviations were always <0.0437.
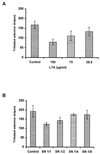
FIG. 5
Inhibition of La1 adhesion to Caco-2 cells at pH 5. Caco-2 cells were preincubated with increasing amounts of purified LTA (A) or La1 culture supernatant (B). Controls were acetate buffer (pH 5) (A) or MRS broth acidified with lactic acid (B). Each assay was done in triplicate. Error bars are standard deviations.
Similar articles
- Improvement of the human intestinal flora by ingestion of the probiotic strain Lactobacillus johnsonii La1.
Yamano T, Iino H, Takada M, Blum S, Rochat F, Fukushima Y. Yamano T, et al. Br J Nutr. 2006 Feb;95(2):303-12. doi: 10.1079/bjn20051507. Br J Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16469146 Clinical Trial. - Cell surface-associated elongation factor Tu mediates the attachment of Lactobacillus johnsonii NCC533 (La1) to human intestinal cells and mucins.
Granato D, Bergonzelli GE, Pridmore RD, Marvin L, Rouvet M, Corthésy-Theulaz IE. Granato D, et al. Infect Immun. 2004 Apr;72(4):2160-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.4.2160-2169.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15039339 Free PMC article. - Biological properties of staphylococcal lipoteichoic acid and related macromolecules.
Ohshima Y, Ko HL, Beuth J, Roszkowski K, Roszkowski W. Ohshima Y, et al. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990 Dec;274(3):359-65. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80693-6. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990. PMID: 2090151 Review. - Targeting aberrant colon cancer-specific DNA methylation with lipoteichoic acid-deficient Lactobacillus acidophilus.
Lightfoot YL, Yang T, Sahay B, Mohamadzadeh M. Lightfoot YL, et al. Gut Microbes. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):84-8. doi: 10.4161/gmic.22822. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Gut Microbes. 2013. PMID: 23137966 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A Review of the Mechanisms of Bacterial Colonization of the Mammal Gut.
Lin Q, Lin S, Fan Z, Liu J, Ye D, Guo P. Lin Q, et al. Microorganisms. 2024 May 19;12(5):1026. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12051026. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38792855 Free PMC article. Review. - The regulation of simulated artificial oro-gastrointestinal transit stress on the adhesion of Lactobacillus plantarum S7.
Chen D, Chen C, Guo C, Zhang H, Liang Y, Cheng Y, Qu H, Wa Y, Zhang C, Guan C, Qian J, Gu R. Chen D, et al. Microb Cell Fact. 2023 Sep 2;22(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12934-023-02174-3. Microb Cell Fact. 2023. PMID: 37660047 Free PMC article. - Health-Promoting Nature of Lactococcus lactis IBB109 and Lactococcus lactis IBB417 Strains Exhibiting Proliferation Inhibition and Stimulation of Interleukin-18 Expression in Colorectal Cancer Cells.
Sałański P, Kowalczyk M, Bardowski JK, Szczepankowska AK. Sałański P, et al. Front Microbiol. 2022 May 25;13:822912. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.822912. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35694291 Free PMC article. - Encapsulation of Lactic Acid Bacteria by Lyophilisation with Its Effects on Viability and Adhesion Properties.
Patil A, Munot N, Patwekar M, Patwekar F, Ahmad I, Alraey Y, Alghamdi S, Kabrah A, Dablool AS, Islam F. Patil A, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 27;2022:4651194. doi: 10.1155/2022/4651194. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35668781 Free PMC article. Retracted. - Synbiotics: a New Route of Self-production and Applications to Human and Animal Health.
Nguyen TT, Nguyen PT, Pham MN, Razafindralambo H, Hoang QK, Nguyen HT. Nguyen TT, et al. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2022 Oct;14(5):980-993. doi: 10.1007/s12602-022-09960-2. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2022. PMID: 35650337 Review.
References
- Alander M, Korpela R, Saxelin M, Vilpponen-Salmela T, Mattila-Sandholm T, von Wright A. Recovery of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG from human colonic biopsies. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1997;24:361–364. - PubMed
- Bahl H, Scholz H, Bayan N, Chami M, Leblon G, Gulik-Krzywicki T, Schechter E, Fouet A, Mesnage S, Tosi-Couture E, Gounon P, Mock M, Conway de Macario E, de Macario A J L, Fernandez-Herrero L A, Olabarria G, Berenguer J, Blaser M J, Kuen B, Lubitz W, Sara M, Pouwels P H, Kolen C P A M, Boot H J, Lechleitner S, Resch S. Molecular biology of S-layers. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1997;20:47–98. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources