p200 ARF-GEP1: a Golgi-localized guanine nucleotide exchange protein whose Sec7 domain is targeted by the drug brefeldin A - PubMed (original) (raw)
p200 ARF-GEP1: a Golgi-localized guanine nucleotide exchange protein whose Sec7 domain is targeted by the drug brefeldin A
S J Mansour et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999.
Abstract
The drug brefeldin A (BFA) disrupts protein traffic and Golgi morphology by blocking activation of ADP ribosylation factors (ARFs) through an unknown mechanism. Here, we investigated the cellular localization and BFA sensitivity of human p200 ARF-GEP1 (p200), a ubiquitously expressed guanine nucleotide exchange factor of the Sec7 domain family. Multiple tagged forms of the full-length polypeptide localized to tight ribbon-like perinuclear structures that overlapped with the Golgi marker mannosidase II and were distinct from the pattern observed with ERGIC53/58. Analysis of several truncated forms mapped the Golgi-localization signal to the N-terminal third of p200. BFA treatment of transiently or stably transfected cells resulted in the redistribution of Golgi markers and in loss of cell viability, thereby indicating that overproduction of p200 may not be sufficient to overcome the toxic effect. A 39-kDa fragment spanning the Sec7 domain catalyzed loading of guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate onto class I ARFs and displayed clear sensitivity to BFA. Kinetic analysis established that BFA did not compete with ARF for interaction with p200 but, rather, acted as an uncompetitive inhibitor that only targeted the p200-ARF complex with an inhibition constant of 7 microM. On the basis of these results, we propose that accumulation of an abortive p200-ARF complex in the presence of BFA likely leads to disruption of Golgi morphology. p200 mapped to chromosome 8q13, 3.56 centirays from WI-6151, and database searches revealed the presence of putative isoforms whose inhibition may account for the effects of BFA on various organelles.
Figures
Figure 1
p200 is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues. mRNA blots were probed with full-length p200 (Upper), were washed at high stringency, and then were visualized by autoradiography. The same blots were stripped and reprobed with actin (Lower). A minor, 7-kb transcript can be detected in the testes sample at lower exposure.
Figure 2
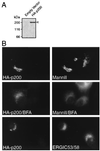
p200 associates with the Golgi apparatus. (A) Production of full-length HA-p200 in 293 HEK-EBNA cells. Detergent extract (60 μg) from stably transfected cells were analyzed by Western blotting to detect HA-tagged p200 (arrowhead). (B) Indirect immunofluorescence. BHK21 cells were transiently transfected with the construct encoding HA-tagged protein by using Lipofectamine and were processed for immunofluorescence by using antibodies against the HA epitope (12CA5) and either mannosidase II or ERGIC53/58, as indicated. Each horizontal pair of panels corresponds to a field of view seen with different filters. The distribution of HA-p200 and mannosidase II in cells exposed to 3.5 μM BFA for 10 min before fixation is shown in the middle panels.
Figure 3
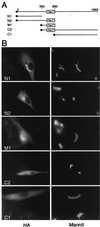
Localization signal maps to the N-terminal domain. (A) Schematic representation of HA-tagged truncations in reference to full-length protein. Numbers refer to the position of amino acids in the full-length polypeptide; the full circle symbolizes the HA tag. (B) Indirect immunofluorescence. BHK21 cells were transiently transfected with constructs encoding HA-tagged truncations by using Fugene 6 and were processed for immunofluorescence by using antibodies against the HA epitope (3F10) and mannosidase II. M1, in contrast to other truncations, was not excluded from the nucleus. Each horizontal pair of panels corresponds to a field of view seen with different filters. These results were reproduced in several independent transfections.
Figure 4
Guanine nucleotide exchange activity of fragment M1. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the region extending from the homology upstream of Sec7 box to the end of the Sec7 domain. *, identical residues on pairwise comparison between human p200 and either human GBF1 or yeast Sec7p. The Sec7 domain corresponds to the bottom half of the sequence. (B) Schematic representation of fragment M1 in reference to full-length protein. The ellipse at the left side symbolizes the N-terminal hexahistidine tag. (C) Partial purification of M1. Dialyzed sample (1 μg) was resolved by SDS/PAGE and was visualized with Coomassie staining. The arrowhead marks the 39-kDa M1 protein. (D) Exchange activity toward a mixture of bovine ARF1 and ARF3. Assays were performed in the presence of 1 μM ARF and 20 nM M1, as described in Materials and Methods. Open circles, no BFA; filled circles, 300 μM BFA. (E) BFA titration at three different ARF concentrations. The exchange rate after 8 min at the indicated BFA concentrations (0, 25, 50, 100, 150, 300, 600, and 900 μM) was measured as in D in the presence of 0.5 μM (▵), 1 μM (●), or 4 μM (□) ARF, with the exception that the concentration of M1 was reduced to 10 nM. Results are expressed as percent of value measured in absence of BFA for each ARF concentration. Similar IC50 values were obtained with 4-min reactions. (F) Dixon plots [1/v vs. (BFA)] of BFA titrations. The extent of exchange after 2 min at the indicated BFA concentrations (0, 25, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, and 300 μM) was measured in duplicate as in D. Results with three ARF concentrations are shown: 0.75 μM (■), 1 μM (●), and 1.5 μM (▴). This result was reproduced three times. (G) Determination of KI. IC50 values were estimated from Dixon plots of several independent measurements as described in Materials and Methods and were replotted as a function of the inverse ARF concentration.
Figure 5
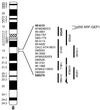
p200 maps to chromosome 8q13. Yeast artificial chromosomes (vertical bars) covering the 8q13 region were screened by PCR for the presence of p200. Only 925d9 scored positive.
Similar articles
- Brefeldin A inhibited activity of the sec7 domain of p200, a mammalian guanine nucleotide-exchange protein for ADP-ribosylation factors.
Morinaga N, Adamik R, Moss J, Vaughan M. Morinaga N, et al. J Biol Chem. 1999 Jun 18;274(25):17417-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.25.17417. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10364170 - Purification and cloning of a brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein for ADP-ribosylation factors.
Togawa A, Morinaga N, Ogasawara M, Moss J, Vaughan M. Togawa A, et al. J Biol Chem. 1999 Apr 30;274(18):12308-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.18.12308. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10212200 - Brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange activity of Sec7 domain from yeast Sec7 with yeast and mammalian ADP ribosylation factors.
Sata M, Donaldson JG, Moss J, Vaughan M. Sata M, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Apr 14;95(8):4204-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4204. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9539714 Free PMC article. - Activation of toxin ADP-ribosyltransferases by eukaryotic ADP-ribosylation factors.
Moss J, Vaughan M. Moss J, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 1999 Mar;193(1-2):153-7. Mol Cell Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10331652 Review. - Arf, Sec7 and Brefeldin A: a model towards the therapeutic inhibition of guanine nucleotide-exchange factors.
Zeghouf M, Guibert B, Zeeh JC, Cherfils J. Zeghouf M, et al. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Dec;33(Pt 6):1265-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0331265. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16246094 Review.
Cited by
- COPI budding within the Golgi stack.
Popoff V, Adolf F, Brügger B, Wieland F. Popoff V, et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Nov 1;3(11):a005231. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a005231. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 21844168 Free PMC article. Review. - The Sec7 N-terminal regulatory domains facilitate membrane-proximal activation of the Arf1 GTPase.
Richardson BC, Halaby SL, Gustafson MA, Fromme JC. Richardson BC, et al. Elife. 2016 Jan 14;5:e12411. doi: 10.7554/eLife.12411. Elife. 2016. PMID: 26765562 Free PMC article. - A novel Golgi membrane protein is a partner of the ARF exchange factors Gea1p and Gea2p.
Chantalat S, Courbeyrette R, Senic-Matuglia F, Jackson CL, Goud B, Peyroche A. Chantalat S, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Jun;14(6):2357-71. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-10-0693. Epub 2003 Mar 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12808035 Free PMC article. - Characterization of class I and II ADP-ribosylation factors (Arfs) in live cells: GDP-bound class II Arfs associate with the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment independently of GBF1.
Chun J, Shapovalova Z, Dejgaard SY, Presley JF, Melançon P. Chun J, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Aug;19(8):3488-500. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-04-0373. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18524849 Free PMC article. - Highly conserved motifs within the large Sec7 ARF guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1 target it to the Golgi and are critical for GBF1 activity.
Pocognoni CA, Viktorova EG, Wright J, Meissner JM, Sager G, Lee E, Belov GA, Sztul E. Pocognoni CA, et al. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018 Jun 1;314(6):C675-C689. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00221.2017. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29443553 Free PMC article.
References
- Orci L, Tagaya M, Amherdt M, Perrelet A, Donaldson J G, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Klausner R D, Rothman J E. Cell. 1991;64:1183–1195. - PubMed
- Donaldson J G, Finazzi D, Klausner R D. Nature (London) 1992;360:350–352. - PubMed
- Helms J B, Rothman J E. Nature (London) 1992;360:352–354. - PubMed
- Randazzo P A, Yang Y C, Rulka C, Kahn R A. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:9555–9563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases