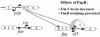Regulatory cross-talk between adhesin operons in Escherichia coli: inhibition of type 1 fimbriae expression by the PapB protein - PubMed (original) (raw)
Regulatory cross-talk between adhesin operons in Escherichia coli: inhibition of type 1 fimbriae expression by the PapB protein
Y Xia et al. EMBO J. 2000.
Abstract
Pathogenic Escherichia coli often carry determinants for several different adhesins. We show a direct communication between two adhesin gene clusters in uropathogenic E.coli: type 1 fimbriae (fim) and pyelonephritis-associated pili (pap). A regulator of pap, PapB, is a key factor in this cross-talk. FimB recombinase turns on type 1 fimbrial expression, and PapB inhibited phase transition by FimB in both off-to-on and on-to-off directions. On-to-off switching requiring FimE was increased by PapB. By analysis of FimB- and FimE-LacZ translational fusions it was concluded that the increase in on-to-off transition rates was via an increase in FimE expression. Inhibition of FimB-promoted switching was via a different mechanism: PapB inhibited FimB-promoted in vitro recombination, indicating that FimB activity was blocked at the fim switch. In vitro analyses showed that PapB bound to several DNA regions of the type 1 fimbrial operon, including the fim switch region. These data show that Pap expression turns off type 1 fimbriae expression in the same cell. Such cross-talk between adhesin gene clusters may bring about appropriate expression at the single cell level.
Figures
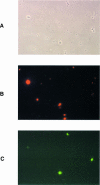
Fig. 1. Immunofluorescence staining of E.coli J96 cells. Bacteria grown in LB at 37°C were prepared for microscopic analysis as described in Materials and methods. (A) Phase-contrast micrograph of bacterial cells. (B) Anti-Pap–lissamine–rhodamine staining. (C) Anti-type-1–fluorescein isothiocyanate staining.
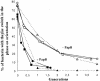
Fig. 2. Effect of papB on the on-to-off switching of strain AAEC198A (fimB+fimE+fimA–lacZYA) in defined rich medium at 37°C. The data from two separate experiments with the strain carrying the PapB-producing plasmid pHMG88 (closed symbols) or the vector plasmid pACYC184 (open symbols) are shown. Model rates of 0.9 (▴) and 0.45 (▵) per cell generation are shown by the dotted lines. The frequencies determined from these data are shown in Table III.
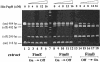
Fig. 3. Effect of purified His-PapB on the in vitro recombination in bacterial extracts containing either FimB or FimE. Recombination assays were set up as described in Materials and methods. Lane 1: control extract (pET11 in NEC26) plus pMM36 (switch starts in the on orientation). Lane 2: FimE extract (pIB382 in NEC26) plus pMM36. Lane 3: FimE extract with 4 μM His-PapB plus pMM36. Lane 4: FimE extract with 8 μM His-PapB plus pMM36. Lane 5: FimE extract with 12 μM His-PapB plus pMM36. Lane 6: FimE extract with 16 μM His-PapB plus pMM36. Lane 7: 1 kb marker. Lane 8: FimB extract (pIB378 in NEC26) plus pMM36. Lane 9: FimB extract with 4 μM His-PapB plus pMM36. Lane 10: FimB extract with 8 μM His-PapB plus pMM36. Lane 11: FimB extract with 12 μM His-PapB plus pMM36. Lane 12: FimB extract with 16 μM His-PapB plus pMM36. Lane 13: control extract (pET11 in NEC26) plus pJL2 (switch in the off orientation). Lane 14: FimB extract plus pJL2. Lane 15: FimB extract with 4 μM His-PapB plus pJL2. Lane 16: FimB extract with 8 μM His-PapB plus pJL2. Lane 17: FimB extract with 12 μM His-PapB plus pJL2. Lane 18: FimB extract with 16 μM His-PapB plus pJL2.
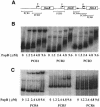
Fig. 4. PapB binding to the fim regulatory DNA region. (A) Outline of the fimB, fimE, fimA regions and positions of the promoters (P). The relative positions and lengths of different PCR fragments are also indicated. (B and C) Gel mobility shift assays of His-PapB binding to DNA fragments (PCR1–6). The assays were carried out as described in Materials and methods.
Fig. 5. Schematic illustration of the cross-talk mediated by PapB between the pap and fim gene clusters.
Similar articles
- PapB paralogues and their effect on the phase variation of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli.
Holden NJ, Uhlin BE, Gally DL. Holden NJ, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2001 Oct;42(2):319-30. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02656.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11703657 - Comparative analysis of FimB and FimE recombinase activity.
Holden N, Blomfield IC, Uhlin BE, Totsika M, Kulasekara DH, Gally DL. Holden N, et al. Microbiology (Reading). 2007 Dec;153(Pt 12):4138-4149. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/010363-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2007. PMID: 18048927 - The Pai-associated leuX specific tRNA5(Leu) affects type 1 fimbriation in pathogenic Escherichia coli by control of FimB recombinase expression.
Ritter A, Gally DL, Olsen PB, Dobrindt U, Friedrich A, Klemm P, Hacker J. Ritter A, et al. Mol Microbiol. 1997 Sep;25(5):871-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1997.mmi517.x. Mol Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9364913 - The intricate workings of a bacterial epigenetic switch.
Hernday A, Braaten B, Low D. Hernday A, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2004;547:83-9. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-8861-4_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2004. PMID: 15230094 Review. - The regulation of pap and type 1 fimbriation in Escherichia coli.
Blomfield IC. Blomfield IC. Adv Microb Physiol. 2001;45:1-49. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(01)45001-6. Adv Microb Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11450107 Review.
Cited by
- Roles of chaperone/usher pathways of Yersinia pestis in a murine model of plague and adhesion to host cells.
Hatkoff M, Runco LM, Pujol C, Jayatilaka I, Furie MB, Bliska JB, Thanassi DG. Hatkoff M, et al. Infect Immun. 2012 Oct;80(10):3490-500. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00434-12. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22851745 Free PMC article. - Transcriptome of uropathogenic Escherichia coli during urinary tract infection.
Snyder JA, Haugen BJ, Buckles EL, Lockatell CV, Johnson DE, Donnenberg MS, Welch RA, Mobley HL. Snyder JA, et al. Infect Immun. 2004 Nov;72(11):6373-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6373-6381.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15501767 Free PMC article. - The yad and yeh fimbrial loci influence gene expression and virulence in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7.
Gonyar LA, Sauder AB, Mortensen L, Willsey GG, Kendall MM. Gonyar LA, et al. mSphere. 2024 Jul 30;9(7):e0012424. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00124-24. Epub 2024 Jun 21. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38904402 Free PMC article. - Regulation of fim genes in uropathogenic Escherichia coli.
Schwan WR. Schwan WR. World J Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Dec 30;1(1):17-25. doi: 10.5495/wjcid.v1.i1.17. World J Clin Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 23638406 Free PMC article. - The UbiI (VisC) Aerobic Ubiquinone Synthase Is Required for Expression of Type 1 Pili, Biofilm Formation, and Pathogenesis in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli.
Floyd KA, Mitchell CA, Eberly AR, Colling SJ, Zhang EW, DePas W, Chapman MR, Conover M, Rogers BR, Hultgren SJ, Hadjifrangiskou M. Floyd KA, et al. J Bacteriol. 2016 Sep 9;198(19):2662-72. doi: 10.1128/JB.00030-16. Print 2016 Oct 1. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27161114 Free PMC article.
References
- Blomfield I.C., Kulasekara, D.H. and Eisenstein, B.I. (1997) Integration host factor stimulates both FimB- and FimE-mediated site-specific DNA inversion that controls phase variation of type 1 fimbriae expression in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol., 23, 705–717. - PubMed
- Bolivar F. (1978) Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique EcoRI sites for selection of EcoRI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene, 4, 121–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials