Hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma: a proposal of a prognostic scoring system - PubMed (original) (raw)
Hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma: a proposal of a prognostic scoring system
S Iwatsuki et al. J Am Coll Surg. 1999 Sep.
Abstract
Background: Hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer provides excellent longterm results in a substantial proportion of patients. Although various prognostic risk factors have been identified, there has been no dependable staging or prognostic scoring system for metastatic hepatic tumors.
Study design: Various clinical and pathologic risk factors were examined in 305 consecutive patients who underwent primary hepatic resections for metastatic colorectal cancer. Survival rates were estimated by the Cox proportional hazards model using the equation: S(t) = [So(t)]exp(R-Ro), where So(t) is the survival rate of patients with none of the identified risk factors and Ro = 0.
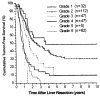
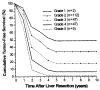
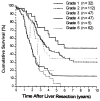
Results: Preliminary multivariate analysis revealed that independently significant negative prognosticators were: (1) positive surgical margins, (2) extrahepatic tumor involvement including the lymph node(s), (3) tumor number of three or more, (4) bilobar tumors, and (5) time from treatment of the primary tumor to hepatic recurrence of 30 months or less. Because the survival rates of the 62 patients with positive margins or extrahepatic tumor were uniformly very poor, multivariate analysis was repeated in the remaining 243 patients who did not have these lethal risk factors. The reanalysis revealed that independently significant poor prognosticators were: (1) tumor number of three or more, (2) tumor size greater than 8 cm, (3) time to hepatic recurrence of 30 months or less, and (4) bilobar tumors. Risk scores (R) for tumor recurrence of the culled cohort (n = 243) were calculated by summation of coefficients from the multivariate analysis and were divided into five groups: grade 1, no risk factors (R = 0); grade 2, one risk factor (R = 0.3 to 0.7); grade 3, two risk factors (R = 0.7 to 1.1); grade 4, three risk factors (R= 1.2 to 1.6); and grade 5, four risk factors (R > 1.6). Grade 6 consisted of the 62 culled patients with positive margins or extrahepatic tumor. Kaplan-Meier and Cox proportional hazards estimated 5-year survival rates of grade 1 to 6 patients were 48.3% and 48.3%, 36.6% and 33.7%, 19.9% and 17.9%, 11.9% and 6.4%, 0% and 1.1%, and 0% and 0%, respectively (p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: The proposed risk-score grading predicted the survival differences extremely well. Estimated survival as determined by the Cox proportional hazards model was similar to that determined by the Kaplan-Meier method. Verification and further improvements of the proposed system are awaited by other centers or international collaborative studies.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests declared.
Figures
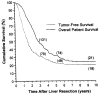
Figure 1
Ten-year overall patient and tumor-free Kaplan-Meier survival.
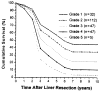
Figure 2
Kaplan–Meier tumor-free survival stratified by six grades.
Figure 3
Estimated (Cox regression model) tumor-free survival stratified by five grades (grade 6 cannot be estimated with this model).
Figure 4
Kaplan-Meier overall patient survival stratified by six grades.
Figure 5
Estimated (Cox regression model) overall patient survival stratified by five grades (grade 6 cannot be estimated with this model).
Similar articles
- Determinants of survival following hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer.
Bakalakos EA, Kim JA, Young DC, Martin EW Jr. Bakalakos EA, et al. World J Surg. 1998 Apr;22(4):399-404; discussion 404-5. doi: 10.1007/s002689900404. World J Surg. 1998. PMID: 9523523 - Experience in hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: analysis of clinical and pathologic risk factors.
Gayowski TJ, Iwatsuki S, Madariaga JR, Selby R, Todo S, Irish W, Starzl TE. Gayowski TJ, et al. Surgery. 1994 Oct;116(4):703-10; discussion 710-1. Surgery. 1994. PMID: 7940169 Free PMC article. - Evaluation of long-term survival after hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: a multifactorial model of 929 patients.
Rees M, Tekkis PP, Welsh FK, O'Rourke T, John TG. Rees M, et al. Ann Surg. 2008 Jan;247(1):125-35. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31815aa2c2. Ann Surg. 2008. PMID: 18156932 - Histopathologic prognostic factors in resected colorectal lung metastases.
Shiono S, Ishii G, Nagai K, Yoshida J, Nishimura M, Murata Y, Tsuta K, Nishiwaki Y, Kodama T, Ochiai A. Shiono S, et al. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005 Jan;79(1):278-82; discussion 283. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.06.096. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005. PMID: 15620957 Review. - Benefits of surgery for patients with pulmonary metastases from colorectal carcinoma.
Inoue M, Ohta M, Iuchi K, Matsumura A, Ideguchi K, Yasumitsu T, Nakagawa K, Fukuhara K, Maeda H, Takeda S, Minami M, Ohno Y, Matsuda H; Thoracic Surgery Study Group of Osaka University. Inoue M, et al. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004 Jul;78(1):238-44. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.02.017. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004. PMID: 15223436 Review.
Cited by
- Efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for initially resectable colorectal liver metastases: A retrospective cohort study.
Takeda K, Sawada Y, Yabushita Y, Honma Y, Kumamoto T, Watanabe J, Matsuyama R, Kunisaki C, Misumi T, Endo I. Takeda K, et al. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Jul 15;14(7):1281-1294. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i7.1281. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36051104 Free PMC article. - Resection of Colorectal Liver Metastases: Prognostic Impact of Tumor Burden Score Varies with Unilateral Versus Bilateral Metastatic Spread.
Moazzam Z, Shaikh CF, Tsilimigras DI, Pawlik TM. Moazzam Z, et al. J Gastrointest Surg. 2023 Feb;27(2):404-406. doi: 10.1007/s11605-022-05431-9. Epub 2022 Aug 1. J Gastrointest Surg. 2023. PMID: 35915380 No abstract available. - Postoperative hepatic arterial chemotherapy in high-risk patients as adjuvant treatment after resection of colorectal liver metastases - a randomized phase II/III trial - PACHA-01 (NCT02494973).
Goéré D, Pignon JP, Gelli M, Elias D, Benhaim L, Deschamps F, Caramella C, Boige V, Ducreux M, de Baere T, Malka D. Goéré D, et al. BMC Cancer. 2018 Aug 6;18(1):787. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4697-7. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30081865 Free PMC article. - Genetic And Morphological Evaluation (GAME) score for patients with colorectal liver metastases.
Margonis GA, Sasaki K, Gholami S, Kim Y, Andreatos N, Rezaee N, Deshwar A, Buettner S, Allen PJ, Kingham TP, Pawlik TM, He J, Cameron JL, Jarnagin WR, Wolfgang CL, D'Angelica MI, Weiss MJ. Margonis GA, et al. Br J Surg. 2018 Aug;105(9):1210-1220. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10838. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Br J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29691844 Free PMC article. - RAS mutations predict radiologic and pathologic response in patients treated with chemotherapy before resection of colorectal liver metastases.
Zimmitti G, Shindoh J, Mise Y, Kopetz S, Loyer EM, Andreou A, Cooper AB, Kaur H, Aloia TA, Maru DM, Vauthey JN. Zimmitti G, et al. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015 Mar;22(3):834-842. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-4042-6. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25227306 Free PMC article.
References
- Ekberg M, Tranberg KG, Anderson R, et al. Determinants of survival in liver resection for colorectal secondaries. Br J Surg. 1986;73:727–731. - PubMed
- Adson MA. Resection of liver metastases—when is it worthwhile? World J Surg. 1987;11:511–520. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials