The prostate expression database (PEDB): status and enhancements in 2000 - PubMed (original) (raw)
The prostate expression database (PEDB): status and enhancements in 2000
P S Nelson et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000.
Abstract
The Prostate Expression Database (PEDB) is an online resource designed to access and analyze gene expression information derived from the human prostate. PEDB archives >55 000 expressed sequence tags (ESTs) from 43 cDNA libraries in a curated relational database that provides detailed library information including tissue source, library construction methods, sequence diversity and sequence abundance. The differential expression of each EST species can be viewed across all libraries using a Virtual Expression Analysis Tool (VEAT), a graphical user interface written in Java for intra- and inter-library species comparisons. Recent enhancements to PEDB include: (i) the functional categorization of annotated EST assemblies using a classification scheme developed at The Institute for Genome Research; (ii) catalogs of expressed genes in specific prostate tissue sources designated as transcriptomes; and (iii) the addition of prostate proteome information derived from two-dimensional electrophoreses and mass spectrometry of prostate cancer cell lines. PEDB may be accessed via the WWW at http://www.mbt.washington.edu/PEDB/
Figures
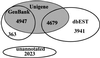
Figure 1
Results of PEDB cluster annotations against the GenBank, Unigene and dbEST nucleotide sequence database. Joining clusters based upon an identical public database sequence annotation reduced the number of distinct species from 21 114 to 15 953. As the Unigene database is comprised of sequences from both GenBank and dbEST, many PEDB clusters share annotations with two databases. Unannotated PEDB sequences represent clusters that do not have significant homology to any public database sequence.
Similar articles
- PEDB: the Prostate Expression Database.
Hawkins V, Doll D, Bumgarner R, Smith T, Abajian C, Hood L, Nelson PS. Hawkins V, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999 Jan 1;27(1):204-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.1.204. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999. PMID: 9847181 Free PMC article. - The human (PEDB) and mouse (mPEDB) Prostate Expression Databases.
Nelson PS, Pritchard C, Abbott D, Clegg N. Nelson PS, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):218-20. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.218. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11752298 Free PMC article. - PGDB: a curated and integrated database of genes related to the prostate.
Li LC, Zhao H, Shiina H, Kane CJ, Dahiya R. Li LC, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jan 1;31(1):291-3. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg008. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12520005 Free PMC article. - Rapid in silico cloning of genes using expressed sequence tags (ESTs).
Gill RW, Sanseau P. Gill RW, et al. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2000;5:25-44. doi: 10.1016/s1387-2656(00)05031-6. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2000. PMID: 10874996 Review. - Genomics of phytopathogenic fungi and the development of bioinformatic resources.
Soanes DM, Skinner W, Keon J, Hargreaves J, Talbot NJ. Soanes DM, et al. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2002 May;15(5):421-7. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2002.15.5.421. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2002. PMID: 12036272 Review.
Cited by
- Inhibition of androgen-independent prostate cancer by estrogenic compounds is associated with increased expression of immune-related genes.
Coleman IM, Kiefer JA, Brown LG, Pitts TE, Nelson PS, Brubaker KD, Vessella RL, Corey E. Coleman IM, et al. Neoplasia. 2006 Oct;8(10):862-78. doi: 10.1593/neo.06328. Neoplasia. 2006. PMID: 17032503 Free PMC article. - British Cancer Research Meeting 2001. Leeds, United Kingdom, 1-4 July 2001. Abstracts.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] Br J Cancer. 2001 Jul;85 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):1-116. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2001.1916. Br J Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11478310 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Molecular biologist's guide to proteomics.
Graves PR, Haystead TA. Graves PR, et al. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2002 Mar;66(1):39-63; table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.66.1.39-63.2002. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2002. PMID: 11875127 Free PMC article. Review. - Prostate cancer genomics.
Li PE, Nelson PS. Li PE, et al. Curr Urol Rep. 2001 Feb;2(1):70-8. doi: 10.1007/s11934-001-0028-6. Curr Urol Rep. 2001. PMID: 12084298 Review. - Adenoviral gene therapy, radiation, and prostate cancer.
Lupold SE, Rodriguez R. Lupold SE, et al. Rev Urol. 2005 Fall;7(4):193-202. Rev Urol. 2005. PMID: 16985830 Free PMC article.
References
- Huang X. (1996) Genomics, 33, 21–31. - PubMed
- Boguski M.S., Lowe,T.M.J. and Tolstoshev,C.M. (1993) Nature Genet., 4, 332–333. - PubMed
- Schuler G.D. (1997) J. Mol. Med., 75, 694–698. - PubMed
- Altschul S.F., Gish,W., Miller,W., Myers,E.W. and Lipman,D.J. (1990) J. Mol. Biol., 215, 403–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials