Myeloid DAP12-associating lectin (MDL)-1 is a cell surface receptor involved in the activation of myeloid cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Myeloid DAP12-associating lectin (MDL)-1 is a cell surface receptor involved in the activation of myeloid cells
A B Bakker et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999.
Abstract
Crosslinking of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)-containing receptor complexes on a variety of cells leads to their activation through the sequential triggering of protein tyrosine kinases. Recently, DAP12 has been identified as an ITAM-bearing signaling molecule that is noncovalently associated with activating isoforms of MHC class I receptors on natural killer cells. In addition to natural killer cells, DAP12 is expressed in peripheral blood monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, suggesting association with other receptors present in these cell types. In the present study, we report the molecular cloning of the myeloid DAP12-associating lectin-1 (MDL-1), a DAP12-associating membrane receptor expressed exclusively in monocytes and macrophages. MDL-1 is a type II transmembrane protein belonging to the C type lectin superfamily and contains a charged residue in the transmembrane region that enables it to pair with DAP12. Crosslinking of MDL-1/DAP12 complexes in J774 mouse macrophage cells resulted in calcium mobilization. These findings suggest that signaling via MDL-1/DAP12 complexes may constitute a significant activation pathway in myeloid cells.
Figures
Figure 1
(A) Rescue of DAP12 cell surface expression on 293T FLAG-DAP12 cells transfected with control plasmid or with pJEF14 vector containing mouse MDL-1 cDNA. (B) Nucleotide and predicted amino acid sequence of mouse MDL-1. The sequence of the cDNA encoding the short form of mouse MDL-1 is presented (GenBank accession no. AF139769). The predicted transmembrane region is underlined, with the charged lysine indicated in bold, and potential N-linked glycosylation sites are depicted with an asterisk. (C) Alignment of the predicted protein sequences of the long form of mouse MDL-1 (GenBank accession no. AA186015) and human MDL-1 (GenBank accession no. AF139768). The additional 25 aa in the stalk region of the long form of mouse MDL-1 are underlined.
Figure 2
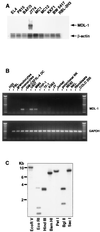
MDL-1 gene and expression. (A) Total RNA of mouse cell lines was analyzed for MDL-1 transcripts by using the short form of the mouse MDL-1 cDNA as a probe. EL4, KKF1, and BW 5417 are cell lines of T cell origin. P815 and BaF/3 are mastocytoma and pre-B cell lines, respectively. MC1 and MC12 are mast cell lines, J774 is a macrophage cell line, and RBL-2H3 is a rat basophilic leukemia. (Inset) Hybridization with a β-actin probe is shown. (B) PCR amplification of cDNA prepared by reverse transcription of RNA from healthy donor peripheral blood leukocyte subpopulations or primary cultures thereof or from human cell lines. U937, MM6, and THP-1 are cell lines of myeloid origin; TF-1 and K562 are of erythroid/myeloid and erythroid origins, respectively. JY is a B lymphoblastoid cell line, and Jurkat is a T cell leukemia cell line. NK92 and NKL are NK cell lines. Fibroblasts were derived from human foreskin samples. Colo 205 is a colon carcinoma cell line. (C) MDL-1 Southern blot analysis. Human genomic DNA was digested with the indicated enzymes and probed with the human MDL-1 cDNA.
Figure 3
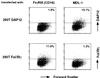
MDL-1 selectively rescues DAP12 cell surface expression. 293T cells stably expressing FLAG-DAP12 or FLAG-FcɛRIγ were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding human CD16 and human MDL-1, respectively. Cell surface expression of FLAG-DAP12 and FLAG-FcɛRIγ was analyzed by flow cytometry by using the anti-FLAG mAb M2.
Figure 4
MDL-1 associates noncovalently with DAP12 on the cell surface. (A) Mouse J774 macrophage cells expressing MDL-1/CD69 or MDL-1/CD69 in which the transmembrane lysine was replaced by an isoleucine (TM K → I) were analyzed by flow cytometry by using isotype control or anti-CD69 mAb Leu-23. (B) J774 MDL-1/CD69 cells (WT) or J774 MDL-1/CD69 TM K → I cells (K → I) were lysed and were immunoprecipitated with control Ig (cIg) or anti-CD69 mAb. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by SDS/PAGE under reducing conditions, blotted, and probed with affinity-purified rabbit anti-mouse DAP12 antiserum.
Figure 5
MDL-1 receptor induces intracellular Ca2+ mobilization. Indo-1 AM-loaded MDL-1/CD69-transfected J774 cells were incubated with anti-H2-Dd mAb (used as a negative control) (A) or anti-CD69 mAb (B), followed by a crosslinking Ab. Intracellular calcium levels were measured as described in Materials and Methods.
Similar articles
- Molecular cloning and expression pattern of porcine myeloid DAP12-associating lectin-1.
Yim D, Jie HB, Sotiriadis J, Kim YS, Kim YB. Yim D, et al. Cell Immunol. 2001 Apr 10;209(1):42-8. doi: 10.1006/cimm.2001.1782. Cell Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11414735 - TREM-1, MDL-1, and DAP12 expression is associated with a mature stage of myeloid development.
Gingras MC, Lapillonne H, Margolin JF. Gingras MC, et al. Mol Immunol. 2002 Mar;38(11):817-24. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00004-4. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11922939 - Myeloid DAP12-associating lectin (MDL)-1 regulates synovial inflammation and bone erosion associated with autoimmune arthritis.
Joyce-Shaikh B, Bigler ME, Chao CC, Murphy EE, Blumenschein WM, Adamopoulos IE, Heyworth PG, Antonenko S, Bowman EP, McClanahan TK, Phillips JH, Cua DJ. Joyce-Shaikh B, et al. J Exp Med. 2010 Mar 15;207(3):579-89. doi: 10.1084/jem.20090516. Epub 2010 Mar 8. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 20212065 Free PMC article. - KARAP/DAP12/TYROBP: three names and a multiplicity of biological functions.
Tomasello E, Vivier E. Tomasello E, et al. Eur J Immunol. 2005 Jun;35(6):1670-7. doi: 10.1002/eji.200425932. Eur J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15884055 Review. - DAP12: a key accessory protein for relaying signals by natural killer cell receptors.
Campbell KS, Colonna M. Campbell KS, et al. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999 Jun;31(6):631-6. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(99)00022-9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10404635 Review.
Cited by
- KSRP: a checkpoint for inflammatory cytokine production in astrocytes.
Li X, Lin WJ, Chen CY, Si Y, Zhang X, Lu L, Suswam E, Zheng L, King PH. Li X, et al. Glia. 2012 Nov;60(11):1773-84. doi: 10.1002/glia.22396. Epub 2012 Jul 28. Glia. 2012. PMID: 22847996 Free PMC article. - Multi-omic comparison of Alzheimer's variants in human ESC-derived microglia reveals convergence at APOE.
Liu T, Zhu B, Liu Y, Zhang X, Yin J, Li X, Jiang L, Hodges AP, Rosenthal SB, Zhou L, Yancey J, McQuade A, Blurton-Jones M, Tanzi RE, Huang TY, Xu H. Liu T, et al. J Exp Med. 2020 Dec 7;217(12):e20200474. doi: 10.1084/jem.20200474. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32941599 Free PMC article. - Crystallization and X-ray diffraction analysis of human CLEC5A (MDL-1), a dengue virus receptor.
Watson AA, O'Callaghan CA. Watson AA, et al. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2010 Jan 1;66(Pt 1):29-31. doi: 10.1107/S1744309109047915. Epub 2009 Dec 25. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2010. PMID: 20057064 Free PMC article. - A potential role of myeloid DAP12-associating lectin (MDL)-1 in the regulation of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Chen DY, Yao L, Chen YM, Lin CC, Huang KC, Chen ST, Lan JL, Hsieh SL. Chen DY, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Jan 21;9(1):e86105. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086105. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465901 Free PMC article. - Innate immune receptors drive dengue virus immune activation and disease.
Sprokholt J, Helgers LC, Geijtenbeek TB. Sprokholt J, et al. Future Virol. 2017 Mar;13(4):287-305. doi: 10.2217/fvl-2017-0146. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Future Virol. 2017. PMID: 29937918 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Weiss A, Littman D R. Cell. 1994;76:263–274. - PubMed
- Lanier L L. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:359–393. - PubMed
- Houchins J P, Lanier L L, Niemi E, Phillips J H, Ryan J C. J Immunol. 1997;158:3603–3609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials