Secretion imbalance between tumour necrosis factor and its inhibitor in inflammatory bowel disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Secretion imbalance between tumour necrosis factor and its inhibitor in inflammatory bowel disease
M Noguchi et al. Gut. 1998 Aug.
Abstract
Background: Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) alpha and TNF-beta are soluble ligands binding to TNF receptors with similar activities; soluble TNF receptors neutralise TNF activity by acting as inhibitors. Little is known about the cytokine/soluble receptor role in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Aims: To test the hypothesis that an imbalance in secretion between TNF and TNF inhibitors plays a role in gut inflammation in patients with IBD.
Methods: The secretion of TNF-alpha, TNF-beta, and soluble TNF receptors was compared in the culture supernatants of colonic biopsy specimens and isolated lamina propria mononuclear cells from patients with active colonic IBD.
Results: Spontaneous secretion of TNF-alpha in involved IBD mucosa was higher than in normal control and self limited colitis mucosa. Secretion of TNF-beta was higher in patients with Crohn's disease than in those with ulcerative colitis. Soluble TNF receptor in IBD mucosa inhibited TNF activity. Type 2 soluble receptor release from IBD mucosa was increased in active inflammation; release from lamina propria cells was not increased. Mucosal TNF-alpha production correlated with severity of disease.
Conclusions: Results showed enhanced secretion of TNF-alpha but failure to release enhanced amounts of soluble TNF receptor in lamina propria mononuclear cells of patients with IBD. An imbalance in secretion between TNF and TNF inhibitor may be implicated in the pathogenesis of IBD.
Figures
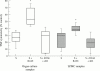
Figure 1
Secretion ratio of TNF-α:sTNF-R2 in organ culture. CD, Crohn's disease; UC, ulcerative colitis.
Figure 2
Secretion ratio of median TNF-α:median sTNF-R2 in LPMCs cultured with LPS. CD, Crohn's disease; UC, ulcerative colitis.
Figure 3
Inhibitory activity of TNF by soluble TNF receptor in supernatant (S) of organ culture and LPMC culture, reversible cytotoxicity by monoclonal antibody to p75sTNF-R2 (R2Ab), and inhibition by recombinant human soluble TNF-R2 (sR2). Culture samples from five patients with IBD were examined in triplicate cultures. Results expressed as median (IQR). *p<0.05 versus S group, R2Ab plus sR2 group.
References
- Gastroenterology. 1994 Jun;106(6):1455-66 - PubMed
- J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):966-74 - PubMed
- Transfus Med. 1994 Dec;4(4):269-72 - PubMed
- Cell Immunol. 1995 Apr 1;161(2):166-72 - PubMed
- Immunol Today. 1995 Mar;16(3):135-40 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical