Evaluation of the discriminatory powers of the Dienes test and ribotyping as typing methods for Proteus mirabilis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Evaluation of the discriminatory powers of the Dienes test and ribotyping as typing methods for Proteus mirabilis
M A Pfaller et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Mar.
Abstract
A total of 63 clinical isolates of Proteus mirabilis collected over a 19-month period were typed by the Dienes test and ribotyping. Ribotyping was performed using the fully automated RiboPrinter Microbial Characterization System (Qualicon, Wilmington, Del.). Isolates that were indistinguishable by the Dienes test and/or ribotyping were characterized further by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Most of the isolates represented unique strains as judged by the Dienes test and ribotyping. Forty isolates represented 40 different ribotypes and Dienes types. The remaining 23 isolates were grouped into 13 Dienes types, 12 ribotypes, and 14 PFGE types. The index of discrimination was 0.980 for the Dienes test, 0.979 for ribotyping, and 0.992 for PFGE. Both the Dienes test and ribotyping are useful methods for identifying individual strains of P. mirabilis. The Dienes test is simple, inexpensive, and easy to perform. It can be performed in virtually any laboratory and should be used in the initial epidemiologic characterization of P. mirabilis isolates.
Figures
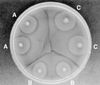
FIG. 1
Dienes test showing three different strains, A, B, and C. Note the absence of Dienes lines between identical strains A and A, B and B, and C and C, respectively. Likewise, note the distinct lines of demarcation between strains A, B, and C.
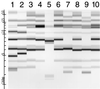
FIG. 2
Ribotype profiles of 10 different isolates of P. mirabilis. Lane 1, ribotype 851.4; lane 2, ribotype 851.8; lanes 3, 8, and 10, ribotype 855.7; lanes 4 and 6, ribotype 858.2; lane 5, ribotype 859.5; lanes 7 and 9, ribotype 637.8. Molecular size markers in terms of kilobase pairs are shown at the left of the figure.
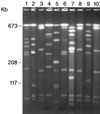
FIG. 3
PFGE profiles of 10 different isolates of P. mirabilis (same order as in Fig. 2). Lane 1, PFGE type 16; lane 2, PFGE type 3; lanes 3, 8, and 10, PFGE type 4; lane 4, PFGE type 8; lane 5, PFGE type 17; lane 6, PFGE type 6; lane 7, PFGE type 11; lane 9, PFGE type 9.
Similar articles
- Molecular epidemiology of Proteus mirabilis infections of the catheterized urinary tract.
Sabbuba NA, Mahenthiralingam E, Stickler DJ. Sabbuba NA, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Nov;41(11):4961-5. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.11.4961-4965.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14605124 Free PMC article. - Diversity of Listeria monocytogenes isolates of human and food origin studied by serotyping, automated ribotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis.
Lukinmaa S, Aarnisalo K, Suihko ML, Siitonen A. Lukinmaa S, et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004 Jun;10(6):562-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.00876.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004. PMID: 15191386 - Typing of Listeria monocytogenes isolates originating from the food processing industry with automated ribotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis.
Aarnisalo K, Autio T, Sjöberg AM, Lundén J, Korkeala H, Suihko ML. Aarnisalo K, et al. J Food Prot. 2003 Feb;66(2):249-55. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-66.2.249. J Food Prot. 2003. PMID: 12597485 - The Brief Case: Proteus mirabilis Causing Coraliform Lithiasis and Bacteremia in an Elderly Catheterized Patient.
Maldonado-Barrueco A, Grandioso-Vas D, Rico-Nieto A, García-Rodríguez J, García-Bujalance S. Maldonado-Barrueco A, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2022 Oct 19;60(10):e0241321. doi: 10.1128/jcm.02413-21. Epub 2022 Oct 19. J Clin Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36259775 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available. - Closing Brief Case: Proteus mirabilis Causing Coraliform Lithiasis and Bacteremia in an Elderly Catheterized Patient.
Maldonado-Barrueco A, Grandioso-Vas D, Rico-Nieto A, García-Rodríguez J, García-Bujalance S. Maldonado-Barrueco A, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2022 Oct 19;60(10):e0241421. doi: 10.1128/jcm.02414-21. Epub 2022 Oct 19. J Clin Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36259776 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Molecular epidemiology of Proteus mirabilis infections of the catheterized urinary tract.
Sabbuba NA, Mahenthiralingam E, Stickler DJ. Sabbuba NA, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Nov;41(11):4961-5. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.11.4961-4965.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14605124 Free PMC article. - Significance and Roles of Proteus spp. Bacteria in Natural Environments.
Drzewiecka D. Drzewiecka D. Microb Ecol. 2016 Nov;72(4):741-758. doi: 10.1007/s00248-015-0720-6. Epub 2016 Jan 9. Microb Ecol. 2016. PMID: 26748500 Free PMC article. Review. - Genomic Characterization of 16S rRNA Methyltransferase-Producing Enterobacterales Reveals the Emergence of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST6260 Harboring rmtF, rmtB, _bla_NDM-5, _bla_OXA-232 and _bla_SFO-1 Genes in a Cancer Hospital in Bulgaria.
Sabtcheva S, Stoikov I, Georgieva S, Donchev D, Hodzhev Y, Dobreva E, Christova I, Ivanov IN. Sabtcheva S, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Oct 10;13(10):950. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13100950. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452216 Free PMC article. - Modification of dienes mutual inhibition test for epidemiological characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates.
Munson EL, Pfaller MA, Doern GV. Munson EL, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Nov;40(11):4285-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.11.4285-4288.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12409411 Free PMC article. - The characteristics of gut microbiota and commensal Enterobacteriaceae isolates in tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri).
Gu W, Tong P, Liu C, Wang W, Lu C, Han Y, Sun X, Kuang X, Li N, Dai J. Gu W, et al. BMC Microbiol. 2019 Sep 2;19(1):203. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1581-9. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31477004 Free PMC article.
References
- Aleksic S, Bockemuhl J. Yersinia and other Enterobacteriaceae. In: Murray P R, Baron E J, Pfaller M A, Tenover F C, Yolken R H, editors. Manual of clinical microbiology. 7th ed. Washington, D.C.: ASM Press; 1999. pp. 483–496.
- Bale M J, Hollis R J. Characterization of organisms for epidemiologic purposes: serotyping, pyocin typing, and Dienes test. In: Isenberg H D, editor. Clinical microbiology procedures handbook. Vol. 2. Washington, D.C.: American Society for Microbiology; 1992. pp. 11.14.1–11.14.2.
- Dienes L. Reproductive processes in Proteus cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1946;63:265–270. - PubMed
- Doern G V, Jones R N, Pfaller M A, Kugler K C, Beach M L The SENTRY Study Group (North America) Bacterial pathogens isolated from patients with skin and soft tissue infections: frequency of occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (United States and Canada, 1997) Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1999;34:65–72. - PubMed
- Gales, A. C., R. N. Jones, K. A. Gordon, H. S. Sader, W. W. Wilke, M. L. Beach, M. A. Pfaller, G. V. Doern, and The SENTRY Study Group (Latin America). 2000. Activity and spectrum of 22 antimicrobial agents tested against urinary tract infection pathogens in hospitalized patients in Latin America: report from the second year of the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (1998). J. Antimicrob. Chemother., in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources