The head inducer Cerberus is a multifunctional antagonist of Nodal, BMP and Wnt signals - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 1999 Feb 25;397(6721):707-10.
doi: 10.1038/17820.
Affiliations
- PMID: 10067895
- PMCID: PMC2323273
- DOI: 10.1038/17820
The head inducer Cerberus is a multifunctional antagonist of Nodal, BMP and Wnt signals
S Piccolo et al. Nature. 1999.
Abstract
Embryological and genetic evidence indicates that the vertebrate head is induced by a different set of signals from those that organize trunk-tail development. The gene cerberus encodes a secreted protein that is expressed in anterior endoderm and has the unique property of inducing ectopic heads in the absence of trunk structures. Here we show that the cerberus protein functions as a multivalent growth-factor antagonist in the extracellular space: it binds to Nodal, BMP and Wnt proteins via independent sites. The expression of cerberus during gastrulation is activated by earlier nodal-related signals in endoderm and by Spemann-organizer factors that repress signalling by BMP and Wnt. In order for the head territory to form, we propose that signals involved in trunk development, such as those involving BMP, Wnt and Nodal proteins, must be inhibited in rostral regions.
Figures
Figure 1
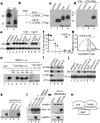
Cerberus protein binds to Xnr-1, BMP-4 and Xwnt-8. a, Cer–Flag secreted by Xenopus animal cap (AC) and cultured 293T cells. b, The two Cer protein products. c, HA-tagged activin, Vg1 and Xnr-1 secreted by Xenopus oocytes. d, Xnr-1 is bound specifically by Cer-S–Flag (lanes 2−4) or Cer-L–Flag (not shown). e, Cer binding inactivates Xnr-1 signalling. Animal cap explants were treated with oocyte control medium, activin (15 pM), Vg1 (0.3 nM) or Xnr-1 (1 nM) proteins, either alone (lanes 2−5) or together with 5 nM Cer-S (lanes 6−8) or Cer-L (lanes 9−11). f, Cer inhibits Xnr-1 with high affinity; 2 nM Xnr-1 was incubated with increasing concentrations of Cer-S (closed circles) or Cer-L (open circles). g, Cer-L–Flag binds BMP-4 with a _K_D of 0.6 nM. h, Binding of Cer-L–Flag to BMP-4 is competed for by BMP-2 but not by TGF-β-1, EGF or PDGF; Cer-S does not bind BMP-4. i, Cer-L (10 nM), but not Cer-S (20 nM), is a direct neural inducer of animal cap cells sensitized by brief dissociation–re-aggregation (but not of intact caps). j, Cer inhibits Xwnt8 but not β-catenin mRNA; induction of Siamois, a target of Wnt signalling, was assayed at stage 10+. k, Lanes 1, 2, soluble Xwnt-8–HA protein is secreted by mRNA-injected oocytes. Lanes 3−5, binding of Xwnt-8-HA (5 nM) to Cer–Flag proteins (10 nM). l, m, The Xwnt-8–HA, Xnr-1–HA and BMP binding sites in Cer-L are independent. Cer-L–Flag (2 nM) was bound to Xnr-1 (1 nM) or Xwnt-8 (2 nM) and competed with BMP-4 (10 nM), BMP-2 (27 nM) or Xnr-1 (8 nM). n, Multiple ligand-binding sites on Cerberus.
Figure 2
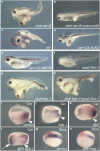
Phenotypic effects of cer-S mRNA, an inhibitor of nodal-related signals. Embryos were injected radially at the 4-cell stage. a–d, In situ hybridization for Xbra (a,b) and Xwnt-8 (c,d) in wild type and in embryos injected with 120 pg of cer-S mRNA per blastomere. e, Anterior endoderm formation requires early nodal-related signals in injected embryos: endogenous cerberus transcripts are inhibited by cer-S mRNA (200 pg total) and induced by Xnr-1 mRNA (50 pg). f, Dual function for Xnr-1; Xnr-1 mRNA (6,12, 24 pg), but not pCS2–Xnr-1 DNA (20, 40, 80 pg), can induce cer expression in animal caps. g–n, Head induction by simultaneous repression of BMP and nodal signals in explants of ventral marginal zone (VMZ). g, k, Wild-type VMZs consisting histologically of endoderm (en) and blood (bl). h, cer-S mRNA (150 pg); i, tBR mRNA (600 pg); j, m, co-injection of tBR mRNA (600 pg) and cer-S mRNA (150 pg) generates head-like structures (76%, n = 17), similar to those produced by cerberus mRNA (l, 50%, n = 10), consisting only of anterior structures with cement gland (CG), brain (br) and eye (ey) containing a lens (le). n, Blocking BMP and Nodal signalling by tBR (600 pg) and tALK4 (1.5 ng) RNAs is sufficient to induce head-like structures.
Figure 3
Head induction requires the triple inhibition of nodal-related, Wnt and BMP signals. Embryos were injected into one ventral blastomere with the indicated mRNAs or DNAs at the 4-cell stage. a, Ectopic head induction by a combination of chd (50 pg) and cer-S (200 pg) mRNA (58%, n = 115). b, pCSKA–Xwnt-8 DNA (50 pg) antagonizes head induction by chd/cer-S (1% ectopic heads, n = 111). c, Ectopic heads formed by injection of 150 pg cer mRNA (57%, n = 66) are abolished in d and e by co-injection of 1 ng CA–ALK4 mRNA (0%, n = 36) or 400 pg of CA–BMPR mRNA (0%, n = 21). f, Dorsal injection of pCS2-Xnr-1 (32 pg) causes head reduction (53%, n = 60). g, Co-injection of chd (25 pg) and Frzb-1 (200 pg) mRNAs mediates formation of a complete secondary axis with cyclopic head (49%, n = 175). h, Co-injection of 16 pg of pCS2–Xnr-1 DNA inhibits head induction by chd/Frzb-1 (5%, n = 133). i–n, Simultaneous repression of BMP and Wnt signalling leads to ectopic activation of cer in endoderm and concomitant downregulation of Xbra in mesoderm. Embryos were cut sagittally in two halves after fixation and before whole-mount hybridization. Arrowhead indicates the dorsal blastopore lip. Frzb-1 mRNA (300 pg) synergizes with tBR mRNA (800 pg) in upregulating cer in the ventral endoderm (arrow). Note in n the inhibition of Xbra in the injected area, correlating with the activation of cer (an anti-Nodal agent) observed in l.
Figure 4
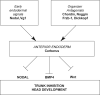
Model of the formation and function of anterior endoderm in Xenopus head development.
Similar articles
- Head induction by simultaneous repression of Bmp and Wnt signalling in Xenopus.
Glinka A, Wu W, Onichtchouk D, Blumenstock C, Niehrs C. Glinka A, et al. Nature. 1997 Oct 2;389(6650):517-9. doi: 10.1038/39092. Nature. 1997. PMID: 9333244 - [The head inducer Cerberus in a multivalent extracellular inhibitor].
Agius PE, Piccolo S, De Robertis EM. Agius PE, et al. J Soc Biol. 1999;193(4-5):347-54. J Soc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10689616 Free PMC article. - Endogenous Cerberus activity is required for anterior head specification in Xenopus.
Silva AC, Filipe M, Kuerner KM, Steinbeisser H, Belo JA. Silva AC, et al. Development. 2003 Oct;130(20):4943-53. doi: 10.1242/dev.00705. Development. 2003. PMID: 12952900 - Dickkopf1 and the Spemann-Mangold head organizer.
Niehrs C, Kazanskaya O, Wu W, Glinka A. Niehrs C, et al. Int J Dev Biol. 2001;45(1):237-40. Int J Dev Biol. 2001. PMID: 11291852 Review. - The Spemann organizer and embryonic head induction.
Niehrs C. Niehrs C. EMBO J. 2001 Feb 15;20(4):631-7. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.4.631. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11179208 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- SFRP2 expression in rabbit myogenic progenitor cells and in adult skeletal muscles.
Levin JM, El Andalousi RA, Dainat J, Reyne Y, Bacou F. Levin JM, et al. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2001;22(4):361-9. doi: 10.1023/a:1013129209062. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2001. PMID: 11808776 - Opposing Nodal/Vg1 and BMP signals mediate axial patterning in embryos of the basal chordate amphioxus.
Onai T, Yu JK, Blitz IL, Cho KW, Holland LZ. Onai T, et al. Dev Biol. 2010 Aug 1;344(1):377-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.05.016. Epub 2010 May 19. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20488174 Free PMC article. - SNW1 is a critical regulator of spatial BMP activity, neural plate border formation, and neural crest specification in vertebrate embryos.
Wu MY, Ramel MC, Howell M, Hill CS. Wu MY, et al. PLoS Biol. 2011 Feb 15;9(2):e1000593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000593. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21358802 Free PMC article. - Apcdd1 is a dual BMP/Wnt inhibitor in the developing nervous system and skin.
Vonica A, Bhat N, Phan K, Guo J, Iancu L, Weber JA, Karger A, Cain JW, Wang ECE, DeStefano GM, O'Donnell-Luria AH, Christiano AM, Riley B, Butler SJ, Luria V. Vonica A, et al. Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 1;464(1):71-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.03.015. Epub 2020 Apr 19. Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32320685 Free PMC article. - Bone morphogenetic protein 15 (BMP15) acts as a BMP and Wnt inhibitor during early embryogenesis.
Di Pasquale E, Brivanlou AH. Di Pasquale E, et al. J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 18;284(38):26127-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.036608. Epub 2009 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19553676 Free PMC article.
References
- Bouwmeester T, Kim SH, Sasai Y, Lu B, De Robertis EM. Cerberus is a head-inducing secreted factor expressed in the anterior endoderm of Spemann's organizer. Nature. 1996;382:595–601. - PubMed
- Thomas P, Beddington R. Anterior primitive endoderm may be responsible for patterning the anterior neural plate in the mouse embryo. Curr. Biol. 1996;6:1487–1496. - PubMed
- Shawlot W, Behringer RR. Requirement for Lim1 in head-organizer function. Nature. 1995;374:425–430. - PubMed
- Glinka A, Wu W, Onichtchouk D, Blumenstock C, Niehrs C. Head induction by simultaneous repression of Bmp and Wnt signalling in Xenopus. Nature. 1997;389:517–519. - PubMed
- Glinka A, et al. Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family of secreted proteins and functions in head induction. Nature. 1998;391:357–362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials