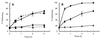Cell death of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils induced by a Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis isolate requires a functional type III secretion system - PubMed (original) (raw)
Cell death of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils induced by a Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis isolate requires a functional type III secretion system
D Dacheux et al. Infect Immun. 1999 Nov.
Abstract
With a coincubation model incorporating Pseudomonas aeruginosa and human polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs), a cystic fibrosis (CF) P. aeruginosa isolate has been shown to resist the bactericidal action of PMNs and to induce their cellular death. An isogenic mutant of this CF isolate in which the type III secretion system was rendered nonfunctional was unable to induce cellular death of PMNs.
Figures
FIG. 1
Kinetics of mortality of PMNs in coincubation experiments with P. aeruginosa strains. The percentages of cytotoxicity were calculated according to the release of LDH activity. Data are the means of results of at least three experiments. (A) Comparison between CHA (●) and PAO1 (⧫) and the effect of cytochalasin D on the cytotoxicity of CHA (■). ▴, PMNs only. (B) Cytotoxicities of CHA-D1 (○) and of the complemented strain CHA-D1(pDD2) (▾). Results obtained with CHA ( ) are shown.
) are shown.
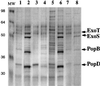
FIG. 2
Extracellular bacterial protein profiles. Silver nitrate-stained 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate–12% PAGE of supernatants of CHA (lanes 1 and 2), CHA-D1 (lanes 3 and 4), CHA-D1(pDD2) (lanes 5 and 6), and PAO1 (lanes 7 and 8) cultured with (lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8) or without (lanes 1, 3, 5, and 7) induction of the type III secretion system by calcium depletion. Molecular weight markers (MW) are shown, with weights being reported in thousands. The positions of ExoT, ExoS, PopB, and PopD are shown.
Similar articles
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis isolates induce rapid, type III secretion-dependent, but ExoU-independent, oncosis of macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils.
Dacheux D, Toussaint B, Richard M, Brochier G, Croize J, Attree I. Dacheux D, et al. Infect Immun. 2000 May;68(5):2916-24. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.5.2916-2924.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10768989 Free PMC article. - Polymorphonuclear leukocytes restrict growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the lungs of cystic fibrosis patients.
Kragh KN, Alhede M, Jensen PØ, Moser C, Scheike T, Jacobsen CS, Seier Poulsen S, Eickhardt-Sørensen SR, Trøstrup H, Christoffersen L, Hougen HP, Rickelt LF, Kühl M, Høiby N, Bjarnsholt T. Kragh KN, et al. Infect Immun. 2014 Nov;82(11):4477-86. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01969-14. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 25114118 Free PMC article. - Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: pyocyanin negative strains are associated with BPI-ANCA and progressive lung disease.
Carlsson M, Shukla S, Petersson AC, Segelmark M, Hellmark T. Carlsson M, et al. J Cyst Fibros. 2011 Jul;10(4):265-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2011.03.004. Epub 2011 Apr 3. J Cyst Fibros. 2011. PMID: 21463973 - Harnessing Neutrophil Survival Mechanisms during Chronic Infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Novel Therapeutic Targets to Dampen Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis.
Marteyn BS, Burgel PR, Meijer L, Witko-Sarsat V. Marteyn BS, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jun 30;7:243. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00243. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28713772 Free PMC article. Review. - Host defenses in patients with cystic fibrosis: modulation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Speert DP. Speert DP. Surv Synth Pathol Res. 1985;4(1):14-33. doi: 10.1159/000156962. Surv Synth Pathol Res. 1985. PMID: 3927464 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- MucA-mediated coordination of type III secretion and alginate synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Wu W, Badrane H, Arora S, Baker HV, Jin S. Wu W, et al. J Bacteriol. 2004 Nov;186(22):7575-85. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.22.7575-7585.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15516570 Free PMC article. - Persistent infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in ventilator-associated pneumonia.
El Solh AA, Akinnusi ME, Wiener-Kronish JP, Lynch SV, Pineda LA, Szarpa K. El Solh AA, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008 Sep 1;178(5):513-9. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200802-239OC. Epub 2008 May 8. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18467510 Free PMC article. - Tryptophan catabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and potential for inter-kingdom relationship.
Bortolotti P, Hennart B, Thieffry C, Jausions G, Faure E, Grandjean T, Thepaut M, Dessein R, Allorge D, Guery BP, Faure K, Kipnis E, Toussaint B, Le Gouellec A. Bortolotti P, et al. BMC Microbiol. 2016 Jul 8;16(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0756-x. BMC Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27392067 Free PMC article. - Epigenetic acquisition of inducibility of type III cytotoxicity in P. aeruginosa.
Filopon D, Mérieau A, Bernot G, Comet JP, Leberre R, Guery B, Polack B, Guespin-Michel J. Filopon D, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 May 30;7:272. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-272. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16734902 Free PMC article. - Activation of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion system requires an intact pyruvate dehydrogenase aceAB operon.
Dacheux D, Epaulard O, de Groot A, Guery B, Leberre R, Attree I, Polack B, Toussaint B. Dacheux D, et al. Infect Immun. 2002 Jul;70(7):3973-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.7.3973-3977.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12065547 Free PMC article.
References
- Attree, I. Unpublished data.
- Coburn J, Wyatt R T, Iglewski B H, Gill D M. Several GTP-binding proteins, including p21c-H-ras, are preferred substrates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:9004–9008. - PubMed
- Delic-Attree I, Toussaint B, Froger A, Willison J C, Vignais P M. Isolation of an IHF-deficient mutant of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid isolate and evaluation of the role of IHF in algD gene expression. Microbiology. 1996;142:2785–2793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical