Novel phospholipase A activity secreted by Legionella species - PubMed (original) (raw)
Novel phospholipase A activity secreted by Legionella species
A Flieger et al. J Bacteriol. 2000 Mar.
Abstract
Bacterial phospholipases are regarded as a major virulence factor in infection. In bacteria associated with pneumonia, destruction of lung surfactant and host cell membranes by bacterial phospholipases secreted during infection is thought to contribute to the disease. Phospholipase C (PLC) activity has been described in several Legionella species (W. B. Baine, J. Gen. Microbiol. 134:489-498, 1988; W. B. Baine, J. Gen. Microbiol. 131:1383-1391, 1985). By using detection methods such as thin-layer chromatography and mass spectrometry, PLC activity could not be detected in several strains of Legionella pneumophila. Instead, phospholipid degradation was identified to be caused by a novel PLA activity. We could demonstrate that PLA secretion starts at the mid-exponential-growth phase when bacteria were grown in liquid culture. Several Legionella species secreted different amounts of PLA. Legionella PLA may act as a powerful agent in the mediation of pathogenicity due to destruction of lung surfactant and epithelial cells.
Figures
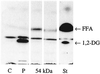
FIG. 1
Apolar and polar lipids after incubation of PC with CCCS of L. pneumophila. PC was incubated with the CCCS of different L. pneumophila strains for 16 h. Apolar (A) and polar (B) lipids were characterized by TLC. A representative experiment is shown. Abbreviations: St, standard (1A, 1,2-dipalmitoylglycerol, palmitic acid; 1B, LPC, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine); C, negative control (concentrated BYE broth or concentrated −P broth, respectively); P, positive control (PLC from C. perfringens); 1, Lp1-MM6; 2, Lp1-MRC; 3, Lp2-ATCC; 4, Lp6-c; 5, Lp12-ATCC.
FIG. 2
Characterization of AEC fractions. CCCS of Lp6-c was applied onto an AEC column. Fractions eluted by 0.1 to 0.7 M sodium chloride were investigated for protein content, hydrolysis of _p_-NPPC (OD410), and hydrolysis of phosphomonoesters (Pi content). A representative experiment is shown.
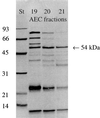
FIG. 3
SDS-PAGE of AEC fractions causing hydrolysis of _p_-NPPC. St, molecular weight standard in kilodaltons; 19–21, AEC fractions. The 54-kDa protein band is designated by the arrow. A representative experiment is shown.
FIG. 4
Apolar lipids after incubation of Alveofact with AEC fractions containing the 54-kDa protein. Alveofact was incubated with AEC fractions containing the 54-kDa protein for 16 h. Apolar lipids were characterized by TLC. A representative experiment is shown. Abbreviations: C, negative control (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.2); P, positive control (PLC from C. perfringens); St, standard (1,2-dipalmitoylglycerol, palmitic acid).
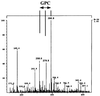
FIG. 5
ESI-MS. CCCS of Lp6-c was incubated with Alveofact for 16 h. Lipids were separated from the water-soluble substances by lipid extraction. Water-soluble substances were analyzed by ESI-MS. A representative experiment is shown.
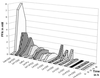
FIG. 6
Kinetics of PLA secretion in different Legionella species. Legionellae were grown in BYE broth. PLA activity was determined after incubation of the culture supernatant with Alveofact for 24 h by detection of FFA release. Data are mean values. For a better survey, standard deviations which were maximally ±0.1 mM were not added to the diagram.
Similar articles
- Phospholipase PlaB of Legionella pneumophila represents a novel lipase family: protein residues essential for lipolytic activity, substrate specificity, and hemolysis.
Bender J, Rydzewski K, Broich M, Schunder E, Heuner K, Flieger A. Bender J, et al. J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 2;284(40):27185-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.026021. Epub 2009 Jul 29. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19640837 Free PMC article. - In vitro secretion kinetics of proteins from Legionella pneumophila in comparison to proteins from non-pneumophila species.
Flieger A, Gong S, Faigle M, Northoff H, Neumeister B. Flieger A, et al. Microbiology (Reading). 2001 Nov;147(Pt 11):3127-34. doi: 10.1099/00221287-147-11-3127. Microbiology (Reading). 2001. PMID: 11700363 - Phospholipase A secreted by Legionella pneumophila destroys alveolar surfactant phospholipids.
Flieger A, Gongab S, Faigle M, Mayer HA, Kehrer U, Mussotter J, Bartmann P, Neumeister B. Flieger A, et al. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000 Jul 15;188(2):129-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09183.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000. PMID: 10913695 - Secreted phospholipases of the lung pathogen Legionella pneumophila.
Hiller M, Lang C, Michel W, Flieger A. Hiller M, et al. Int J Med Microbiol. 2018 Jan;308(1):168-175. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Oct 28. Int J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29108710 Review. - The manifold phospholipases A of Legionella pneumophila - identification, export, regulation, and their link to bacterial virulence.
Banerji S, Aurass P, Flieger A. Banerji S, et al. Int J Med Microbiol. 2008 Apr;298(3-4):169-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2007.11.004. Epub 2008 Jan 4. Int J Med Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18178130 Review.
Cited by
- Cloning and characterization of the gene encoding the major cell-associated phospholipase A of Legionella pneumophila, plaB, exhibiting hemolytic activity.
Flieger A, Rydzewski K, Banerji S, Broich M, Heuner K. Flieger A, et al. Infect Immun. 2004 May;72(5):2648-58. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.5.2648-2658.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15102773 Free PMC article. - Characterization of the major secreted zinc metalloprotease- dependent glycerophospholipid:cholesterol acyltransferase, PlaC, of Legionella pneumophila.
Banerji S, Bewersdorff M, Hermes B, Cianciotto NP, Flieger A. Banerji S, et al. Infect Immun. 2005 May;73(5):2899-909. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.5.2899-2909.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15845496 Free PMC article. - Secreted enzymatic activities of wild-type and pilD-deficient Legionella pneumophila.
Aragon V, Kurtz S, Flieger A, Neumeister B, Cianciotto NP. Aragon V, et al. Infect Immun. 2000 Apr;68(4):1855-63. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.4.1855-1863.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10722574 Free PMC article. - Phospholipase PlaB of Legionella pneumophila represents a novel lipase family: protein residues essential for lipolytic activity, substrate specificity, and hemolysis.
Bender J, Rydzewski K, Broich M, Schunder E, Heuner K, Flieger A. Bender J, et al. J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 2;284(40):27185-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.026021. Epub 2009 Jul 29. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19640837 Free PMC article. - The global regulatory proteins LetA and RpoS control phospholipase A, lysophospholipase A, acyltransferase, and other hydrolytic activities of Legionella pneumophila JR32.
Broich M, Rydzewski K, McNealy TL, Marre R, Flieger A. Broich M, et al. J Bacteriol. 2006 Feb;188(4):1218-26. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.4.1218-1226.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16452402 Free PMC article.
References
- Aronson J F, Johns L W. Injury of lung alveolar cells by lysolecithin. Exp Mol Pathol. 1977;27:35–42. - PubMed
- Baine W B. A phospholipase C from the Dallas 1E strain of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 5: purification and characterization of conditions of optimal activity with an artificial substrate. J Gen Microbiol. 1988;134:489–498. - PubMed
- Baine W B. Cytolytic and phospholipase C activity in Legionella species. J Gen Microbiol. 1985;13:1383–1391. - PubMed
- Belyi Y F. Intracellular parasitism of Legionella and signaling in eukaryotic cells. FASEB J. 1993;7:1011–1005. - PubMed
- Bligh E G, Dyer W J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959;37:911–917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources