An IL-13 inhibitor blocks the development of hepatic fibrosis during a T-helper type 2-dominated inflammatory response - PubMed (original) (raw)
An IL-13 inhibitor blocks the development of hepatic fibrosis during a T-helper type 2-dominated inflammatory response
M G Chiaramonte et al. J Clin Invest. 1999 Sep.
Abstract
In schistosomiasis, chronic parasite egg-induced granuloma formation can lead to tissue destruction and fibrosis, which causes much of the morbidity and mortality associated with this disease. Here we show the importance of IL-13 in the pathogenesis of schistosomiasis, and demonstrate, perhaps for the first time, the therapeutic efficacy of an IL-13 inhibitor, sIL-13Ralpha2-Fc, in the control of hepatic fibrosis. T-helper type 2 (Th2) cytokines dominate the immune response in mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni, yet the specific contributions of IL-13 and IL-4 to the development of fibrosis were not previously investigated. Our studies demonstrate that both cytokines play redundant roles in granuloma formation, which explains the ability of IL-4-deficient mice to form granulomas around eggs. More importantly, however, these studies demonstrate that IL-13 is the dominant Th2-type cytokine regulating fibrosis. IL-13 stimulated collagen production in fibroblasts, and procollagen I and procollagen III mRNA expression was decreased in sIL-13Ralpha2-Fc-treated mice. Moreover, the reduction in fibrosis observed in IL-4-deficient mice was much less pronounced than that in sIL-13Ralpha2-Fc-treated animals. Fibrosis is a major pathological manifestation of a number of allergic, autoimmune, and infectious diseases. Thus, our findings provide evidence that IL-13 inhibitors may be of general therapeutic benefit in preventing damaging tissue fibrosis resulting from Th2-dominated inflammatory responses.
Figures
Figure 1
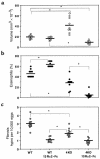
Characterization of the roles of IL-4 and IL-13 in schistosomiasis pathogenesis. C57BL/6 WT and IL-4–deficient (4KO) mice were sacrificed 8 weeks after infection to evaluate the size of liver granulomas (a), tissue eosinophilia (b), and hepatic fibrosis (c). Separate groups of mice were treated with control-Fc or sIL-13Rα2-Fc as described in Methods. The data shown are measurements from individual mice. The bars designate the means for each group. Significant comparisons are indicated by asterisks. Similar data were reproduced in 3 separate studies.
Figure 2
The Th1/Th2-type cytokine profile is unaffected by sIL-13Rα2-Fc treatment. Infected C57BL/6 WT and IL-4–deficient (4KO) mice were treated with control-Fc or sIL-13Rα2-Fc as described in Methods MLN cells were isolated from individual mice, and single-cell suspensions were prepared (3 × 106 cells per well in 24-well plates) and stimulated with medium (squares), SEA at 20 μg/mL (circles), or SEA and 50 μg/mL of anti-CD4 mAb (triangles). All cytokines were assayed in culture supernatants by ELISA 72 hours after stimulation, as described in Methods. The symbols represent values for individual mice, and the bars indicate the means within each group.
Figure 3
Th2-type cytokine mRNA expression is reduced in the livers of infected IL-4–deficient mice, but is unaffected by IL-13 blockade. Infected and treated C57BL/6 WT and IL-4–deficient (4KO) mice were sacrificed on week 8 after infection, and liver specimens were prepared for RT-PCR. The data shown are the individual values of 9–10 animals per group, and the bars indicate the average within each group. The average values from 5 uninfected WT (filled circles) and 5 uninfected IL-4–deficient mice (open circles) are shown on the y-axis for each cytokine. All data were reproduced in a second study. *Data are significantly different from the WT control-Fc group, as determined by ANOVA (P < 0.05).
Figure 4
Collagen I and collagen III mRNA expression is reduced in the livers of infected sIL-13Rα2-Fc–treated mice, but is unaffected by IL-4 deficiency (4KO). RT-PCR analysis was performed for collagen I and III as described in the legend to Figure 3. These data were reproduced in a separate study.
Figure 5
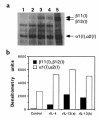
IL-13 induces type I collagen synthesis in murine 3T3 fibroblasts. Cells were stimulated with media (lane 1), rIL-4 at 1,000 U/mL (lane 2), or rIL-13 at 20 ng/mL (lanes 3 and 4) for 48 hours. Total cell lysates were separated on 6% SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, were transferred to nitrocellulose membrane, and were probed with rabbit IgG anti-mouse type I collagen. The anti-collagen type I antibody identifies purified collagen type I, including β11(I),β12(I) and α1(I),α2(I) collagen, which were separated in lane 5 (a). Assay specificity was confirmed by digestion with collagenase in separate experiments. (b) Densitometric values (arbitrary pixel units).
Similar articles
- Anti-IL-4 treatment of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice inhibits development of T cells and non-B, non-T cells expressing Th2 cytokines while decreasing egg-induced hepatic fibrosis.
Cheever AW, Williams ME, Wynn TA, Finkelman FD, Seder RA, Cox TM, Hieny S, Caspar P, Sher A. Cheever AW, et al. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 15;153(2):753-9. J Immunol. 1994. PMID: 8021510 - An IL-12-based vaccination method for preventing fibrosis induced by schistosome infection.
Wynn TA, Cheever AW, Jankovic D, Poindexter RW, Caspar P, Lewis FA, Sher A. Wynn TA, et al. Nature. 1995 Aug 17;376(6541):594-6. doi: 10.1038/376594a0. Nature. 1995. PMID: 7637808 - Regulation and function of the interleukin 13 receptor alpha 2 during a T helper cell type 2-dominant immune response.
Chiaramonte MG, Mentink-Kane M, Jacobson BA, Cheever AW, Whitters MJ, Goad ME, Wong A, Collins M, Donaldson DD, Grusby MJ, Wynn TA. Chiaramonte MG, et al. J Exp Med. 2003 Mar 17;197(6):687-701. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020903. J Exp Med. 2003. PMID: 12642601 Free PMC article. - The role of cytokines in the formation of the schistosome egg granuloma.
Boros DL. Boros DL. Immunobiology. 1994 Oct;191(4-5):441-50. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80450-X. Immunobiology. 1994. PMID: 7713558 Review. - Immunopathogenesis of schistosomiasis.
Wynn TA, Thompson RW, Cheever AW, Mentink-Kane MM. Wynn TA, et al. Immunol Rev. 2004 Oct;201:156-67. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00176.x. Immunol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15361239 Review.
Cited by
- Intra-specific variations in Schistosoma mansoni and their possible contribution to inconsistent virulence and diverse clinical outcomes.
Dannenhaus TA, Winkelmann F, Reinholdt C, Bischofsberger M, Dvořák J, Grevelding CG, Löbermann M, Reisinger EC, Sombetzki M. Dannenhaus TA, et al. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Oct 28;18(10):e0012615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012615. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39466851 Free PMC article. - Endogenous PGD2 acting on DP2 receptor counter regulates Schistosoma mansoni infection-driven hepatic granulomatous fibrosis.
Pezzella-Ferreira GN, Pão CRR, Bellas I, Luna-Gomes T, Muniz VS, Paiva LA, Amorim NRT, Canetti C, Bozza PT, Diaz BL, Bandeira-Melo C. Pezzella-Ferreira GN, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2024 Aug 22;20(8):e1011812. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011812. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39173086 Free PMC article. - Immunology of human fibrosis.
Bhattacharya M, Ramachandran P. Bhattacharya M, et al. Nat Immunol. 2023 Sep;24(9):1423-1433. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01551-9. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Nat Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37474654 Review. - Hepatic inflammatory responses in liver fibrosis.
Hammerich L, Tacke F. Hammerich L, et al. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Oct;20(10):633-646. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00807-x. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37400694 Review. - The link between immunity and hypertension in the kidney and heart.
Benson LN, Guo Y, Deck K, Mora C, Liu Y, Mu S. Benson LN, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Mar 9;10:1129384. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1129384. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36970367 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Rosenstein BJ, Zeitlin PL. Cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1998;351:277–282. - PubMed
- Trojanowska M, LeRoy EC, Eckes B, Krieg T. Pathogenesis of fibrosis: type 1 collagen and the skin. J Mol Med. 1998;76:266–274. - PubMed
- Johnson LL, Dyer R, Hupe DJ. Matrix metalloproteinases. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1998;2:466–471. - PubMed
- Cheever AW, Yap GS. Immunologic basis of disease and disease regulation in schistosomiasis. Chem Immunol. 1997;66:159–176. - PubMed
- Bergquist NR. Schistosomiasis vaccine development: progress and prospects. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1998;93:95–101. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases