Lessons learned from the development of an abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor for chronic myelogenous leukemia - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Lessons learned from the development of an abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor for chronic myelogenous leukemia
B J Druker et al. J Clin Invest. 2000 Jan.
No abstract available
Figures
Figure 1
Structure of the Bcr-Abl gene. The Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22. Potential breakpoints are indicated by arrows. This resulting translocation replaces the first exon of c-abl with sequences from the Bcr gene.
Figure 2
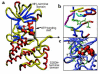
The crystal structure of AMP-PNP bound to Lck was used to made a model of the Abl kinase domain. (a) The general architecture of the Abl kinase domain. The NH2-terminal domain has a 5-strand β-sheet (blue) and 1 α-helix (red). The COOH-terminal domain is made up of several α-helices. ATP is shown in the ATP-binding cleft. (b) Topology of the ATP-binding cleft of the Abl protein kinase. The ATP-binding cleft can be subdivided into 6 regions: adenine-binding region (yellow), hydrophobic region I (blue), hydrophobic region II (aqua), phosphate-binding region (red-orange), the ribose pocket (purple), and the linker region (pink). The ligated ATP is shown in green-blue. (c) Amino acid side chains lining the ATP-binding cleft.
Figure 3
Model of STI 571 bound within the active site of the Abl kinase. (a) Overlay of ATP (red) and STI 571 (orange). Key amino acids that interact with ATP are shown. Binding mode of STI 571 shown from above (b) and from the side (c).
Similar articles
- Cancer research. Why some leukemia cells resist STI-571.
Marx J. Marx J. Science. 2001 Jun 22;292(5525):2231-3. doi: 10.1126/science.292.5525.2231a. Science. 2001. PMID: 11423629 No abstract available. - Targeting the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia.
Goldman JM, Melo JV. Goldman JM, et al. N Engl J Med. 2001 Apr 5;344(14):1084-6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200104053441409. N Engl J Med. 2001. PMID: 11287980 No abstract available. - Inhibition of the Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase as a therapeutic strategy for CML.
Druker BJ. Druker BJ. Oncogene. 2002 Dec 9;21(56):8541-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206081. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12476300 Review. No abstract available. - Quick success for cancer kinase treatment.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] Nat Med. 2001 Jun;7(6):637. doi: 10.1038/88961. Nat Med. 2001. PMID: 11385473 No abstract available. - Recent success with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI-571--lessons for targeted therapy of cancer.
Shah NP, Sawyers CL. Shah NP, et al. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2001 Mar;2(3):422-3. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11575716 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Selecting the best frontline treatment in chronic myeloid leukemia.
Yilmaz M, Abaza Y, Jabbour E. Yilmaz M, et al. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2015 Jun;10(2):145-57. doi: 10.1007/s11899-015-0254-5. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2015. PMID: 25921387 Free PMC article. Review. - Development of an effective therapy for chronic myelogenous leukemia.
Woessner DW, Lim CS, Deininger MW. Woessner DW, et al. Cancer J. 2011 Nov-Dec;17(6):477-86. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e318237e5b7. Cancer J. 2011. PMID: 22157291 Free PMC article. Review. - Exploiting Replication Stress as a Novel Therapeutic Intervention.
Martin JC, Hoegel TJ, Lynch ML, Woloszynska A, Melendy T, Ohm JE. Martin JC, et al. Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Feb;19(2):192-206. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0651. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33020173 Free PMC article. Review. - Are breast cancers driven by fusion genes?
Edwards PA, Howarth KD. Edwards PA, et al. Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 16;14(2):303. doi: 10.1186/bcr3122. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22424054 Free PMC article. - Regulation of survivin expression through Bcr-Abl/MAPK cascade: targeting survivin overcomes imatinib resistance and increases imatinib sensitivity in imatinib-responsive CML cells.
Carter BZ, Mak DH, Schober WD, Cabreira-Hansen M, Beran M, McQueen T, Chen W, Andreeff M. Carter BZ, et al. Blood. 2006 Feb 15;107(4):1555-63. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-12-4704. Epub 2005 Oct 27. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16254145 Free PMC article.
References
- Kolibaba KS, Druker BJ. Protein tyrosine kinases and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1333:F217–F248. - PubMed
- Rowley JD. A new consistent abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and giemsa staining. Nature. 1973;243:290–293. - PubMed
- Heisterkamp N, et al. Localization of the c-abl oncogene adjacent to a translocation break point in chronic myelocytic leukemia. Nature. 1983;306:239–242. - PubMed
- Bartram CR, et al. Translocation of c-abl correlates with the presence of a Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelocytic leukemia. Nature. 1983;306:277–280. - PubMed
- Shtivelman E, Lifshitz B, Gale RP, Canaani E. Fused transcript of abl and bcr genes in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nature. 1985;315:550–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous