Host cyclooxygenase-2 modulates carcinoma growth - PubMed (original) (raw)
Host cyclooxygenase-2 modulates carcinoma growth
C S Williams et al. J Clin Invest. 2000 Jun.
Abstract
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2; Ptgs2) acts as a tumor promoter in rodent models for colorectal cancer, but its precise role in carcinogenesis remains unclear. We evaluated the contribution of host-derived COX-1 and COX-2 in tumor growth using both genetic and pharmacological approaches. Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells grow rapidly as solid tumors when implanted in C57BL/6 mice. We found that tumor growth was markedly attenuated in COX-2(-/-), but not COX-1(-/-) or wild-type mice. Treatment of wild-type C57BL/6 mice bearing LLC tumors with a selective COX-2 inhibitor also reduced tumor growth. A decrease in vascular density was observed in tumors grown in COX-2(-/-) mice when compared with those in wild-type mice. Because COX-2 is expressed in stromal fibroblasts of human and rodent colorectal carcinomas, we evaluated COX-2(-/-) mouse fibroblasts and found a 94% reduction in their ability to produce the proangiogenic factor, VEGF. Additionally, treatment of wild-type mouse fibroblasts with a selective COX-2 inhibitor reduced VEGF production by 92%.
Figures
Figure 1
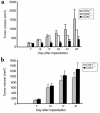
Host-derived COX-2 is important for LLC tumor growth. (a) A total of 2 × 106 LLC cells were implanted into COX-2+/+ (gray bars), COX-2+/– (white bars), or COX-2–/– (black bars) C57BL/6 mice; (b) a total of 2 × 106 LLC cells were implanted into COX-1+/+ (gray bars) or COX-1–/– (black bars) C57BL/6 mice. Tumor volumes were calculated from tumor measurements scored at the indicated day. Results are presented as the mean tumor volume ± SEM.
Figure 2
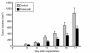
Celecoxib inhibits LLC tumor growth. A total of 2 × 106 LLC cells were implanted into C57BL/6 mice. Mice were fed either control chow (gray bars) or 1,500 mg/kg celecoxib-containing chow (black bars). Tumor volumes were calculated from tumor measurements taken at the indicated day and are represented as the average of each group ± SEM.
Figure 3
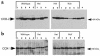
COX-1 and COX-2 are expressed within LLC tumors. Tumor lysates from LLC tumors grown in COX-2+/+ (wild-type), COX-2+/– (heterozygote), and COX-2–/– (null) mice were produced and 50 μg of lysate was fractionated on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel. (a) COX-2 and (b) COX-1 specific antisera were used to blot the membranes. Het, heterozygote.
Figure 4
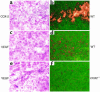
COX-2 and VEGF are expressed in LLC isografts. COX-2 (upper panels, a and b, wild-type host), VEGF (middle panels, c and d, wild-type host), and VEGF (lower panels, e and f, COX-2–/– host) riboprobes were hybridized to sections from tumors grown in C57BL/6 mice with the designated genotype (×400). Control hybridizations with sense cRNA riboprobes were performed to validate the specificity of Rnase-A–resistant hybrids. WT, wild-type.
Figure 5
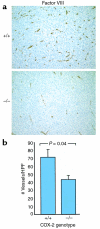
Decreased vascular density in LLC tumors when grown in COX-2–/– mice. (a) Representative photomicrographs of factor VIII–stained tumor sections from LLC tumors grown in wild-type (+/+) or _Ptgs2_–/– (–/–) mice (×200). (b) Factor VIII–positive vessel counts obtained by morphometric analysis of LLC tumors. Values represent the average number of vessels at ×200 ± the SD (Student’s t test; P = 0.04). HPF, high power field.
Figure 6
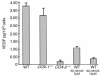
VEGF production in fibroblasts is regulated by COX-2. Production of VEGF by wild-type, COX-1–/–, and COX-2–/– fibroblasts was determined. Each treatment condition is listed below its respective bar graph. WT denotes wild-type mouse fibroblasts. We observed a 93% reduction in VEGF production in COX-2–/– fibroblasts when compared with wild-type fibroblasts. Additionally, treatment of wild-type fibroblasts with a selective COX-2 inhibitor (10 μM SC-58125) led to a ∼90% reduction in VEGF levels.
Comment in
- Is cyclooxygenase-2 the alpha and the omega in cancer?
Prescott SM. Prescott SM. J Clin Invest. 2000 Jun;105(11):1511-3. doi: 10.1172/JCI10241. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 10841506 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 is involved in vascular endothelial growth factor production in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
Murono S, Inoue H, Tanabe T, Joab I, Yoshizaki T, Furukawa M, Pagano JS. Murono S, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jun 5;98(12):6905-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.121016998. Epub 2001 May 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11381123 Free PMC article. - Cyclooxygenase 2- and prostaglandin E(2) receptor EP(2)-dependent angiogenesis in Apc(Delta716) mouse intestinal polyps.
Seno H, Oshima M, Ishikawa TO, Oshima H, Takaku K, Chiba T, Narumiya S, Taketo MM. Seno H, et al. Cancer Res. 2002 Jan 15;62(2):506-11. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11809702 - Cyclooxygenase inhibitors suppress angiogenesis and reduce tumor growth in vivo.
Sawaoka H, Tsuji S, Tsujii M, Gunawan ES, Sasaki Y, Kawano S, Hori M. Sawaoka H, et al. Lab Invest. 1999 Dec;79(12):1469-77. Lab Invest. 1999. PMID: 10616198 - [Colon cancer and COX-2].
Ota S, Bamba H, Imai Y, Arai S, Fujiwara K. Ota S, et al. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2002 Mar;99(3):253-63. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2002. PMID: 11925862 Review. Japanese. No abstract available. - COX-2 inhibitors. A new class of antiangiogenic agents.
Masferrer JL, Koki A, Seibert K. Masferrer JL, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;889:84-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb08726.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10668485 Review.
Cited by
- The expression of phospholipase A2 group X is inversely associated with metastasis in colorectal cancer.
Hiyoshi M, Kitayama J, Kazama S, Taketomi Y, Murakami M, Tsuno NH, Hongo K, Kaneko M, Sunami E, Watanabe T. Hiyoshi M, et al. Oncol Lett. 2013 Feb;5(2):533-538. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.1067. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23420493 Free PMC article. - Interaction between head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells and fibroblasts in the biosynthesis of PGE2.
Alcolea S, Antón R, Camacho M, Soler M, Alfranca A, Avilés-Jurado FX, Redondo JM, Quer M, León X, Vila L. Alcolea S, et al. J Lipid Res. 2012 Apr;53(4):630-42. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M019695. Epub 2012 Feb 4. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22308510 Free PMC article. - Non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs, prostaglandins, and cancer.
Allaj V, Guo C, Nie D. Allaj V, et al. Cell Biosci. 2013 Feb 6;3(1):8. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-3-8. Cell Biosci. 2013. PMID: 23388178 Free PMC article. - Potential use of COX-2-aromatase inhibitor combinations in breast cancer.
Bundred NJ, Barnes NL. Bundred NJ, et al. Br J Cancer. 2005 Aug;93 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S10-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602690. Br J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16100520 Free PMC article. Review. - Aspirin use and survival after diagnosis of colorectal cancer.
Chan AT, Ogino S, Fuchs CS. Chan AT, et al. JAMA. 2009 Aug 12;302(6):649-58. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1112. JAMA. 2009. PMID: 19671906 Free PMC article.
References
- Williams CS, Mann M, DuBois RN. The role of cyclooxygenases in inflammation, cancer and development. Oncogene. 1999;18:7908–7916. - PubMed
- Oshima M, et al. Suppression of intestinal polyposis in Apc delta716 knockout mice by inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) Cell. 1996;87:803–809. - PubMed
- Kawamori T, Rao CV, Seibert K, Reddy BS. Chemopreventive activity of celecoxib, a specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, against colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1998;58:409–412. - PubMed
- Pentland AP, Schoggins JW, Scott GA, Khan KN, Han R. Reduction of UV-induced skin tumors in hairless mice by selective COX-2 inhibition. Carcinogenesis. 1999;20:1939–1944. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 HD012304/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK 47297/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA77839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA077839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK047297/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK047297/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials