Aldosterone-mediated regulation of ENaC alpha, beta, and gamma subunit proteins in rat kidney - PubMed (original) (raw)
Aldosterone-mediated regulation of ENaC alpha, beta, and gamma subunit proteins in rat kidney
S Masilamani et al. J Clin Invest. 1999 Oct.
Abstract
Aldosterone stimulates sodium transport in the renal collecting duct by activating the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC). To investigate the basis of this effect, we have developed a novel set of rabbit polyclonal antibodies to the 3 subunits of ENaC and have determined the abundance and distribution of ENaC subunits in the principal cells of the rat renal collecting duct. Elevated circulating aldosterone (due to either dietary NaCl restriction or aldosterone infusion) markedly increased the abundance of alphaENaC protein without increasing the abundance of the beta and gamma subunits. Thus, alphaENaC is selectively induced by aldosterone. In addition, immunofluorescence immunolocalization showed a striking redistribution in ENaC labeling to the apical region of the collecting duct principal cells. Finally, aldosterone induced a shift in molecular weight of gammaENaC from 85 kDa to 70 kDa, consistent with physiological proteolytic clipping of the extracellular loop as postulated previously. Thus, at the protein level, the response of ENaC to aldosterone stimulation is heterogenous, with both quantitative and qualitative changes that can explain observed increases in ENaC-mediated sodium transport.
Figures
Figure 1
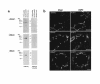
Characterization of ENaC subunit antibodies. (a) Immunoblots of rat renal cortical proteins obtained by differential centrifugation. Blots were probed with the 3 ENaC subunit antibodies and with the antibodies preadsorbed with 1 mg of the respective immunizing peptides. Differential centrifugation was carried out as described (6), yielding membrane fractions (17,000 g and 200,000 g pellets) and a cytosolic fraction (200,000 g supernatant). (b) Immunofluorescence localization of ENaC subunits in rat renal cortical collecting duct. Three sections are shown, each double-labeled with 1 of 3 rabbit antibodies to ENaC subunits (left-hand panels) and a chicken anti–aquaporin-2 (right-hand panels). Arrows point to cells lacking aquaporin-2, i.e., intercalated cells. All tissue sections were from sodium-restricted rats. Scale bars: 10 μm.
Figure 2
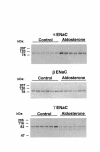
Effect of dietary NaCl restriction for 10 days. (a) Semiquantitative immunoblots for ENaC subunits and other major renal sodium transporters. For each blot, each lane was loaded with a homogenate from a different rat (n = 6 for both control and sodium-restricted rats). Preliminary Coomassie-stained gels demonstrated equality of loading among lanes. Asterisks mark statistically significant increases. (b) Deglycosylation with PNGase. SDS-solubilized samples from control rats and NaCl-restricted rats were incubated with PNGase F (200 U/40 μg protein; New England Biolabs Inc., Beverly, Massachusetts, USA) or vehicle.
Figure 3
Semiquantitative immunoblots showing effect of aldosterone infusion for 10 days on the abundance and molecular weight of each ENaC subunit in whole kidneys of rat. For each blot, each lane was loaded with 30 μg cortical homogenate from a different rat.
Figure 4
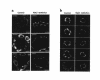
Immunofluorescence localization of ENaC subunit proteins in control rats and rats undergoing dietary NaCl restriction. (a) Comparison of the 3 subunits. Left-hand panels are from rats on control diet; right-hand panels are from salt-restricted rats. Scale bars: 10 μm. (b) γENaC labeling in multiple rat renal cortical collecting ducts. Left-hand panels are from rats on control diet; right-hand panels are from salt-restricted rats. Scale bars: 10 μm.
Comment in
- AlphaENaC: leading the charge.
Oh YS, Saxena S, Warnock DG. Oh YS, et al. J Clin Invest. 1999 Oct;104(7):849-50. doi: 10.1172/JCI8378. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 10510324 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Lithium-induced NDI in rats is associated with loss of alpha-ENaC regulation by aldosterone in CCD.
Nielsen J, Kwon TH, Frøkiaer J, Knepper MA, Nielsen S. Nielsen J, et al. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 May;290(5):F1222-33. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00321.2005. Epub 2005 Dec 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16332930 - Long-term regulation of ENaC expression in kidney by angiotensin II.
Beutler KT, Masilamani S, Turban S, Nielsen J, Brooks HL, Ageloff S, Fenton RA, Packer RK, Knepper MA. Beutler KT, et al. Hypertension. 2003 May;41(5):1143-50. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000066129.12106.E2. Epub 2003 Apr 7. Hypertension. 2003. PMID: 12682079 - Molecular biology of Na+ absorption.
Barbry P, Hofman P. Barbry P, et al. Am J Physiol. 1997 Sep;273(3 Pt 1):G571-85. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1997.273.3.G571. Am J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9316461 Review. - The sgk, an aldosterone-induced gene in mineralocorticoid target cells, regulates the epithelial sodium channel.
Náray-Fejes-Tóth A, Fejes-Tóth G. Náray-Fejes-Tóth A, et al. Kidney Int. 2000 Apr;57(4):1290-4. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00964.x. Kidney Int. 2000. PMID: 10760056 Review.
Cited by
- Low Na, high K diet and the role of aldosterone in BK-mediated K excretion.
Cornelius RJ, Wen D, Li H, Yuan Y, Wang-France J, Warner PC, Sansom SC. Cornelius RJ, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Jan 21;10(1):e0115515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115515. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25607984 Free PMC article. - Potassium transport in the maturing kidney.
Gurkan S, Estilo GK, Wei Y, Satlin LM. Gurkan S, et al. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007 Jul;22(7):915-25. doi: 10.1007/s00467-007-0432-3. Epub 2007 Mar 2. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17333000 Review. - Regulation of αENaC expression by the circadian clock protein Period 1 in mpkCCD(c14) cells.
Gumz ML, Cheng KY, Lynch IJ, Stow LR, Greenlee MM, Cain BD, Wingo CS. Gumz ML, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Sep;1799(9):622-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.09.003. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20868778 Free PMC article. - cAMP increases density of ENaC subunits in the apical membrane of MDCK cells in direct proportion to amiloride-sensitive Na(+) transport.
Morris RG, Schafer JA. Morris RG, et al. J Gen Physiol. 2002 Jul;120(1):71-85. doi: 10.1085/jgp.20018547. J Gen Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12084777 Free PMC article. - Distribution and regulation of expression of serum- and glucocorticoid-induced kinase-1 in the rat kidney.
Alvarez de la Rosa D, Coric T, Todorovic N, Shao D, Wang T, Canessa CM. Alvarez de la Rosa D, et al. J Physiol. 2003 Sep 1;551(Pt 2):455-66. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.042903. Epub 2003 Jun 19. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12816971 Free PMC article.
References
- Garty H, Palmer LG. Epithelial sodium channels: function, structure, and regulation. Physiol Rev. 1997;77:359–396. - PubMed
- Canessa CM, Horisberger J-D, Rossier BC. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature. 1993;361:467–470. - PubMed
- Canessa CM, et al. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature. 1994;367:463–467. - PubMed
- Renard S, Voilley N, Bassilana F, Lazdunski M, Barbry P. Localization and regulation by steroids of the α, β, and γ subunits of the amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel in colon, lung and kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1995;430:299–307. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical