Yeast Upf proteins required for RNA surveillance affect global expression of the yeast transcriptome - PubMed (original) (raw)
Yeast Upf proteins required for RNA surveillance affect global expression of the yeast transcriptome
M J Lelivelt et al. Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Oct.
Abstract
mRNAs are monitored for errors in gene expression by RNA surveillance, in which mRNAs that cannot be fully translated are degraded by the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway (NMD). RNA surveillance ensures that potentially deleterious truncated proteins are seldom made. NMD pathways that promote surveillance have been found in a wide range of eukaryotes. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the proteins encoded by the UPF1, UPF2, and UPF3 genes catalyze steps in NMD and are required for RNA surveillance. In this report, we show that the Upf proteins are also required to control the total accumulation of a large number of mRNAs in addition to their role in RNA surveillance. High-density oligonucleotide arrays were used to monitor global changes in the yeast transcriptome caused by loss of UPF gene function. Null mutations in the UPF genes caused altered accumulation of hundreds of mRNAs. The majority were increased in abundance, but some were decreased. The same mRNAs were affected regardless of which of the three UPF gene was inactivated. The proteins encoded by UPF-dependent mRNAs were broadly distributed by function but were underrepresented in two MIPS (Munich Information Center for Protein Sequences) categories: protein synthesis and protein destination. In a UPF(+) strain, the average level of expression of UPF-dependent mRNAs was threefold lower than the average level of expression of all mRNAs in the transcriptome, suggesting that highly abundant mRNAs were underrepresented. We suggest a model for how the abundance of hundreds of mRNAs might be controlled by the Upf proteins.
Figures
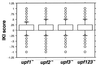
FIG. 1
Box plots representing the distribution of upf IKI scores. The box delineates the interquartile region between the 25th and 75th percentiles. Whiskers delineate the 10th and 90th percentiles. Values lying outside this region are displayed as circles. Each circle represents IKI scores for multiple mRNAs that happen to fall at the same position.
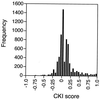
FIG. 2
Distribution of all CKI scores across 6,421 mRNAs analyzed by HDOA. A score of −1.0 indicates a _UPF_-dependent decrease in every trial for every _upf_− strain; a score of +1.0 indicates a _UPF_-dependent increase in every trial for every _upf_− strain; a score of zero represents no average change.
Similar articles
- Genetic background affects relative nonsense mRNA accumulation in wild-type and upf mutant yeast strains.
Kebaara B, Nazarenus T, Taylor R, Atkin AL. Kebaara B, et al. Curr Genet. 2003 Jun;43(3):171-7. doi: 10.1007/s00294-003-0386-3. Epub 2003 Apr 15. Curr Genet. 2003. PMID: 12695845 - Nonsense-containing mRNAs that accumulate in the absence of a functional nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway are destabilized rapidly upon its restitution.
Maderazo AB, Belk JP, He F, Jacobson A. Maderazo AB, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Feb;23(3):842-51. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.3.842-851.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12529390 Free PMC article. - Upf1p control of nonsense mRNA translation is regulated by Nmd2p and Upf3p.
Maderazo AB, He F, Mangus DA, Jacobson A. Maderazo AB, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Jul;20(13):4591-603. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.13.4591-4603.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10848586 Free PMC article. - RNA surveillance. Unforeseen consequences for gene expression, inherited genetic disorders and cancer.
Culbertson MR. Culbertson MR. Trends Genet. 1999 Feb;15(2):74-80. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(98)01658-8. Trends Genet. 1999. PMID: 10098411 Review. - Upf proteins: highly conserved factors involved in nonsense mRNA mediated decay.
Gupta P, Li YR. Gupta P, et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2018 Feb;45(1):39-55. doi: 10.1007/s11033-017-4139-7. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Mol Biol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29282598 Review.
Cited by
- Ribosome-associated complex and Ssb are required for translational repression induced by polylysine segments within nascent chains.
Chiabudini M, Conz C, Reckmann F, Rospert S. Chiabudini M, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Dec;32(23):4769-79. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00809-12. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23007158 Free PMC article. - Genetic background affects relative nonsense mRNA accumulation in wild-type and upf mutant yeast strains.
Kebaara B, Nazarenus T, Taylor R, Atkin AL. Kebaara B, et al. Curr Genet. 2003 Jun;43(3):171-7. doi: 10.1007/s00294-003-0386-3. Epub 2003 Apr 15. Curr Genet. 2003. PMID: 12695845 - Ending a bad start: Triggers and mechanisms of co-translational protein degradation.
Eisenack TJ, Trentini DB. Eisenack TJ, et al. Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jan 4;9:1089825. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1089825. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36660423 Free PMC article. Review. - Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay: Degradation of Defective Transcripts Is Only Part of the Story.
He F, Jacobson A. He F, et al. Annu Rev Genet. 2015;49:339-66. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-112414-054639. Epub 2015 Oct 2. Annu Rev Genet. 2015. PMID: 26436458 Free PMC article. Review. - Functional characterization of Upf1 targets in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.
Matia-González AM, Hasan A, Moe GH, Mata J, Rodríguez-Gabriel MA. Matia-González AM, et al. RNA Biol. 2013 Jun;10(6):1057-65. doi: 10.4161/rna.24569. Epub 2013 Apr 16. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23619768 Free PMC article.
References
- Atkin A L, Schenkman L R, Eastham M, Dahlseid J N, Lelivelt M J, Culbertson M R. Relationship between yeast polyribosomes and Upf proteins required for nonsense mRNA decay. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:22163–22172. - PubMed
- Badcock, K., C. M. Churcher, B. G. Barrell, M. A. Rajandream, and S. V. Walsh. 1997. Swiss-Prot accession no. , gene name SPAC16C9.06C.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases