Activation of Broca's area by syntactic processing under conditions of concurrent articulation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Activation of Broca's area by syntactic processing under conditions of concurrent articulation
D Caplan et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2000 Feb.
Abstract
Regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) was measured with positron emission tomography (PET) when 11 subjects made plausibility judgments about written sentences that varied in their syntactic complexity. While making their judgments, subjects uttered the word "double" aloud at a rate of one utterance per second to inhibit their ability to rehearse the sentences. Blood flow increased in Broca's area when subjects made judgments about the more complex sentences. This result replicates and extends previous findings that blood flow increases in this region when subjects process complex syntax under no interference conditions. The results of this experiment provide strong evidence that the increase in blood flow seen in Broca's area in association with processing syntactically complex structures is not due to subvocal rehearsal of those structures, but rather results from processing syntactic forms themselves.
Figures
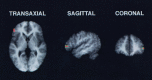
Figure 1
Statistical parameter mapping (SPM) image showing an increase in rCBF in Broca's area when subjects processed syntactically more complex sentences under conditions of concurrent articulation.
Similar articles
- Localization of syntactic comprehension by positron emission tomography.
Stromswold K, Caplan D, Alpert N, Rauch S. Stromswold K, et al. Brain Lang. 1996 Mar;52(3):452-73. doi: 10.1006/brln.1996.0024. Brain Lang. 1996. PMID: 8653390 - Effects of syntactic structure and propositional number on patterns of regional cerebral blood flow.
Caplan D, Alpert N, Waters G. Caplan D, et al. J Cogn Neurosci. 1998 Jul;10(4):541-52. doi: 10.1162/089892998562843. J Cogn Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9712683 - PET studies of syntactic processing with auditory sentence presentation.
Caplan D, Alpert N, Waters G. Caplan D, et al. Neuroimage. 1999 Mar;9(3):343-51. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1998.0412. Neuroimage. 1999. PMID: 10075904 - Serial aspects of language and speech related to prefrontal cortical activity. A selective review.
Ingvar DH. Ingvar DH. Hum Neurobiol. 1983;2(3):177-89. Hum Neurobiol. 1983. PMID: 6365859 Review. - The role of Broca's area in sentence comprehension.
Rogalsky C, Hickok G. Rogalsky C, et al. J Cogn Neurosci. 2011 Jul;23(7):1664-80. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2010.21530. Epub 2010 Jul 9. J Cogn Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 20617890 Review.
Cited by
- The BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism Influences Reading Ability and Patterns of Neural Activation in Children.
Jasińska KK, Molfese PJ, Kornilov SA, Mencl WE, Frost SJ, Lee M, Pugh KR, Grigorenko EL, Landi N. Jasińska KK, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Aug 23;11(8):e0157449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157449. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27551971 Free PMC article. - Differences in neural activation between preterm and full term born adolescents on a sentence comprehension task: implications for educational accommodations.
Barde LH, Yeatman JD, Lee ES, Glover G, Feldman HM. Barde LH, et al. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2012 Feb 15;2 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S114-28. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2011.10.002. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22682901 Free PMC article. - Functional MRI of language in aphasia: a review of the literature and the methodological challenges.
Crosson B, McGregor K, Gopinath KS, Conway TW, Benjamin M, Chang YL, Moore AB, Raymer AM, Briggs RW, Sherod MG, Wierenga CE, White KD. Crosson B, et al. Neuropsychol Rev. 2007 Jun;17(2):157-77. doi: 10.1007/s11065-007-9024-z. Epub 2007 May 25. Neuropsychol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17525865 Free PMC article. Review. - Cognitive modules utilized for narrative comprehension in children: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study.
Schmithorst VJ, Holland SK, Plante E. Schmithorst VJ, et al. Neuroimage. 2006 Jan 1;29(1):254-66. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.07.020. Epub 2005 Aug 18. Neuroimage. 2006. PMID: 16109491 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Anatomical substrates of visual and auditory miniature second-language learning.
Newman-Norlund RD, Frey SH, Petitto LA, Grafton ST. Newman-Norlund RD, et al. J Cogn Neurosci. 2006 Dec;18(12):1984-97. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2006.18.12.1984. J Cogn Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17129186 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Alpert N, Berdichevsky D, Weise S, Tang J, Rauch S. 1993. Stereotactic transformation of PET scans by nonlinear least squares In: Uemura K, editor. Quantifications of brain functions: tracer kinetics and image analysis in brain PET. New York: Elsevier, p 459–463.
- Alpert NM, Berdichevsky D, Levin Z, Morris ED, Faschman AJ. 1996. Improved methods for image registration. NeuroImage 3: 10–18. - PubMed
- Amunts K, Schleicher A, Bergell U, Mohlberg J, Uylings HBM, Zilles K. 1999. Broca's region re‐visited: cytoarchitecture and intersubject variability. J Comp Neurol (in press). - PubMed
- Baddeley AD. 1986. Working memory. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Baddeley AD, Thompson N, Buchanan M. 1975. Word length and the structure of short‐term memory. J Verbal Learning Verbal Behavior 14: 575–589.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources