Brassinosteroid-insensitive dwarf mutants of Arabidopsis accumulate brassinosteroids - PubMed (original) (raw)
Brassinosteroid-insensitive dwarf mutants of Arabidopsis accumulate brassinosteroids
T Noguchi et al. Plant Physiol. 1999 Nov.
Abstract
Seven dwarf mutants resembling brassinosteroid (BR)-biosynthetic dwarfs were isolated that did not respond significantly to the application of exogenous BRs. Genetic and molecular analyses revealed that these were novel alleles of BRI1 (Brassinosteroid-Insensitive 1), which encodes a receptor kinase that may act as a receptor for BRs or be involved in downstream signaling. The results of morphological and molecular analyses indicated that these represent a range of alleles from weak to null. The endogenous BRs were examined from 5-week-old plants of a null allele (bri1-4) and two weak alleles (bri1-5 and bri1-6). Previous analysis of endogenous BRs in several BR-biosynthetic dwarf mutants revealed that active BRs are deficient in these mutants. However, bri1-4 plants accumulated very high levels of brassinolide, castasterone, and typhasterol (57-, 128-, and 33-fold higher, respectively, than those of wild-type plants). Weaker alleles (bri1-5 and bri1-6) also accumulated considerable levels of brassinolide, castasterone, and typhasterol, but less than the null allele (bri1-4). The levels of 6-deoxoBRs in bri1 mutants were comparable to that of wild type. The accumulation of biologically active BRs may result from the inability to utilize these active BRs, the inability to regulate BR biosynthesis in bri1 mutants, or both. Therefore, BRI1 is required for the homeostasis of endogenous BR levels.
Figures
Figure 1
Wild type and four representative alleles of bri1 at 5 weeks of age. A, Wild type; B, bri1-3; C, bri1-4; D, bri1-5; and E, bri1-6.
Figure 2
Schematic of the BRI1 locus including the positions of the bri1 mutations. aa, Amino acid.
Figure 3
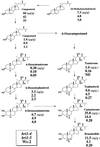
The proposed brassinolide biosynthetic pathway and the quantification of endogenous sterols and BRs from bri1-4 (a null allele), bri1-5 (a weaker allele), and wild type (Ws-2). Values in top, middle, and bottom represent endogenous levels (per gram fresh weight) in bri1-4, bri1-5, and the wild type, respectively. Most of the data for the wild type have been already published (Choe et al., 1999b). Data quantifying teasterone were not available in our previous study because of low recovery. In this study, we repeated the analysis using the same plant materials. Endogenous teasterone was not detected, while recovery of the internal standard ([2H6]teasterone) was very good.
Similar articles
- Arabidopsis brassinosteroid-insensitive dwarf12 mutants are semidominant and defective in a glycogen synthase kinase 3beta-like kinase.
Choe S, Schmitz RJ, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Lee MO, Yoshida S, Feldmann KA, Tax FE. Choe S, et al. Plant Physiol. 2002 Nov;130(3):1506-15. doi: 10.1104/pp.010496. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12428015 Free PMC article. - TWISTED DWARF 1 Associates with BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE 1 to Regulate Early Events of the Brassinosteroid Signaling Pathway.
Zhao B, Lv M, Feng Z, Campbell T, Liscum E, Li J. Zhao B, et al. Mol Plant. 2016 Apr 4;9(4):582-92. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.01.007. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Mol Plant. 2016. PMID: 26802250 - BIN2, a new brassinosteroid-insensitive locus in Arabidopsis.
Li J, Nam KH, Vafeados D, Chory J. Li J, et al. Plant Physiol. 2001 Sep;127(1):14-22. doi: 10.1104/pp.127.1.14. Plant Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11553730 Free PMC article. - Ligand perception, activation, and early signaling of plant steroid receptor brassinosteroid insensitive 1.
Jiang J, Zhang C, Wang X. Jiang J, et al. J Integr Plant Biol. 2013 Dec;55(12):1198-211. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12081. Epub 2013 Sep 9. J Integr Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23718739 Review. - Molecular Lesions in BRI1 and Its Orthologs in the Plant Kingdom.
Zada A, Lv M, Li J. Zada A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 25;25(15):8111. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158111. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125682 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Teaching an old hormone new tricks: cytosolic Ca2+ elevation involvement in plant brassinosteroid signal transduction cascades.
Zhao Y, Qi Z, Berkowitz GA. Zhao Y, et al. Plant Physiol. 2013 Oct;163(2):555-65. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.213371. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23852441 Free PMC article. - Structural basis for differential recognition of brassinolide by its receptors.
She J, Han Z, Zhou B, Chai J. She J, et al. Protein Cell. 2013 Jun;4(6):475-82. doi: 10.1007/s13238-013-3027-8. Epub 2013 May 25. Protein Cell. 2013. PMID: 23709366 Free PMC article. - A novel single-base mutation in CaBRI1 confers dwarf phenotype and brassinosteroid accumulation in pepper.
Yang B, Zhou S, Ou L, Liu F, Yang L, Zheng J, Chen W, Zhang Z, Yang S, Ma Y, Zou X. Yang B, et al. Mol Genet Genomics. 2020 Mar;295(2):343-356. doi: 10.1007/s00438-019-01626-z. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Mol Genet Genomics. 2020. PMID: 31745640 - Brassinosteroid-6-oxidases from Arabidopsis and tomato catalyze multiple C-6 oxidations in brassinosteroid biosynthesis.
Shimada Y, Fujioka S, Miyauchi N, Kushiro M, Takatsuto S, Nomura T, Yokota T, Kamiya Y, Bishop GJ, Yoshida S. Shimada Y, et al. Plant Physiol. 2001 Jun;126(2):770-9. doi: 10.1104/pp.126.2.770. Plant Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11402205 Free PMC article. - Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like gene screen reveals that Nicotiana RXEG1 regulates glycoside hydrolase 12 MAMP detection.
Wang Y, Xu Y, Sun Y, Wang H, Qi J, Wan B, Ye W, Lin Y, Shao Y, Dong S, Tyler BM, Wang Y. Wang Y, et al. Nat Commun. 2018 Feb 9;9(1):594. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03010-8. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29426870 Free PMC article.
References
- Altmann T. Recent advances in brassinosteroid molecular genetics. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 1998;1:378–383. - PubMed
- Appleford NEJ, Lenton JR. Gibberellins and leaf expansion in near-isogenic wheat lines containing Rht1 and Rht3 dwarfing alleles. Planta. 1991;183:229–236. - PubMed
- Bell CJ, Ecker JR. Assignment of thirty microsatellite loci to the linkage map of Arabidopsis. Genomics. 1994;19:137–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases