Identification of the novobiocin biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces spheroides NCIB 11891 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Identification of the novobiocin biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces spheroides NCIB 11891
M Steffensky et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000 May.
Abstract
The novobiocin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces spheroides NCIB 11891 was cloned by using homologous deoxynucleoside diphosphate (dNDP)-glucose 4,6-dehydratase gene fragments as probes. Double-stranded sequencing of 25.6 kb revealed the presence of 23 putative open reading frames (ORFs), including the gene for novobiocin resistance, gyrB(r), and at least 11 further ORFs to which a possible role in novobiocin biosynthesis could be assigned. An insertional inactivation experiment with a dNDP-glucose 4, 6-dehydratase fragment resulted in abolishment of novobiocin production, since biosynthesis of the deoxysugar moiety of novobiocin was blocked. Heterologous expression of a key enzyme of novobiocin biosynthesis, i.e., novobiocic acid synthetase, in Streptomyces lividans TK24 further confirmed the involvement of the analyzed genes in the biosynthesis of the antibiotic.
Figures
FIG. 1
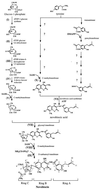
Hypothetical biosynthetic pathway of novobiocin. Roman numerals refer to the putative assignments of genes identified in the biosynthetic reactions (see Table 1). SAM, _S_-adenosylmethionine.
FIG. 2
Organization of the novobiocin biosynthetic gene cluster. (A) Map of the core sequence, obtained by double-strand sequencing of S. spheroides genomic DNA (cosmid 9-6G). The roman numerals after the proposed gene functions refer to the reactions marked in Fig. 1. (B) Schematic representation of constructs used for heterologous expression of novobiocic acid synthetase. ABC, ATP-binding cassette.
FIG. 3
Comparison of the conserved core motifs of the deduced amino acid (aa) sequence of NovH with other peptide synthetase modules and with NovL. Alignment was performed by using the DNASIS program. GRSA, gramicidin _S_-synthetase I from Bacillus cereus (32); PCZA361.18, peptide synthetase from Amycolatopsis orientalis (64); SpsnbDE, pristinamycin I synthetase 3 from Streptomyces pristinaespiralis (11); TycA, tyrocidine synthetase 1 from Bacillus brevis (44); SvsnbDE, virginiamycin S synthetase from Streptomyces virginiae (12). The consensus line contains capital letters for amino acids with 100% conservation and lowercase letters for conservative amino acid substitutions. Motifs A1 to A8 are core motifs of the adenylation domain, and motif T represents the 4′-phosphopantetheine cofactor attachment site (40).
FIG. 4
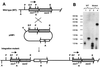
Insertional gene inactivation of deoxysugar biosynthesis. (A) Schematic presentation of the integration event. The 520-bp _Fsp_I-_Pst_I-DNA fragment used as the probe is indicated as a black arrow. Relevant restriction sites are identified as follows: A, _Acc_I; E, _Eco_RI; F, _Fsp_I; P, _Pvu_II. tsr, Thiostrepton resistance. Hatched arrows indicate genes. (B) Southern analysis of S. spheroides NCIB 11891 wild type (WT) and a disrupted mutant. Lanes 1 and 2, genomic DNA of the wild type restricted with _Pvu_II in lane 1 (expected band at 1.07 kb) and with _Acc_I in lane 2 (expected band at 1.47 kb); lanes 3 and 4, genomic DNA of an integration mutant restricted with _Pvu_II in lane 3 (expected bands at 1.07 and 0.91 kb) and _Acc_I in lane 4 (expected bands at 1.47 and 3.98 kb).
FIG. 5
HPLC chromatogram of secondary metabolites of S. spheroides NCIB 11891 (wild type, dotted line) and of an integration mutant (solid line). Peak 1, novobiocic acid; peak 2, novobiocin. See text for further explanations.
Similar articles
- Identification of the coumermycin A(1) biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces rishiriensis DSM 40489.
Wang ZX, Li SM, Heide L. Wang ZX, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000 Nov;44(11):3040-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.44.11.3040-3048.2000. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000. PMID: 11036020 Free PMC article. - Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the clorobiocin biosynthetic gene cluster: new insights into the biosynthesis of aminocoumarin antibiotics.
Pojer F, Li SM, Heide L. Pojer F, et al. Microbiology (Reading). 2002 Dec;148(Pt 12):3901-3911. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-12-3901. Microbiology (Reading). 2002. PMID: 12480894 - Cloning, overexpression, and purification of novobiocic acid synthetase from Streptomyces spheroides NCIMB 11891.
Steffensky M, Li SM, Heide L. Steffensky M, et al. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 14;275(28):21754-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003066200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10801869 - Cloning and analysis of the simocyclinone biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces antibioticus Tü 6040.
Galm U, Schimana J, Fiedler HP, Schmidt J, Li SM, Heide L. Galm U, et al. Arch Microbiol. 2002 Aug;178(2):102-14. doi: 10.1007/s00203-002-0429-z. Epub 2002 May 14. Arch Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12115055 - The biosynthetic gene clusters of aminocoumarin antibiotics.
Li SM, Heide L. Li SM, et al. Planta Med. 2006 Oct;72(12):1093-9. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-946699. Epub 2006 Jul 25. Planta Med. 2006. PMID: 16868863 Review.
Cited by
- Coumarins as Fungal Metabolites with Potential Medicinal Properties.
Tsivileva OM, Koftin OV, Evseeva NV. Tsivileva OM, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Aug 26;11(9):1156. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11091156. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139936 Free PMC article. Review. - ActDES - a curated Actinobacterial Database for Evolutionary Studies.
Schniete JK, Selem-Mojica N, Birke AS, Cruz-Morales P, Hunter IS, Barona-Gomez F, Hoskisson PA. Schniete JK, et al. Microb Genom. 2021 Jan;7(1):mgen000498. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000498. Microb Genom. 2021. PMID: 33433310 Free PMC article. - Identification of Sare0718 as an alanine-activating adenylation domain in marine actinomycete Salinispora arenicola CNS-205.
Xia S, Ma Y, Zhang W, Yang Y, Wu S, Zhu M, Deng L, Li B, Liu Z, Qi C. Xia S, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37487. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037487. Epub 2012 May 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22655051 Free PMC article. - Discovery of a Cryptic Intermediate in Late Steps of Mithramycin Biosynthesis.
Wheeler R, Yu X, Hou C, Mitra P, Chen JM, Herkules F, Ivanov DN, Tsodikov OV, Rohr J. Wheeler R, et al. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Jan 7;59(2):826-832. doi: 10.1002/anie.201910241. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 31702856 Free PMC article. - Recent developments in self-resistance gene directed natural product discovery.
Yan Y, Liu N, Tang Y. Yan Y, et al. Nat Prod Rep. 2020 Jul 1;37(7):879-892. doi: 10.1039/c9np00050j. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Nat Prod Rep. 2020. PMID: 31912842 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Altenbuchner J, Cullum J. DNA amplification and an unstable arginine gene in Streptomyces lividans 66. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195:134–138. - PubMed
- Bannister B, Zapotocky B A. Protorubradirin, an antibiotic containing a C-nitroso-sugar fragment, is the true secondary metabolite produced by Streptomyces achromogenes var. rubradiris. Rubradirin, described earlier, is its photo-oxidation product. J Antibiot Tokyo. 1992;45:1313–1324. - PubMed
- Birch A J, Holloway P W, Rickards R W. The biosynthesis of noviose, a branched-chain monosaccharide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962;57:143–145. - PubMed
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases