Participation of Bir1p, a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis family, in yeast chromosome segregation events - PubMed (original) (raw)
Participation of Bir1p, a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis family, in yeast chromosome segregation events
H J Yoon et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999.
Abstract
Yeast two-hybrid and genetic interaction screens indicate that Bir1p, a yeast protein containing phylogenetically conserved antiapoptotic repeat domains called baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis repeats (BIRs), is involved in chromosome segregation events. In the two-hybrid screen, Bir1p specifically interacts with Ndc10p, an essential component of the yeast kinetochore. Although Bir1p carries two BIR motifs in the N-terminal region, the C-terminal third of the protein is sufficient to provide strong interaction with Ndc10p and moderate interaction with Skp1p, another essential component of the yeast kinetochore. In addition, deletion of BIR1 is synthetically lethal with deletion of CBF1 or CTF19, genes specifying two other components of the yeast kinetochore. Yeast cells deleted of BIR1 have a chromosome-loss phenotype, which can be completely rescued by elevating NDC10 dosage. Furthermore, overexpression of either full-length or the C-terminal region of Bir1p can efficiently suppress the chromosome-loss phenotype of both bir1Delta null and skp1-4 mutants. Our data suggest that Bir1p participates in chromosome segregation events, either directly or via interaction with kinetochore proteins, and these effects are apparently not mediated by the BIR domains of Bir1p.
Figures
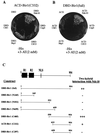
Figure 1
In vivo binding of Bir1p to Ndc10p. (A) Two-hybrid interaction between a Bir1p fragment and known kinetochore proteins. A tester strain PJ69–4A (17) carrying the plasmid pACD-Bir1 (C332) was transformed with various plasmids that express DBD alone or DBD-fused Ndc10p, Cep3p, Ctf13p, Skp1p, or Cbf1p. The transformants were streaked on SD/His− medium containing 2 mM 3-AT (3-amino-1 2,4-triazole) to test expression of the HIS3 reporter gene. (B) Two-hybrid assay with strain PJ69-4A carrying pDBD-Bir1 (full). Strain PJ69-4A/pDBD-Bir1 (full) bearing plasmids expressing ACD-fused Mif2p, Cse4p, Ctf19p, Mcm21p, Okp1p, or Slk19p did not grow on minimal salt-dextrose/His− medium containing 2 mM 3-AT (not shown). (C) Identification of Bir1p regions interacting with Ndc10p. (Top) Schematic view of Bir1p showing the relative locations of BIR domains 1 (R1), 2 (R2), and of nuclear localization signal (NLS), a bipartite nuclear localization signal. Various truncated Bir1p fragments as shown here (See Materials and Methods) were tested for two-hybrid interactions with Ndc10p on SD/His− medium containing 2 mM 3-AT.
Similar articles
- The inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein Bir1p protects against apoptosis in S. cerevisiae and is a substrate for the yeast homologue of Omi/HtrA2.
Walter D, Wissing S, Madeo F, Fahrenkrog B. Walter D, et al. J Cell Sci. 2006 May 1;119(Pt 9):1843-51. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02902. Epub 2006 Apr 11. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 16608876 - A Bir1p Sli15p kinetochore passenger complex regulates septin organization during anaphase.
Thomas S, Kaplan KB. Thomas S, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Oct;18(10):3820-34. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-03-0201. Epub 2007 Jul 25. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17652458 Free PMC article. - The kinetochore protein Ndc10p is required for spindle stability and cytokinesis in yeast.
Bouck DC, Bloom KS. Bouck DC, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Apr 12;102(15):5408-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405925102. Epub 2005 Apr 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15809434 Free PMC article. - Revealing hidden relationships among yeast genes involved in chromosome segregation using systematic synthetic lethal and synthetic dosage lethal screens.
Baetz K, Measday V, Andrews B. Baetz K, et al. Cell Cycle. 2006 Mar;5(6):592-5. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.6.2583. Epub 2006 Mar 15. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16582600 Review. - Structure and function of kinetochores in budding yeast.
Hyman AA, Sorger PK. Hyman AA, et al. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995;11:471-95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.11.110195.002351. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995. PMID: 8689566 Review.
Cited by
- The composition, functions, and regulation of the budding yeast kinetochore.
Biggins S. Biggins S. Genetics. 2013 Aug;194(4):817-46. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.145276. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23908374 Free PMC article. Review. - Tension sensing by Aurora B kinase is independent of survivin-based centromere localization.
Campbell CS, Desai A. Campbell CS, et al. Nature. 2013 May 2;497(7447):118-21. doi: 10.1038/nature12057. Epub 2013 Apr 21. Nature. 2013. PMID: 23604256 Free PMC article. - Human survivin is a kinetochore-associated passenger protein.
Skoufias DA, Mollinari C, Lacroix FB, Margolis RL. Skoufias DA, et al. J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 25;151(7):1575-82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.7.1575. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11134084 Free PMC article. - The TGL2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes an active acylglycerol lipase located in the mitochondria.
Ham HJ, Rho HJ, Shin SK, Yoon HJ. Ham HJ, et al. J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 29;285(5):3005-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.046946. Epub 2009 Dec 3. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19959834 Free PMC article. - The Schizosaccharomyces pombe aurora-related kinase Ark1 interacts with the inner centromere protein Pic1 and mediates chromosome segregation and cytokinesis.
Leverson JD, Huang HK, Forsburg SL, Hunter T. Leverson JD, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Apr;13(4):1132-43. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-07-0330. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 11950927 Free PMC article.
References
- Uren A G, Coulson E J, Vaux D L. Trends Biochem Sci. 1998;23:159–162. - PubMed
- Deveraux Q L, Reed J C. Genes Dev. 1999;13:239–252. - PubMed
- Miller L K. Trends Cell Biol. 1999;9:323–328. - PubMed
- Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu E Y, Plescia J, Tognin S, Marchisio P C, Altieri D C. Nature (London) 1998;396:580–584. - PubMed
- Fraser A G, James C, Evan G I, Hengartner M O. Curr Biol. 1999;9:292–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases