Duplication and maintenance of heterochromatin domains - PubMed (original) (raw)
Duplication and maintenance of heterochromatin domains
A Taddei et al. J Cell Biol. 1999.
Abstract
To investigate the mechanisms that assure the maintenance of heterochromatin regions, we took advantage of the fact that clusters of heterochromatin DNA replicate late in S phase and are processed in discrete foci with a characteristic nuclear distribution. At the light microscopy level, within these entities, we followed DNA synthesis, histone H4 acetylation, heterochromatin protein 1 (Hp1alpha and -beta), and chromatin assembly factor 1 (CAF-1). During replication, Hp1alpha and -beta domains of concentration are stably maintained, whereas heterochromatin regions are enriched in both CAF-1 and replication-specific acetylated isoforms of histone H4 (H4Ac 5 and 12). We defined a time window of 20 min for the maintenance of this state. Furthermore, treatment with Trichostatin A (TSA), during and after replication, sustains the H4Ac 5 and 12 state in heterochromatin excluding H4Ac 8 and 16. In comparison, early replication foci, at the same level, did not display any specific enrichment in H4Ac 5 and 12. These data emphasize the specific importance for heterochromatin of the replication-associated H4 isoforms. We propose that perpetuation of heterochromatin involves self-maintenance factors, including local concentration of Hp1alpha and -beta, and that a degree of plasticity is provided by the cycle of H4 acetylation/deacetylation assisted by CAF-1.
Figures
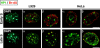
Figure 1
Domains rich in Hp1α and -β can be found at late replicating foci. Visualization of DNA replication sites in asynchronous populations of mouse (L929) and human (HeLa) cells was performed by in vivo BrdU pulse labeling and detected by immunofluorescence (red). Hp1α and -β were localized using specific mAbs (green). DNA was visualized by DAPI counterstaining (blue). Images of cells harboring replication foci patterns characteristic of either early (top) or late (bottom) S phase are shown. Bars, 10 μm.
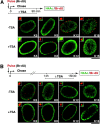
Figure 7
Dynamics of H4 acetylation in heterochromatin regions is restricted to the time of their DNA replication. A, Sites of DNA synthesis in an asynchronous population of HeLa cells were first labeled in vivo by BrdU pulse (red), and chased for 90 min either in the presence or absence of TSA (50 ng/ml). Different acetylated isoforms of H4 were localized using specific pAbs (K5, K8, K12, and K16, green). B, Sites of DNA synthesis in an asynchronous population of HeLa cells were first labeled in vivo by BrdU pulse (red), and chased for 14 h to allow late replicating cells, labeled during the pulse, to exit mitosis, before prolonged incubation in the absence or presence of TSA (50 ng/ml) for 90 min. Different acetylated isoforms of H4 were localized using specific pAbs (green). Digital merge of both signals, corresponding to single optical sections, are shown in each case. Bars, 10 μm. Note that these images were processed differently to permit visualization, because the intensities recorded were very different + or − TSA. Enlarged inserts (top left of each images) correspond to selected foci.
Similar articles
- Localizing Replication Sites and Nuclear Proteins.
Taddei A, Roche D, Sibarita JB, Huart S, Maison C, Bailly D, Almouzni G. Taddei A, et al. In: Mapping Protein/DNA Interactions by Cross-Linking [Internet]. Paris: Institut national de la santé et de la recherche médicale; 2001. In: Mapping Protein/DNA Interactions by Cross-Linking [Internet]. Paris: Institut national de la santé et de la recherche médicale; 2001. PMID: 21413362 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Histone deacetylase inhibition redistributes topoisomerase IIβ from heterochromatin to euchromatin.
Cowell IG, Papageorgiou N, Padget K, Watters GP, Austin CA. Cowell IG, et al. Nucleus. 2011 Jan-Feb;2(1):61-71. doi: 10.4161/nucl.2.1.14194. Nucleus. 2011. PMID: 21647300 Free PMC article. - Heterochromatin dynamics in mouse cells: interaction between chromatin assembly factor 1 and HP1 proteins.
Murzina N, Verreault A, Laue E, Stillman B. Murzina N, et al. Mol Cell. 1999 Oct;4(4):529-40. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80204-x. Mol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10549285 - Fission yeast chromatin assembly factor 1 assists in the replication-coupled maintenance of heterochromatin.
Dohke K, Miyazaki S, Tanaka K, Urano T, Grewal SI, Murakami Y. Dohke K, et al. Genes Cells. 2008 Oct;13(10):1027-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2008.01225.x. Epub 2008 Aug 29. Genes Cells. 2008. PMID: 18761674 - Replication of heterochromatin: insights into mechanisms of epigenetic inheritance.
Wallace JA, Orr-Weaver TL. Wallace JA, et al. Chromosoma. 2005 Dec;114(6):389-402. doi: 10.1007/s00412-005-0024-6. Epub 2005 Nov 15. Chromosoma. 2005. PMID: 16220346 Review.
Cited by
- Interplay between histone H3 lysine 56 deacetylation and chromatin modifiers in response to DNA damage.
Simoneau A, Delgoshaie N, Celic I, Dai J, Abshiru N, Costantino S, Thibault P, Boeke JD, Verreault A, Wurtele H. Simoneau A, et al. Genetics. 2015 May;200(1):185-205. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.175919. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 25786853 Free PMC article. - Co-repressor, co-activator and general transcription factor: the many faces of the Sin3 histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex.
Adams GE, Chandru A, Cowley SM. Adams GE, et al. Biochem J. 2018 Dec 14;475(24):3921-3932. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170314. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 30552170 Free PMC article. Review. - Chromosome regions enriched in hyperacetylated histone H4 are preferred sites for endonuclease- and radiation-induced breakpoints.
Martínez-López W, Folle GA, Obe G, Jeppesen P. Martínez-López W, et al. Chromosome Res. 2001;9(1):69-75. doi: 10.1023/a:1026747801728. Chromosome Res. 2001. PMID: 11272794 - Phase separation drives heterochromatin domain formation.
Strom AR, Emelyanov AV, Mir M, Fyodorov DV, Darzacq X, Karpen GH. Strom AR, et al. Nature. 2017 Jul 13;547(7662):241-245. doi: 10.1038/nature22989. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28636597 Free PMC article. - Chromatin and DNA replication.
MacAlpine DM, Almouzni G. MacAlpine DM, et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Aug 1;5(8):a010207. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a010207. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23751185 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Aagaard L., Laible G., Selenko P., Schmid M., Dorn R., Schotta G., Kuhfittig S., Wolf A., Lebersorger A., Singh P.B. Functional mammalian homologues of the Drosophila PEV-modifier Su(var)3-9 encode centromere-associated proteins which complex with the heterochromatin component M31. EMBO (Eur. Mol. Biol. Organ.) J. 1999;18:1923–1938. - PMC - PubMed
- Annunziato A.T. Histone acetylation during chromatin replication and nucleosome assembly. In: Wolffe A., editor. Nucleus. Vol. 1. JAI Press; Greenwich, CT: 1995. pp. 31–56.
- Belyaev N.D., Keohane A.M., Turner B.M. Histone H4 acetylation and replication timing in Chinese hamster chromosomes. Exp. Cell Res. 1996;225:277–285. - PubMed
- Bird A. The essentials of DNA methylation. Cell. 1992;70:5–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials