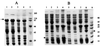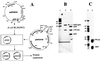Study of the interaction between bacteriophage T4 asiA and Escherichia coli sigma(70), using the yeast two-hybrid system: neutralization of asiA toxicity to E. coli cells by coexpression of a truncated sigma(70) fragment - PubMed (original) (raw)
Study of the interaction between bacteriophage T4 asiA and Escherichia coli sigma(70), using the yeast two-hybrid system: neutralization of asiA toxicity to E. coli cells by coexpression of a truncated sigma(70) fragment
U K Sharma et al. J Bacteriol. 1999 Sep.
Abstract
The interaction of T4 phage-encoded anti-sigma factor, asiA, and Escherichia coli sigma(70) was studied by using the yeast two-hybrid system. Truncation of sigma(70) to identify the minimum region involved in the interaction showed that the fragment containing amino acid residues proximal to the C terminus (residues 547 to 603) was sufficient for complexing to asiA. Studies also indicated that some of the truncated C-terminal fragments (residues 493 to 613) had higher affinity for asiA as judged by the increased beta-galactosidase activity. It is proposed that the observed higher affinity may be due to the unmasking of the binding region of asiA on the sigma protein. Advantage was taken of the increased affinity of truncated sigma(70) fragments to asiA in designing a coexpression system wherein the toxicity of asiA expression in E. coli could be neutralized and the complex of truncated sigma(70) and asiA could be expressed in large quantities and purified.
Figures
FIG. 1
Interaction of full-length and truncated E. coli ς70s with asiA in a yeast two-hybrid system. (A) Recombinant plasmids showing Gal4BD:ς70 and Gal4AD:asiA fusions in binding domain and activation domain vectors pGBT9 and pGAD424, respectively. The truncated rpoD fragments were generated by PCR and fused to Gal4BD in pGBT9 as _Eco_RI-_Sal_I fragments to obtain recombinants pARC8217 through pARC8276 as shown in panel B. The position of the oligonucleotides corresponds to the amino acid numbers indicated. The nucleotide sequences will be made available on request. Only relevant restriction sites are shown. (B) β-gal activities obtained upon interaction of full-length and truncated ς70 fusions with Gal4AD:asiA fusions in S. cerevisiae SFY526. β-gal activity on Whatman membrane was approximated using a scale of + to +++, depending upon the time taken for appearance of blue in the presence of X-Gal (e.g., yeast culture showing blue in 30 min was marked +++ and the one showing blue in 90 min was marked +). At least five independent transformants were tested for β-gal activity. Numbers at right are units of β-gal activity in yeast liquid cultures calculated according to the method of Miller (15). Each value is the average of at least three independent experiments ± standard deviation. ND, not done; B, _Bam_HI; X, _Xho_I.
FIG. 2
Analysis by SDS-PAGE of distribution of full-length ς70, ς70C121, and ς70C166 in soluble and inclusion body fractions. Cytosolic and inclusion body fractions were isolated as described in the text, and 100 μg of protein was applied in each lane. (A) Distribution of ς70. Lanes: 1 and 2, uninduced and induced cytosolic fractions, respectively; 3 and 4, uninduced and induced membrane-inclusion body fractions, respectively. (B) Lanes: 1 to 4, ς70C121; 5 to 8, ς70C166; 1 and 5, uninduced cytosolic fractions; 2 and 6, induced cytosolic fractions; 3 and 7, uninduced membrane-inclusion body fractions; 4 and 8, induced membrane-inclusion body fractions. The full-length ς70 fractions were run on SDS–10% PAGE gels, and the truncated ς70 fractions were run on a 12.5% gel. The protein size marker sizes are shown.
FIG. 3
Coexpression and purification of GST:asiA-ς70C121 complex. (A) Design of coexpression system using two compatible plasmids. (B and C) Purification of asiA-ς70C121 complex from E. coli BL26(DE3) cells coexpressing GST:asiA and ς70C121. (B) Results of 10% SDS-PAGE. Lane 2, GST:asiA-ς70C121 complex obtained after purification through glutathione sepharose column; lane 3, factor Xa cleavage of GST:asiA. (C) Results of 15% SDS-PAGE. Lane 2, pure asiA-ς70C121 complex after removal of GST. The protein size markers are shown.
Similar articles
- Mutational analysis of bacteriophage T4 AsiA: involvement of N- and C-terminal regions in binding to sigma(70) of Escherichia coli in vivo.
Sharma UK, Praveen PV, Balganesh TS. Sharma UK, et al. Gene. 2002 Jul 24;295(1):125-34. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(02)00831-4. Gene. 2002. PMID: 12242019 - Mapping the molecular interface between the sigma(70) subunit of E. coli RNA polymerase and T4 AsiA.
Minakhin L, Camarero JA, Holford M, Parker C, Muir TW, Severinov K. Minakhin L, et al. J Mol Biol. 2001 Mar 2;306(4):631-42. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4445. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11243776 - Transcriptional takeover by sigma appropriation: remodelling of the sigma70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase by the bacteriophage T4 activator MotA and co-activator AsiA.
Hinton DM, Pande S, Wais N, Johnson XB, Vuthoori M, Makela A, Hook-Barnard I. Hinton DM, et al. Microbiology (Reading). 2005 Jun;151(Pt 6):1729-1740. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27972-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2005. PMID: 15941982 Review. - Transcription regulation by bacteriophage T4 AsiA.
Minakhin L, Severinov K. Minakhin L, et al. Protein Expr Purif. 2005 May;41(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2004.09.019. Protein Expr Purif. 2005. PMID: 15802215 Review.
Cited by
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis WhiB3 interacts with RpoV to affect host survival but is dispensable for in vivo growth.
Steyn AJ, Collins DM, Hondalus MK, Jacobs WR Jr, Kawakami RP, Bloom BR. Steyn AJ, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Mar 5;99(5):3147-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.052705399. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11880648 Free PMC article. - The bacteriophage T4 transcription activator MotA interacts with the far-C-terminal region of the sigma70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase.
Pande S, Makela A, Dove SL, Nickels BE, Hochschild A, Hinton DM. Pande S, et al. J Bacteriol. 2002 Jul;184(14):3957-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.14.3957-3964.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12081968 Free PMC article. - Transcriptional control in the prereplicative phase of T4 development.
Hinton DM. Hinton DM. Virol J. 2010 Oct 28;7:289. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-289. Virol J. 2010. PMID: 21029433 Free PMC article. Review. - Substitutions in bacteriophage T4 AsiA and Escherichia coli sigma(70) that suppress T4 motA activation mutations.
Cicero MP, Sharp MM, Gross CA, Kreuzer KN. Cicero MP, et al. J Bacteriol. 2001 Apr;183(7):2289-97. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.7.2289-2297.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11244069 Free PMC article. - Differential mechanisms of binding of anti-sigma factors Escherichia coli Rsd and bacteriophage T4 AsiA to E. coli RNA polymerase lead to diverse physiological consequences.
Sharma UK, Chatterji D. Sharma UK, et al. J Bacteriol. 2008 May;190(10):3434-43. doi: 10.1128/JB.01792-07. Epub 2008 Mar 21. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18359804 Free PMC article.
References
- Adelman K, Orsini G, Colb A, Graziani L, Brody E N. The interaction between the asiA protein of bacteriophage T4 and the ς70 subunit of E. coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:27435–27443. - PubMed
- Borukhow S, Goldfarb A. Recombinant E. coli RNA polymerase: purification of individually overexpressed subunits and in-vitro assembly. Protein Expr Purif. 1993;4:503–511. - PubMed
- Brody E N, Cassavetis G A, Ouhammouch M, Sanders G M, Geiduschek E P. Old phage, new insights: two recently recognised mechanisms of transcriptional regulation in bacteriophage T4 development. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995;128:1–8. - PubMed
- Brown K L, Hughes K T. The role of anti-sigma factors in gene regulation. Mol Microbiol. 1995;16:397–404. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources