Y chromosomes traveling south: the cohen modal haplotype and the origins of the Lemba--the "Black Jews of Southern Africa" - PubMed (original) (raw)
Y chromosomes traveling south: the cohen modal haplotype and the origins of the Lemba--the "Black Jews of Southern Africa"
M G Thomas et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Feb.
Abstract
The Lemba are a traditionally endogamous group speaking a variety of Bantu languages who live in a number of locations in southern Africa. They claim descent from Jews who came to Africa from "Sena." "Sena" is variously identified by them as Sanaa in Yemen, Judea, Egypt, or Ethiopia. A previous study using Y-chromosome markers suggested both a Bantu and a Semitic contribution to the Lemba gene pool, a suggestion that is not inconsistent with Lemba oral tradition. To provide a more detailed picture of the Lemba paternal genetic heritage, we analyzed 399 Y chromosomes for six microsatellites and six biallelic markers in six populations (Lemba, Bantu, Yemeni-Hadramaut, Yemeni-Sena, Sephardic Jews, and Ashkenazic Jews). The high resolution afforded by the markers shows that Lemba Y chromosomes are clearly divided into Semitic and Bantu clades. Interestingly, one of the Lemba clans carries, at a very high frequency, a particular Y-chromosome type termed the "Cohen modal haplotype," which is known to be characteristic of the paternally inherited Jewish priesthood and is thought, more generally, to be a potential signature haplotype of Judaic origin. The Bantu Y-chromosome samples are predominantly (>80%) YAP+ and include a modal haplotype at high frequency. Assuming a rapid expansion of the eastern Bantu, we used variation in microsatellite alleles in YAP+ sY81-G Bantu Y chromosomes to calculate a rough date, 3,000-5,000 years before the present, for the start of their expansion.
Figures
Figure 1
Cladogram of UEP, distinguishing UEP groups. Explanations of abbreviations are as in table 1.
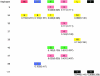
Figure 2
Frequently encountered haplotypes (frequency >10% in any population), in AI (red), SI (blue), Y (green), S (pink), L (yellow), and B (black); the colors indicate the population with the most chromosomes of the given haplotype. Numbers within the boxes are number of Y chromosomes in the population; numbers below the boxes are the frequency within the population (i.e., frequency within a UEP group). Explanations of abbreviations are as in table 1.
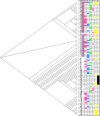
Figure 3
UEP group 1 genealogical tree of Y-chromosome haplotypes. The neighbor-joining tree was drawn by use of NEIGHBOR (part of the PHYLIP package), with the distance measure ASD calculated by use of the program MICROSAT. Colors next to the haplotype index numbers indicate the presence of Y chromosomes in the relevant population. H.I. = haplotype index number, H/L = high (⩾15 [_brown_]), low (⩽12 [_white_]), or intermediate (13 or 14 [_gray_]) number of repeats for microsatellite DYS388. Results are for AI (red), SI (blue), Y (green), S (pink), L (yellow), and B (black). Explanations of abbreviations are as in table 1.
Similar articles
- The origins of the Lemba "Black Jews" of southern Africa: evidence from p12F2 and other Y-chromosome markers.
Spurdle AB, Jenkins T. Spurdle AB, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Nov;59(5):1126-33. Am J Hum Genet. 1996. PMID: 8900243 Free PMC article. - Lemba origins revisited: tracing the ancestry of Y chromosomes in South African and Zimbabwean Lemba.
Soodyall H. Soodyall H. S Afr Med J. 2013 Oct 11;103(12 Suppl 1):1009-13. doi: 10.7196/samj.7297. S Afr Med J. 2013. PMID: 24300649 - The Y chromosome pool of Jews as part of the genetic landscape of the Middle East.
Nebel A, Filon D, Brinkmann B, Majumder PP, Faerman M, Oppenheim A. Nebel A, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Nov;69(5):1095-112. doi: 10.1086/324070. Epub 2001 Sep 25. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11573163 Free PMC article. - Constructing black Jews: genetic tests and the Lemba--the 'black Jews' of South Africa.
Parfitt T. Parfitt T. Dev World Bioeth. 2003 Dec;3(2):112-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-8731.2003.00066.x. Dev World Bioeth. 2003. PMID: 14768642 - Bantu siderosis--a review.
Buchanan WM. Buchanan WM. Cent Afr J Med. 1969 May;15(5):105-13. Cent Afr J Med. 1969. PMID: 4895575 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Evaluating the Y chromosomal STR dating in deep-rooting pedigrees.
Wang CC, Li H. Wang CC, et al. Investig Genet. 2015 May 28;6:8. doi: 10.1186/s13323-015-0025-z. eCollection 2015. Investig Genet. 2015. PMID: 26060571 Free PMC article. - Bimodal allele frequency distribution at Y-STR loci DYS392 and DYS438: no evidence for a deviation from the stepwise mutation model.
Gusmão L, Krawczak M, Sánchez-Diz P, Alves C, Lopes A, Beleza S, Carracedo A, Amorim A. Gusmão L, et al. Int J Legal Med. 2003 Oct;117(5):287-90. doi: 10.1007/s00414-003-0388-1. Epub 2003 Jul 12. Int J Legal Med. 2003. PMID: 12861418 - Portuguese crypto-Jews: the genetic heritage of a complex history.
Nogueiro I, Teixeira JC, Amorim A, Gusmão L, Alvarez L. Nogueiro I, et al. Front Genet. 2015 Feb 2;6:12. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00012. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25699075 Free PMC article. Review. - The multiple meanings of Jewish genes.
Kahn SM. Kahn SM. Cult Med Psychiatry. 2005 Jun;29(2):179-92. doi: 10.1007/s11013-005-7424-5. Cult Med Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 16249949 - The making of the African mtDNA landscape.
Salas A, Richards M, De la Fe T, Lareu MV, Sobrino B, Sánchez-Diz P, Macaulay V, Carracedo A. Salas A, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Nov;71(5):1082-111. doi: 10.1086/344348. Epub 2002 Oct 22. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 12395296 Free PMC article.
References
- Bradman N, Thomas M, Goldstein DG. The genetic origins of Old Testament priests. In: Renfrew C (ed) Population specific polymorphisms. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (in press)
- Cavalli-Sforza LL, Menozzi P, Piazza A (1994) The history and geography of human genes. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ
- Encyclopedia Judaica (1972) Keter Publishing House, Jerusalem
- Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP (phylogeny inference package) version 3.5c. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle
- Goldstein DB, Pollock DD (1997) Launching microsatellites: a review of mutation processes and methods of phylogenetic inference. J Hered 88:335–342 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources