The role of alphav integrins during angiogenesis: insights into potential mechanisms of action and clinical development - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 1999 May;103(9):1227-30.
doi: 10.1172/JCI6869.
Affiliations
- PMID: 10225964
- PMCID: PMC408360
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI6869
Review
The role of alphav integrins during angiogenesis: insights into potential mechanisms of action and clinical development
B P Eliceiri et al. J Clin Invest. 1999 May.
No abstract available
Figures
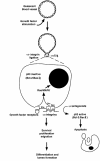
Figure 1
Hypothetical model for the role of αv integrins in angiogenesis. Angiogenic stimulus by growth factors induces expression of αvβ3 and causes cells to invade the surrounding ECM and enter the cell cycle. When ligation of αv integrins is blocked, proliferating vascular cells undergo apoptosis, accompanied by an increase in p53 activity. Angiogenic growth factors induce the activation of Ras/MAP kinase in vascular cells and lead to cell proliferation, differentiation, and migration.
Similar articles
- The role of alphav integrins during angiogenesis.
Eliceiri BP, Cheresh DA. Eliceiri BP, et al. Mol Med. 1998 Dec;4(12):741-50. Mol Med. 1998. PMID: 9990860 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available. - Functional overlap and cooperativity among alphav and beta1 integrin subfamilies during skin angiogenesis.
Perruzzi CA, de Fougerolles AR, Koteliansky VE, Whelan MC, Westlin WF, Senger DR. Perruzzi CA, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2003 Jun;120(6):1100-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12236.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 12787141 - Extensive vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and organogenesis precede lethality in mice lacking all alpha v integrins.
Bader BL, Rayburn H, Crowley D, Hynes RO. Bader BL, et al. Cell. 1998 Nov 13;95(4):507-19. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81618-9. Cell. 1998. PMID: 9827803 - Adhesion events in angiogenesis.
Eliceiri BP, Cheresh DA. Eliceiri BP, et al. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;13(5):563-8. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00252-0. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11544024 Review. - αV integrins in angiogenesis and cancer.
Weis SM, Cheresh DA. Weis SM, et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2011 Sep;1(1):a006478. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006478. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2011. PMID: 22229119 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- miR-758-3p/ILK signaling modulated angiogenesis by regulating VEGFA in wound healing.
Wang R, Jia J, Zhou L, Zhu X, Tang Z, Shen H, Qiao Y, Nan G, Yang Z, Ma W. Wang R, et al. Int J Med Sci. 2024 Jan 1;21(1):175-187. doi: 10.7150/ijms.86733. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38164357 Free PMC article. - Targeting receptor-mediated endocytotic pathways with nanoparticles: rationale and advances.
Xu S, Olenyuk BZ, Okamoto CT, Hamm-Alvarez SF. Xu S, et al. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Jan;65(1):121-38. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.041. Epub 2012 Sep 29. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 23026636 Free PMC article. Review. - αVβ3 integrin regulates macrophage inflammatory responses via PI3 kinase/Akt-dependent NF-κB activation.
Antonov AS, Antonova GN, Munn DH, Mivechi N, Lucas R, Catravas JD, Verin AD. Antonov AS, et al. J Cell Physiol. 2011 Feb;226(2):469-76. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22356. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 20672329 Free PMC article. - Crystal structure of the extracellular segment of integrin alpha Vbeta3.
Xiong JP, Stehle T, Diefenbach B, Zhang R, Dunker R, Scott DL, Joachimiak A, Goodman SL, Arnaout MA. Xiong JP, et al. Science. 2001 Oct 12;294(5541):339-45. doi: 10.1126/science.1064535. Epub 2001 Sep 6. Science. 2001. PMID: 11546839 Free PMC article. - Angiogenesis blockade as a new therapeutic approach to experimental colitis.
Danese S, Sans M, Spencer DM, Beck I, Doñate F, Plunkett ML, de la Motte C, Redline R, Shaw DE, Levine AD, Mazar AP, Fiocchi C. Danese S, et al. Gut. 2007 Jun;56(6):855-62. doi: 10.1136/gut.2006.114314. Epub 2006 Dec 14. Gut. 2007. PMID: 17170016 Free PMC article.
References
- Aplin AE, Howe A, Alahari SK, Juliano RL. Signal transduction and signal modulation by cell adhesion receptors: the role of integrins, cadherins, immunoglobulin-cell adhesion molecules, and selectins. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50:197–263. - PubMed
- Enenstein J, Kramer RH. Confocal microscopic analysis of integrin expression on the microvasculature and its sprouts in the neonatal foreskin. J Invest Dermatol. 1994;103:381–386. - PubMed
- Brooks PC, Clark RA, Cheresh DA. Requirement of vascular integrin αvβ3 for angiogenesis. Science. 1994;264:569–571. - PubMed
- Brooks PC, et al. Integrin αvβ3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell. 1994;79:1157–1164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 CA050286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-50286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA050286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA078045/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA045726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL009435/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-45726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32 HL-09435/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources