Diastolic function abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis. Evaluation By echo Doppler transmitral flow and pulmonary venous flow: relation with duration of disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Diastolic function abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis. Evaluation By echo Doppler transmitral flow and pulmonary venous flow: relation with duration of disease
M Di Franco et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Mar.
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate left ventricular filling in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), analysing transmitral flow and pulmonary venous flow, with special regard to age and disease duration.
Methods: 32 patients affected by RA according to ARA criteria were selected, without evidence of cardiac disease, and compared with matched control subjects. All patients and the control group were submitted to M-mode, two dimensional, Doppler and colour Doppler (continuous and pulsed wave) echocardiography. The following diastolic parameters were evaluated: transmitralic flow (E/A ratio), pulmonary venous flow (S/D ratio), a-Pw, IVRT and DT.
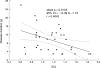
Results: In RA patients left ventricular filling abnormalities were found characterised by a reduced E/A ratio (mean (SD) 1.16 (0.31) v. controls 1.37 (0.32); p = 0.02) and an increased S/D ratio (1.43 (0.40) v. controls 1.22 (0.29); p = 0.017). In the group of patients a relation was found between E/A ratio and disease duration (r= 0.40, p = 0.01 Spearman rank correlation).
Conclusions: At present, it is concluded that RA patients, in absence of clinical evidence of heart disease, show diastolic dysfunction characterised by impaired E/A and S/D ratio. The relation between transmitral flow alteration and disease duration suggests a sub-clinical myocardial involvement.
Figures
Figure 1
Scatterplot of the relation between mitral E/A wave velocity ratio and disease duration.
Similar articles
- Diastolic function abnormalities in active rheumatoid arthritis evaluation by conventional Doppler and tissue Doppler: relation with duration of disease.
Arslan S, Bozkurt E, Sari RA, Erol MK. Arslan S, et al. Clin Rheumatol. 2006 May;25(3):294-9. doi: 10.1007/s10067-005-0014-3. Epub 2005 Oct 13. Clin Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 16222411 - Diastolic function abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis: relation with duration of disease.
Udayakumar N, Venkatesan S, Rajendiran C. Udayakumar N, et al. Singapore Med J. 2007 Jun;48(6):537-42. Singapore Med J. 2007. PMID: 17538753 - Tissue Doppler imaging in the evaluation of the left and right ventricular diastolic functions in rheumatoid arthritis.
Birdane A, Korkmaz C, Ata N, Cavusoglu Y, Kasifoglu T, Dogan SM, Gorenek B, Goktekin O, Unalir A, Timuralp B. Birdane A, et al. Echocardiography. 2007 May;24(5):485-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2007.00422.x. Echocardiography. 2007. PMID: 17456067 - [Evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function using Doppler echocardiography].
Vlahović A, Popović AD. Vlahović A, et al. Med Pregl. 1999 Jan-Feb;52(1-2):13-8. Med Pregl. 1999. PMID: 10352498 Review. Croatian. - Grade I diastolic dysfunction and elevated left ventricular end-diastolic pressure: Mitral Doppler inflow, pulmonary vein atrial reversal, and the M-mode mitral B-bump.
Kerut EK, McIlwain E, Nishimura RA. Kerut EK, et al. Echocardiography. 2017 Sep;34(9):1371-1373. doi: 10.1111/echo.13631. Epub 2017 Jul 23. Echocardiography. 2017. PMID: 28737016 Review.
Cited by
- Combined use of propagation velocity and intraventricular dispersion of E wave velocity for the evaluation of diastolic functions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Canturk F, Yazici M, Alayli G, Menekse EB, Demircan S, Ibrahimli F, Menekse S. Canturk F, et al. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2006 Jun-Aug;22(3-4):369-76. doi: 10.1007/s10554-005-9059-2. Epub 2006 Mar 4. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2006. PMID: 16518665 - Diastolic function abnormalities in active rheumatoid arthritis evaluation by conventional Doppler and tissue Doppler: relation with duration of disease.
Arslan S, Bozkurt E, Sari RA, Erol MK. Arslan S, et al. Clin Rheumatol. 2006 May;25(3):294-9. doi: 10.1007/s10067-005-0014-3. Epub 2005 Oct 13. Clin Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 16222411 - [Echocardiographic functional analysis of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and collagen diseases].
Hagendorff A, Pfeiffer D. Hagendorff A, et al. Z Rheumatol. 2005 May;64(4):239-48. doi: 10.1007/s00393-005-0734-4. Z Rheumatol. 2005. PMID: 15909084 Review. German. - Cardiovascular comorbidity in rheumatic diseases: a focus on heart failure.
Wright K, Crowson CS, Gabriel SE. Wright K, et al. Heart Fail Clin. 2014 Apr;10(2):339-52. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2013.10.003. Epub 2014 Jan 10. Heart Fail Clin. 2014. PMID: 24656110 Free PMC article. Review. - Preclinical impairment of myocardial function in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Detection of myocardial strain by speckle tracking echocardiography.
Baktir AO, Sarli B, Cebicci MA, Saglam H, Dogan Y, Demirbaş M, Sutbeyaz ST, Arinc H. Baktir AO, et al. Herz. 2015 Jun;40(4):669-74. doi: 10.1007/s00059-014-4068-3. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Herz. 2015. PMID: 24595319
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical