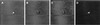Vibro-acoustography: an imaging modality based on ultrasound-stimulated acoustic emission - PubMed (original) (raw)
Vibro-acoustography: an imaging modality based on ultrasound-stimulated acoustic emission
M Fatemi et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999.
Abstract
We describe theoretical principles of an imaging modality that uses the acoustic response of an object to a highly localized dynamic radiation force of an ultrasound field. In this method, named ultrasound-stimulated vibro-acoustography (USVA), ultrasound is used to exert a low-frequency (in kHz range) force on the object. In response, a portion of the object vibrates sinusoidally in a pattern determined by its viscoelastic properties. The acoustic emission field resulting from object vibration is detected and used to form an image that represents both the ultrasonic and low-frequency (kHz range) mechanical characteristics of the object. We report the relation between the emitted acoustic field and the incident ultrasonic pressure field in terms of object parameters. Also, we present the point-spread function of the imaging system. The experimental images in this report have a resolution of about 700 microm, high contrast, and high signal-to-noise ratio. USVA is sensitive enough to detect object motions on the order of nanometers. Possible applications include medical imaging and material evaluation.
Figures
Figure 1
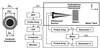
Principle of ultrasound-stimulated vibro-acoustography.
Figure 2
Ultrasound-stimulated vibro-acoustography system. The confocal ultrasound annular array transducer with two elements is shown on the left.
Figure 3
Acoustic-emission field intensity vs. the combined ultrasound intensity.
Figure 4
USVA images of a 380-μm glass bead: (A) in-phase, (B) quadrature, (C) phase, and (D) magnitude. The phase in C ranges from −π radians (black regions) to +π radians (white regions), and was normalized to be zero at the center of the glass bead. (Modified with permission from ref. , copyright 1998, American Association for the Advancement of Science.)
Figure 5
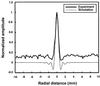
The theoretical PSF profile of the USVA system according to Eq. 24 and the glass-bead in-phase image profile (Fig. 4_A_) obtained from the experiment.
Similar articles
- Vibro-magnetometry: theoretical aspects and simulations.
Carneiro AO, Baffa O, Silva GT, Fatemi M. Carneiro AO, et al. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2009 May;56(5):1065-73. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2009.1140. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2009. PMID: 19473925 - Multifrequency vibro-acoustography.
Urban MW, Silva GT, Fatemi M, Greenleaf JF. Urban MW, et al. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2006 Oct;25(10):1284-95. doi: 10.1109/tmi.2006.882142. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2006. PMID: 17024832 - A Review of Vibro-acoustography and its Applications in Medicine.
Urban MW, Alizad A, Aquino W, Greenleaf JF, Fatemi M. Urban MW, et al. Curr Med Imaging Rev. 2011 Nov 1;7(4):350-359. doi: 10.2174/157340511798038648. Curr Med Imaging Rev. 2011. PMID: 22423235 Free PMC article. - Critical issues in breast imaging by vibro-acoustography.
Alizad A, Whaley DH, Greenleaf JF, Fatemi M. Alizad A, et al. Ultrasonics. 2006 Dec 22;44 Suppl 1:e217-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2006.06.021. Epub 2006 Jun 30. Ultrasonics. 2006. PMID: 16843513 Review. - Potential applications of vibro-acoustography in breast imaging.
Alizad A, Whaley DH, Greenleaf JF, Fatemi M. Alizad A, et al. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2005 Apr;4(2):151-8. doi: 10.1177/153303460500400204. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2005. PMID: 15773784 Review.
Cited by
- Pulsed Vibro-Acoustic Analysis Technique for Monitoring Bone Health in Preterm Infants: A Pilot Study.
Chaudhary PK, Gu J, Rosen DP, Larson NB, Brumbaugh JE, Fatemi M, Alizad A. Chaudhary PK, et al. IEEE Access. 2024;12:106707-106719. doi: 10.1109/access.2024.3437375. Epub 2024 Aug 2. IEEE Access. 2024. PMID: 39148928 - On the inverse problem of vibro-acoustography.
Kaltenbacher B. Kaltenbacher B. Meccanica. 2023;58(6):1061-1072. doi: 10.1007/s11012-022-01485-w. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Meccanica. 2023. PMID: 37351186 Free PMC article. - Recent advances in optical elastography and emerging opportunities in the basic sciences and translational medicine [Invited].
Leartprapun N, Adie SG. Leartprapun N, et al. Biomed Opt Express. 2022 Dec 16;14(1):208-248. doi: 10.1364/BOE.468932. eCollection 2023 Jan 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2022. PMID: 36698669 Free PMC article. Review. - An Efficient and Multi-Focal Focused Ultrasound Technique for Harmonic Motion Imaging.
Saharkhiz N, Kamimura HAS, Konofagou EE. Saharkhiz N, et al. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2023 Apr;70(4):1150-1161. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2022.3211465. Epub 2023 Mar 21. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 36191094 Free PMC article. - Imaging of Single Transducer-Harmonic Motion Imaging-Derived Displacements at Several Oscillation Frequencies Simultaneously.
Hossain MM, Konofagou EE. Hossain MM, et al. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2022 Nov;41(11):3099-3115. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2022.3178897. Epub 2022 Oct 27. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35635828 Free PMC article.
References
- Maynard J. Phys Today. 1996;49(1):26–31.
- O’Donnell M, Skovoroda A R, Shapo B M, Emelianov S Y. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Contr. 1994;41:314–325.
- Ophir J, Cespedes I, Ponnenkanti H, Yazdi Y, Li X. Ultrason Imaging. 1991;13:111–134. - PubMed
- Yamakoshi Y, Sato J, Sato T. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Contr. 1990;47:45–53. - PubMed
- Krouskop T A, Dougherty D R, Vinson F S. J Rehabil Res Dev. 1987;24:1–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources