Roles of Wnt proteins in neural development and maintenance - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Roles of Wnt proteins in neural development and maintenance
A Patapoutian et al. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000 Jun.
Abstract
Many constituents of Wnt signaling pathways are expressed in the developing and mature nervous systems. Recent work has shown that Wnt signaling controls initial formation of the neural plate and many subsequent patterning decisions in the embryonic nervous system, including formation of the neural crest. Wnt signaling continues to be important at later stages of development. Wnts have been shown to regulate the anatomy of the neuronal cytoskeleton and the differentiation of synapses in the cerebellum. Wnt signaling has been demonstrated to regulate apoptosis and may participate in degenerative processes leading to cell death in the aging brain.
Figures
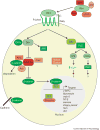
Figure 1
Model for Wnt signaling. Adapted from the Web pages of Nusse [3]and Moon [72]laboratories. Molecules shown in shades of green are positive regulators of the Wnt pathway, while those shown in red are negative regulators. See manuscript for details.
Similar articles
- Differential role of Axin RGS domain function in Wnt signaling during anteroposterior patterning and maternal axis formation.
Schneider PN, Slusarski DC, Houston DW. Schneider PN, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44096. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044096. Epub 2012 Sep 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22957046 Free PMC article. - Dysregulation of Neurite Outgrowth and Cell Migration in Autism and Other Neurodevelopmental Disorders.
Prem S, Millonig JH, DiCicco-Bloom E. Prem S, et al. Adv Neurobiol. 2020;25:109-153. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-45493-7_5. Adv Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32578146 - Far Posterior Approach for Rib Fracture Fixation: Surgical Technique and Tips.
Manes TJ, DeGenova DT, Taylor BC, Patel JN. Manes TJ, et al. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2024 Dec 6;14(4):e23.00094. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.23.00094. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2024. PMID: 39650795 Free PMC article. - Neuron-glia synapses in the brain.
Bergles DE, Jabs R, Steinhäuser C. Bergles DE, et al. Brain Res Rev. 2010 May;63(1-2):130-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2009.12.003. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Brain Res Rev. 2010. PMID: 20018210 Free PMC article. Review. - Deciphering the function of canonical Wnt signals in development and disease: conditional loss- and gain-of-function mutations of beta-catenin in mice.
Grigoryan T, Wend P, Klaus A, Birchmeier W. Grigoryan T, et al. Genes Dev. 2008 Sep 1;22(17):2308-41. doi: 10.1101/gad.1686208. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18765787 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Uncovering novel actors in astrocyte-neuron crosstalk in Parkinson's disease: the Wnt/β-catenin signaling cascade as the common final pathway for neuroprotection and self-repair.
Marchetti B, L'Episcopo F, Morale MC, Tirolo C, Testa N, Caniglia S, Serapide MF, Pluchino S. Marchetti B, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2013 May;37(10):1550-63. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12166. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23461676 Free PMC article. Review. - The Role of Fluoxetine in Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Repressing β-Amyloid Production in an Alzheimer Mouse Model.
Huang M, Liang Y, Chen H, Xu B, Chai C, Xing P. Huang M, et al. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Jun 1;10:164. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00164. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29910725 Free PMC article. - Modelling of a targeted nanotherapeutic 'stroma' to deliver the cytokine LIF, or XAV939, a potent inhibitor of Wnt-β-catenin signalling, for use in human fetal dopaminergic grafts in Parkinson's disease.
Zhao JW, Dyson SC, Kriegel C, Tyers P, He X, Fahmy TM, Metcalfe SM, Barker RA. Zhao JW, et al. Dis Model Mech. 2014 Oct;7(10):1193-203. doi: 10.1242/dmm.015859. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Dis Model Mech. 2014. PMID: 25085990 Free PMC article. - Spinal Wnt5a Plays a Key Role in Spinal Dendritic Spine Remodeling in Neuropathic and Inflammatory Pain Models and in the Proalgesic Effects of Peripheral Wnt3a.
Simonetti M, Kuner R. Simonetti M, et al. J Neurosci. 2020 Aug 26;40(35):6664-6677. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2942-19.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 2. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32616667 Free PMC article. - Moringin activates Wnt canonical pathway by inhibiting GSK3β in a mouse model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
Giacoppo S, Soundara Rajan T, De Nicola GR, Iori R, Bramanti P, Mazzon E. Giacoppo S, et al. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Oct 4;10:3291-3304. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S110514. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27784989 Free PMC article.
References
- Brown JD, Moon RT. Wnt signaling: why is everything so negative? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998;10:182–187. - PubMed
- Wodarz A, Nusse R. Mechanisms of Wnt signaling in development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1998;14:59–88. This paper provides an excellent review of Wnts and their functions. - PubMed
- Nusse laboratory. Web pages: http://www.stanford.edu/∼rnusse/wntwindow.html.
- Rattner A, Hsieh JC, Smallwood PM, Gilbert DJ. A family of secreted proteins contains homology to the cysteine-rich ligand-binding domain of frizzled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:2859–2863. The important discovery of Wnt receptor homologues that function as competitive antagonists of frizzled receptors is presented in this paper. - PMC - PubMed
- Salinas PC. Wnt factors in axonal remodelling and synaptogenesis. Biochem Soc Symp. 1999;65:101–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources