Genomic analysis of Blastocystis hominis strains isolated from two long-term health care facilities - PubMed (original) (raw)
Genomic analysis of Blastocystis hominis strains isolated from two long-term health care facilities
H Yoshikawa et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Apr.
Abstract
The genotype Blastocystis hominis is highly polymorphic. Therefore, a genetic marker would be a powerful tool for the identification or classification of B. hominis subtypes and could be used as a means to resolve the transmission route or origin of the parasite. To this end, 32 B. hominis isolates were collected from patients and/or staff members of two long-term health care facilities (facilities A and B), and these organisms were subjected to genotype analysis based on diagnostic PCR primers and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) of small subunit rRNA gene (rDNA). Based on PCR amplification using diagnostic primers which were developed from randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of known strains of B. hominis, the 32 isolates of B. hominis were classified into three different subtypes. Thirty isolates, including twenty-four that were isolated from patients and a staff member, from facility A and all isolates isolated from six patients from facility B showed the same genotype. Two of six patients of facility B had been transferred from facility A, and these two patients also had the same-genotype B. hominis that corresponded to 24 isolates from facility A. This genotype strain may have been transmitted by these two patients from facility A to facility B, suggesting human-to-human transmission. In contrast, 2 of 26 isolates from facility A showed distinct genotypes, suggesting that the colonization by these two isolates is attributable to another infectious route. These different subtypes were subjected to RFLP analysis, and the RFLP profiles were correlated with the results obtained by diagnostic PCR primers. This study presents the first molecular evidence of possible human-to-human B. hominis infection between and/or among two small communities.
Figures
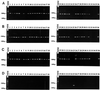
FIG. 1
The specificity of diagnostic primer sets SB82 (A), SB83 (B), and SB155 (C) with 32 isolates from patients and staff members of two facilities (lanes 1 to 32) and four control strains (lanes 33 to 36) of B. hominis. Strains Nand II (lane 33) and HE87-1 (lane 34) were amplified with primer sets SB82 (462 bp) and SB83 (351 bp), while HJ96A-29 (lane 24) showed two minor bands (350 and 400 bp) with primer set SB83. With primer set SB155, strain B (lane 35) was only amplified and showed a single band of 650 bp. Lanes: MM, molecular marker of a 100-bp ladder; 1, HJ96A-1; 2, HJ96A-2; 3, HJ96A-3; 4, HJ96A-4; 5, HJ96A-5; 6, HJ96A-6; 7, HJ96A-7; 8, HJ96A-10; 9, HJ96A-13; 10, HJ96A-14; 11, HJ96A-15; 12, HJ96A-16; 13, HJ96A-17; 14, HJ96A-18; 15, HJ96A-19; 16, HJ96A-20; 17, HJ96A-22; 18, HJ96A-23; 19, HJ96A-24; 20, HJ96A-25; 21, HJ96A-26; 22, HJ96A-27; 23, HJ96A-28; 24, HJ96A-29; 25, HJ96AS-1; 26, HJ96AS-2; 27, HJ96B-1;28, HJ96B-2; 29, HJ96B-3; 30, HJ96B-4; 31, HJ96B-5; 32, HJ96B-6; 33, Nand II; 34, HE87-1; 35, B; 36, HV93-13.
FIG. 2
The specificity of diagnostic primer sets SB227 (A), SB228 (B), SB229 (C), and SB332 (D). The molecular size marker and sample for each lane were as described in the legend of Fig. 1. Of 32 isolates from patients and staff members of two facilities, 30 isolates (lanes 1 to 23 and 26 to 32) and strain HV93-13 (lane 36) showed a single band with primer sets SB227 (526 bp), SB228 (473 bp), and SB229 (631 bp). Isolates HJ96A-29 (lane 24) and HJ96AS-1 (lane 25) and strains Nand II (lane 33), HE87-1 (lane 34), and B (lane 35) were not amplified with these three primer sets. HJ96AS-1 was only amplified with primer set SB332 (panel D, lane 25) and showed a single band of 338 bp.
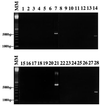
FIG. 3
The specificity of four diagnostic primers was tested against other intestinal protozoa and a yeast. Lanes 1 to 7 were amplified by using primer sets SB227, lanes 8 to 14 were amplified with SB228, lanes 15 to 21 were amplified with SB229, and lanes 22 to 28 were amplified with SB332. Only positive controls (lanes 7, 14, 21, and 28) showed a single band. Lanes: MM, molecular marker of a 100-bp ladder; 1, 8, 15, and 22, E. histolytica; 2, 9, 16, and 23, E. moshkovskii; 3, 10, 17, and 24, G. intestinalis; 4, 11, 18, and 25, C. muris; 5, 12, 19, and 26, C. parvum; 6, 13, 20, and 27, S. cerevisiae; 7 and 14, HV93-13; 21, HV96A-26; 28, HJ96AS-1.
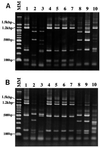
FIG. 4
Restriction enzyme profiles of SSU rDNA digested with _Hin_fI (A) and _Rsa_I (B). The _Hin_fI restriction enzyme produced five patterns, while the _Rsa_I restriction product showed four kinds of patterns. Strains HJ96A-26, HJ96B-1, HJ96B-4, HJ96B-6, and HV93-13 showed the same RFLP pattern with both _Hin_fI and _Rsa_I enzymes. HJ96A-29 strain showed the same RFLP pattern with Nand II and HE87-1 strains with _Rsa_I enzyme, while with _Hin_fI enzyme the HJ96A-29 strain showed two bands of 180 and 100 bp instead of a band of 280 bp as with the Nand II and HE87-1 strains. Strains HJ96AS-1 and B also showed distinct banding patterns. Lanes: MM, molecular marker of a 100-bp ladder; 1, HJ96A-26; 2, HJ96A-29; 3, HJ96AS-1; 4, HJ96B-1; 5, HJ96B-4; 6, HJ96B-6; 7, HV93-13; 8, Nand II; 9, HE87-1; 10, B strain.
Similar articles
- Polymerase chain reaction-based genotype classification among human Blastocystis hominis populations isolated from different countries.
Yoshikawa H, Wu Z, Kimata I, Iseki M, Ali IK, Hossain MB, Zaman V, Haque R, Takahashi Y. Yoshikawa H, et al. Parasitol Res. 2004 Jan;92(1):22-9. doi: 10.1007/s00436-003-0995-2. Epub 2003 Nov 4. Parasitol Res. 2004. PMID: 14598169 - [Blastocystis hominis- parasites or commensals? ].
Duda A, Kosik-Bogacka D, Lanocha N, Szymański S. Duda A, et al. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2014;60(1):23-8. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2014. PMID: 25518089 Review. Polish. - Recent advances in Blastocystis hominis research: hot spots in terra incognita.
Tan KS, Singh M, Yap EH. Tan KS, et al. Int J Parasitol. 2002 Jun 15;32(7):789-804. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(02)00005-x. Int J Parasitol. 2002. PMID: 12062550 Review.
Cited by
- Colorectal cancer and Blastocystis sp. infection.
Sulżyc-Bielicka V, Kołodziejczyk L, Adamska M, Skotarczak B, Jaczewska S, Safranow K, Bielicki P, Kładny J, Bielicki D. Sulżyc-Bielicka V, et al. Parasit Vectors. 2021 Apr 14;14(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04681-x. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 33853659 Free PMC article. - Unveiling Blastocystis epidemiology in Morocco: subtype diversity among clinical patients with and without gastrointestinal manifestations in the Meknes region.
Boutahar M, Belaouni M, Ibrahimi A, Eljaoudi R, Aanniz T, Er-Rami M, Köster PC, Dashti A, Carmena D. Boutahar M, et al. Parasitol Res. 2024 Jul 17;123(7):273. doi: 10.1007/s00436-024-08288-w. Parasitol Res. 2024. PMID: 39017986 - Identification of Blastocystis hominis isolates from asymptomatic and symptomatic patients by PCR.
Eroglu F, Genc A, Elgun G, Koltas IS. Eroglu F, et al. Parasitol Res. 2009 Nov;105(6):1589-92. doi: 10.1007/s00436-009-1595-6. Epub 2009 Aug 15. Parasitol Res. 2009. PMID: 19685075 - Is the genetic variability of Cathepsin B important in the pathogenesis of Blastocystis spp.?
Gonzalez-Arenas NR, Villalobos G, Vargas-Sanchez GB, Avalos-Galarza CA, Marquez-Valdelamar LM, Ramirez-Miranda ME, Olivo-Diaz A, Romero-Valdovinos M, Martinez-Hernandez F, Maravilla P. Gonzalez-Arenas NR, et al. Parasitol Res. 2018 Dec;117(12):3935-3943. doi: 10.1007/s00436-018-6103-4. Epub 2018 Oct 8. Parasitol Res. 2018. PMID: 30298236 - Subtype distribution of Blastocystis isolates in Sebha, Libya.
Abdulsalam AM, Ithoi I, Al-Mekhlafi HM, Al-Mekhlafi AM, Ahmed A, Surin J. Abdulsalam AM, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Dec 20;8(12):e84372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084372. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376805 Free PMC article.
References
- Boreham P F L, Stenzel D J. Blastocystis in humans and animals: morphology, biology, and epizootiology. Adv Parasitol. 1993;32:1–70. - PubMed
- Boreham P F L, Upcroft J A, Dunn L A. Protein and DNA evidence for two demes of Blastocystis hominis from humans. Int J Parasitol. 1992;22:49–53. - PubMed
- Brumpt E. Blastocystis hominis n.sp. et formes voisines. Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 1912;5:725–730.
- Clark C G. Extensive genetic diversity in Blastocystis hominis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1997;87:79–83. - PubMed
- Kain K C, Noble M A, Freeman H J, Barteluk R L. Epidemiology and clinical features associated with Blastocystis hominis infection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987;8:235–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical