Sex dimorphisms in the rate of age-related decline in spatial memory: relevance to alterations in the estrous cycle - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Sex dimorphisms in the rate of age-related decline in spatial memory: relevance to alterations in the estrous cycle
A L Markowska. J Neurosci. 1999.
Abstract
The present experiments demonstrate the existence of sex differences in the rate of development and the magnitude of age-dependent impairments in cognitive and sensorimotor abilities. Although no sex differences were found in spatial reference memory at a young age, the mnemonic ability of female rats deteriorated more rapidly than that of male rats. A major drop in reference memory of the females occurred at the age of 12 months, whereas in the males the onset of impairments occurred later, at the age of 18 months. In spatial working memory, on the other hand, the magnitude of decline was greater in females than in males, although the onset of these impairments occurred at the age of 24 months in both sexes. A sexual dimorphism-aging interaction also was observed in sensorimotor performance. Up to the age of 18 months the females outperformed the males. Subsequently, by the age of 24 months, the performance of the females declined to a level similar to that of the males. The deficits observed in reference and working memory seem to be cognitive in origin and not attributable to alterations in sensory and motor abilities. In addition, the earlier onset of reference memory impairments in females generally coincides with the onset of alterations in the estrous cycle, suggesting that a decline in the estrogenic milieu of the females could be a factor in accelerating the rate of age-related cognitive impairments in the female rat.
Figures
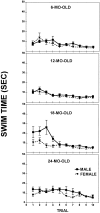
Fig. 1.
Straight Swim test; a comparison of the mean swim time (± SEM) of males and females at four different ages.
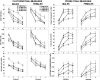
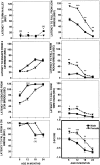
Fig. 2.
Place discrimination in the water maze; a comparison of the mean performance (± SEM) of males (filled symbols) and females (open symbols) across sessions in platform trial measures (two left columns): swim time (top), swim distance (center), and heading angle (bottom) and in probe trial measures (two right columns): target quadrant (top), annulus-40 (center), and platform crossings (bottom).
Fig. 3.
Place discrimination in the water maze; a comparison of the session averages (± SEM) of males (solid line) and females (dashed line) across four different ages. Shown are significant sex differences at ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p<0.05.
Fig. 4.
Repeated acquisition in the water maze; a comparison of the session averages (± SEM) from swim time ratio and swim distance ratio of males and females across four different ages. ***Sex differences at p < 0.001 between 14-month-old males and females.
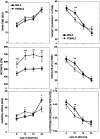
Fig. 5.
Sensorimotor skills; a comparison of the mean performance (± SEM) of males (solid line) and females (dashed line) across four different ages. Shown are significant sex differences at ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, and *p < 0.05, respectively, in the ANOVA and (⊙) at p < 0.05 in the ANCOVA.
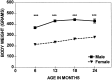
Fig. 6.
Comparison of the mean body weight (± SEM) of females and males across four ages. Shown are significant sex differences at ***p < 0.001.
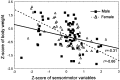
Fig. 7.
Relationship between body weight and performance in sensorimotor tasks in males (solid line) and females (dashed line). The lines represent results from Pearson correlations, significant at p< 0.001. Symbols in the scatter plots represent the data for the individual animals.
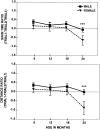
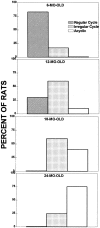
Fig. 8.
Regularity of estrous cycle at four different age groups.
Fig. 9.
Place discrimination in the water maze (Target Quadrant measure); a comparison of the session averages (± SEM) of females with a different cyclic status at four different age groups.
Similar articles
- Reference memory, anxiety and estrous cyclicity in C57BL/6NIA mice are affected by age and sex.
Frick KM, Burlingame LA, Arters JA, Berger-Sweeney J. Frick KM, et al. Neuroscience. 2000;95(1):293-307. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(99)00418-2. Neuroscience. 2000. PMID: 10619486 - Age- and sex-related disturbance in a battery of sensorimotor and cognitive tasks in Kunming mice.
Chen GH, Wang YJ, Zhang LQ, Zhou JN. Chen GH, et al. Physiol Behav. 2004 Dec 15;83(3):531-41. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.09.012. Physiol Behav. 2004. PMID: 15581676 - Age-related spatial reference and working memory deficits assessed in the water maze.
Frick KM, Baxter MG, Markowska AL, Olton DS, Price DL. Frick KM, et al. Neurobiol Aging. 1995 Mar-Apr;16(2):149-60. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(94)00155-3. Neurobiol Aging. 1995. PMID: 7777133 - Age-related impairments in spatial memory are independent of those in sensorimotor skills.
Gage FH, Dunnett SB, Bjorklund A. Gage FH, et al. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Jul-Aug;10(4):347-52. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90047-x. Neurobiol Aging. 1989. PMID: 2682316 Review. - Estrogens and age-related memory decline in rodents: what have we learned and where do we go from here?
Frick KM. Frick KM. Horm Behav. 2009 Jan;55(1):2-23. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2008.08.015. Epub 2008 Sep 16. Horm Behav. 2009. PMID: 18835561 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Some hormone, cytokine and chemokine levels that change across lifespan vary by cognitive status in male Fischer 344 rats.
Scheinert RB, Asokan A, Rani A, Kumar A, Foster TC, Ormerod BK. Scheinert RB, et al. Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Oct;49:216-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 26093306 Free PMC article. - The decline of verbal and visuospatial working memory across the adult life span.
Cansino S, Hernández-Ramos E, Estrada-Manilla C, Torres-Trejo F, Martínez-Galindo JG, Ayala-Hernández M, Gómez-Fernández T, Osorio D, Cedillo-Tinoco M, Garcés-Flores L, Beltrán-Palacios K, García-Lázaro HG, García-Gutiérrez F, Cadena-Arenas Y, Fernández-Apan L, Bärtschi A, Rodríguez-Ortiz MD. Cansino S, et al. Age (Dordr). 2013 Dec;35(6):2283-302. doi: 10.1007/s11357-013-9531-1. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Age (Dordr). 2013. PMID: 23558670 Free PMC article. - Characterizing the effects of tonic 17β-estradiol administration on spatial learning and memory in the follicle-deplete middle-aged female rat.
Koebele SV, Mennenga SE, Poisson ML, Hewitt LT, Patel S, Mayer LP, Dyer CA, Bimonte-Nelson HA. Koebele SV, et al. Horm Behav. 2020 Nov;126:104854. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2020.104854. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Horm Behav. 2020. PMID: 32949557 Free PMC article. - Young and aged TLR4 deficient mice show sex-dependent enhancements in spatial memory and alterations in interleukin-1 related genes.
Potter OV, Giedraitis ME, Johnson CD, Cox MN, Kohman RA. Potter OV, et al. Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Feb;76:37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.10.010. Epub 2018 Oct 27. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 30394314 Free PMC article. - Effects of testosterone on spatial learning and memory in adult male rats.
Spritzer MD, Daviau ED, Coneeny MK, Engelman SM, Prince WT, Rodriguez-Wisdom KN. Spritzer MD, et al. Horm Behav. 2011 Apr;59(4):484-96. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2011.01.009. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Horm Behav. 2011. PMID: 21295035 Free PMC article.
References
- Archer J. Inbreeding and sex differences in rats and mice: a rejoinder to Gray. Br J Psychol. 1979;70:37.
- Beatty WW. Gonadal hormones and sex differences in nonreproductive behaviors in rodents: organizational and activational influences. Horm Behav. 1979;12:112–163. - PubMed
- Berger-Sweeney J, Arnold A, Gabeau D, Mills J. Sex differences in learning and memory in mice: effects of sequence of testing and cholinergic blockade. Behav Neurosci. 1995;109:859–873. - PubMed
- Bucci DJ, Chiba AA, Gallagher M. Spatial learning in male and female Long–Evans rats. Behav Neurosci. 1995;109:180–183. - PubMed
- Coleman PD, Finch CE, Joseph JA. The need for multiple time points in aging studies. Neurobiol Aging. 1990;11:1–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical