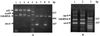PCR-Based assay for discrimination between invasive and contaminating Staphylococcus epidermidis strains - PubMed (original) (raw)
PCR-Based assay for discrimination between invasive and contaminating Staphylococcus epidermidis strains
N B Frebourg et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Feb.
Abstract
The discrimination between Staphylococcus epidermidis strains that contaminate and infect blood cultures is a daily challenge for clinical laboratories. The results of PCR detection of putative virulence genes were compared for contaminating strains, sepsis-related strains, catheter strains, and saprophytic strains. Multiplex PCR was used to explore the atlE gene, which is involved in initial adherence, the intercellular adhesion gene cluster (ica), which mediates the formation of the biofilm, and the agrA, sarA, and mecA genes, which might contribute to the pathogenicity of S. epidermidis. Whereas the atlE, agrA, and sarA genes were almost ubiquitously amplified, the ica and mecA genes were detected significantly more in infecting strains than in contaminating strains (P </= 0.02) and thus appeared to be related to the potential virulence of S. epidermidis.
Figures
FIG. 1
Multiplex amplifications of representative S. epidermidis strains. (A) Multiplex PCR of altE, icaAB, and 16S rRNA gene fragments (lanes 1 to 4) and of mecA and 16S rRNA gene fragments (lanes 6 to 9). Lanes 1, 4, 7, and 8, blood culture-contaminating isolates; lanes 2, 3, and 6, sepsis-related isolates; lane 5, molecular weight marker (pBR322 DNA-_Msp_I digest); lane 9, healthy volunteer isolate. (B) Multiplex PCR of agrA, 16S rRNA, and sarA gene fragments. Lane 1, sepsis-related isolate; lane 2, blood culture-contaminating isolate; lane 3, molecular weight marker (pBR322 DNA-_Msp_I digest).
Similar articles
- Detection of virulence-associated genes not useful for discriminating between invasive and commensal Staphylococcus epidermidis strains from a bone marrow transplant unit.
Rohde H, Kalitzky M, Kröger N, Scherpe S, Horstkotte MA, Knobloch JK, Zander AR, Mack D. Rohde H, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Dec;42(12):5614-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.12.5614-5619.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15583290 Free PMC article. - The effect of iatrogenic Staphylococcus epidermidis intercellar adhesion operon on the formation of bacterial biofilm on polyvinyl chloride surfaces.
Lianhua Y, Yunchao H, Guangqiang Z, Kun Y, Xing L, Fengli G. Lianhua Y, et al. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2014 Dec;15(6):768-73. doi: 10.1089/sur.2013.129. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2014. PMID: 25402758 Free PMC article. - Strong biofilm production but not adhesion virulence factors can discriminate between invasive and commensal Staphylococcus epidermidis strains.
Mekni MA, Bouchami O, Achour W, Ben Hassen A. Mekni MA, et al. APMIS. 2012 Aug;120(8):605-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2012.02877.x. Epub 2012 Mar 5. APMIS. 2012. PMID: 22779682 - Staphylococcus epidermidis as a cause of bacteremia.
Kleinschmidt S, Huygens F, Faoagali J, Rathnayake IU, Hafner LM. Kleinschmidt S, et al. Future Microbiol. 2015;10(11):1859-79. doi: 10.2217/fmb.15.98. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Future Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26517189 Review. - Molecular genetics of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms on indwelling medical devices.
Vadyvaloo V, Otto M. Vadyvaloo V, et al. Int J Artif Organs. 2005 Nov;28(11):1069-78. doi: 10.1177/039139880502801104. Int J Artif Organs. 2005. PMID: 16353113 Review.
Cited by
- Capillary flow velocity-based length identification of PCR and RPA products on paper microfluidic chips.
Buchanan BC, Loeffler RS, Liang R, Yoon JY. Buchanan BC, et al. Biosens Bioelectron. 2025 Jan 1;267:116861. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2024.116861. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Biosens Bioelectron. 2025. PMID: 39455308 - Analysis of the Presence of the Virulence and Regulation Genes from Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) in Coagulase Negative Staphylococci and the Influence of the Staphylococcal Cross-Talk on Their Functions.
Grazul M, Balcerczak E, Sienkiewicz M. Grazul M, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Mar 15;20(6):5155. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20065155. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36982064 Free PMC article. - Improved Genomic Prediction of Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolation Sources with a Novel Polygenic Score.
Hellmann KT, Challagundla L, Gray BM, Robinson DA. Hellmann KT, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2023 Mar 23;61(3):e0141222. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01412-22. Epub 2023 Feb 22. J Clin Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36840569 Free PMC article. - May Staphylococcus lugdunensis Be an Etiological Factor of Chronic Maxillary Sinuses Infection?
Kosecka-Strojek M, Wolska-Gębarzewska M, Podbielska-Kubera A, Samet A, Krawczyk B, Międzobrodzki J, Michalik M. Kosecka-Strojek M, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 9;23(12):6450. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126450. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35742895 Free PMC article. - Comparative profiling of agr locus, virulence, and biofilm-production genes of human and ovine non-aureus staphylococci.
Azara E, Longheu CM, Attene S, Sanna S, Sale M, Addis MF, Tola S. Azara E, et al. BMC Vet Res. 2022 Jun 2;18(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03257-w. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35655210 Free PMC article.
References
- Archer G L. Alteration of cutaneous staphylococcal flora as a consequence of antimicrobial prophylaxis. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13(Suppl. 10):805–809. - PubMed
- Brun-Buisson C, Abrouk F, Legrand P, Huet Y, Larabi S, Rapin M. Diagnosis of central venous catheter-related sepsis. Critical level of quantitative tip cultures. Arch Intern Med. 1987;147:873–877. - PubMed
- Christensen G D, Baddour L M, Madison B M, Parisi J T, Abraham S N, Hasty D L, Lowrance J H, Josephs J A, Simpson W A. Colonial morphology of staphylococci on Memphis agar: phase variation of slime production, resistance to β-lactam antibiotics, and virulence. J Infect Dis. 1990;161:1153–1159. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous