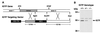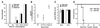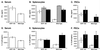Pathogen-specific loss of host resistance in mice lacking the IFN-gamma-inducible gene IGTP - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2000 Jan 18;97(2):751-5.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.2.751.
C M Collazo, G S Yap, K Nguyen, T A Gregorio, L S Taylor, B Eagleson, L Secrest, E A Southon, S W Reid, L Tessarollo, M Bray, D W McVicar, K L Komschlies, H A Young, C A Biron, A Sher, G F Vande Woude
Affiliations
- PMID: 10639151
- PMCID: PMC15402
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.2.751
Pathogen-specific loss of host resistance in mice lacking the IFN-gamma-inducible gene IGTP
G A Taylor et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000.
Abstract
Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) is critical for defense against pathogens, but the molecules that mediate its antimicrobial responses are largely unknown. IGTP is the prototype for a family of IFN-gamma-regulated genes that encode 48-kDa GTP-binding proteins that localize to the endoplasmic reticulum. We have generated IGTP-deficient mice and found that, despite normal immune cell development and normal clearance of Listeria monocytogenes and cytomegalovirus infections, the mice displayed a profound loss of host resistance to acute infections of the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. By contrast, IFN-gamma receptor-deficient mice have increased susceptibility to all three pathogens. Thus, IGTP defines an IFN-gamma-regulated pathway with a specialized role in antimicrobial resistance.
Figures
Figure 1
Targeting the IGTP gene. (A) An IGTP replacement targeting vector was prepared from the indicated IGTP gene fragments and used to generate IGTP-deficient mice. (B) Thymic protein from mice of the indicated genotypes was resolved by 10% SDS/PAGE and used for Western blotting with anti-C-terminal IGTP antisera. The positions of selected molecular weight markers are shown at the left.
Figure 2
Induction of IGTP expression by different pathogens. Pairs of wild-type mice (B and C), or wild-type and IGTP-deficient mice (A), were inoculated with 1,000 L. monocytogenes for 3 days (A), 105 plaque-forming units MCMV for 36 or 72 hr (B), or 20 cysts ME49 strain T. gondii for 5 days (C). Protein lysates were prepared from the indicated tissues or cells and used for Western blotting with an anti-IGTP antibody. The positions of selected molecular weight markers are indicated at the left.
Figure 3
Differential susceptibility of IGTP-deficient mice to pathogens. (A) Wild-type, IGTP-deficient (IGTP KO), or IFN-γ receptor-deficient (IFNgR KO) mice were inoculated i.p. with the indicated doses of L. monocytogenes, and mortality was assessed over a 14-day period. (B) Wild-type, IGTP-deficient, or IFN-γ receptor-deficient mice were inoculated i.p. with 1,000 L. monocytogenes; after 3 days, the number of bacteria in the liver was determined. (C) Wild-type or IGTP-deficient mice were inoculated with 105 plaque-forming units MCMV i.p.; after 36 or 72 h, the number of virus in the liver was determined. (D) Wild-type and IGTP-deficient mice were inoculated i.p. with 20 cysts ME49 strain T. gondii. The cumulative mortality of the indicated numbers of IGTP-deficient mice (◊) or wild-type mice (□) was followed for 40 days after infection. The graph is representative of three experiments.
Figure 4
Undiminished IL-12 p40 and IFN-γ production in _T. gondii_-infected IGTP-deficient mice. Mice were inoculated i.p. with 20 cysts ME49 strain T. gondii. Five days postinoculation of IGTP-deficient or wild-type mice, IL-12 p40 and IFN-γ levels were determined in sera (A and D) and the conditioned media of cultures splenocytes (B and E) or PECs (C and F). Splenocytes and PECs were incubated in control medium (open bars), medium supplemented with anti-CD3 antibody (striped bars), or medium supplemented with a soluble Toxoplasma antigen mixture, STAg (filled bars). SD for groups of four mice are shown.
Figure 5
Undiminished iNOS production in _T. gondii_-infected IGTP-deficient mice. Wild-type, IGTP-deficient (IGTP KO), and IFN-γ receptor-deficient (IFNgR KO) mice were inoculated i.p. with 20 cysts ME49 strain T. gondii. Eight days postinoculation, hepatic mRNA was prepared and used for sequential Northern blotting with iNOS and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase probes. Positions of the major ribosomal RNA species are indicated as determined from the stained gel.
Similar articles
- Inactivation of LRG-47 and IRG-47 reveals a family of interferon gamma-inducible genes with essential, pathogen-specific roles in resistance to infection.
Collazo CM, Yap GS, Sempowski GD, Lusby KC, Tessarollo L, Vande Woude GF, Sher A, Taylor GA. Collazo CM, et al. J Exp Med. 2001 Jul 16;194(2):181-8. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.2.181. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11457893 Free PMC article. - The function of gamma interferon-inducible GTP-binding protein IGTP in host resistance to Toxoplasma gondii is Stat1 dependent and requires expression in both hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cellular compartments.
Collazo CM, Yap GS, Hieny S, Caspar P, Feng CG, Taylor GA, Sher A. Collazo CM, et al. Infect Immun. 2002 Dec;70(12):6933-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.12.6933-6939.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12438372 Free PMC article. - Gamma interferon-induced inhibition of Toxoplasma gondii in astrocytes is mediated by IGTP.
Halonen SK, Taylor GA, Weiss LM. Halonen SK, et al. Infect Immun. 2001 Sep;69(9):5573-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.9.5573-5576.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11500431 Free PMC article. - p47 GTPases: regulators of immunity to intracellular pathogens.
Taylor GA, Feng CG, Sher A. Taylor GA, et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004 Feb;4(2):100-9. doi: 10.1038/nri1270. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15040583 Review.
Cited by
- Striking a balance: new perspectives on homeostatic dendritic cell maturation.
Bosteels V, Janssens S. Bosteels V, et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024 Sep 17. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01079-5. Online ahead of print. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39289483 Review. - IL-12 Mediates T-bet-Expressing Myeloid Cell-Dependent Host Resistance against Toxoplasma gondii.
Schanz ML, Bitters AM, Zadeii KE, Joulani D, Chamberlain AK, López-Yglesias AH. Schanz ML, et al. Immunohorizons. 2024 Apr 1;8(4):355-362. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2400029. Immunohorizons. 2024. PMID: 38687282 Free PMC article. - iNOS is necessary for GBP-mediated T. gondii clearance in murine macrophages via vacuole nitration and intravacuolar network collapse.
Zhao XY, Lempke SL, Urbán Arroyo JC, Brown IG, Yin B, Magaj MM, Holness NK, Smiley J, Redemann S, Ewald SE. Zhao XY, et al. Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 27;15(1):2698. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46790-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38538595 Free PMC article. - IFNs in host defence and parasite immune evasion during Toxoplasma gondii infections.
Lüder CGK. Lüder CGK. Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 7;15:1356216. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1356216. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38384452 Free PMC article. Review. - Transcriptomic Variation of Amphiprion Percula (Lacepède, 1802) in Response to Infection with Cryptocaryon Irritans Brown, 1951.
T A JP, Karunakaran C, Nath A, Kappalli S. T A JP, et al. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2023 Dec;25(6):858-890. doi: 10.1007/s10126-023-10246-z. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2023. PMID: 37695540
References
- Stark G R, Kerr I M, Williams B R G, Silverman R H, Schreiber R D. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:227–264. - PubMed
- Boehm U, Klamp T, Groot M, Howard J C. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:749–795. - PubMed
- Billiau A. Adv Immunol. 1996;62:61–130. - PubMed
- Dalton D K, Pitts-Meek S, Keshav S, Figari I S, Bradley A, Stewart T. Science. 1993;259:1739–1742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials