Differential expression of over 60 chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli by constitutive expression of MarA - PubMed (original) (raw)
Differential expression of over 60 chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli by constitutive expression of MarA
T M Barbosa et al. J Bacteriol. 2000 Jun.
Abstract
In Escherichia coli, the MarA protein controls expression of multiple chromosomal genes affecting resistance to antibiotics and other environmental hazards. For a more-complete characterization of the mar regulon, duplicate macroarrays containing 4,290 open reading frames of the E. coli genome were hybridized to radiolabeled cDNA populations derived from mar-deleted and mar-expressing E. coli. Strains constitutively expressing MarA showed altered expression of more than 60 chromosomal genes: 76% showed increased expression and 24% showed decreased expression. Although some of the genes were already known to be MarA regulated, the majority were newly determined and belonged to a variety of functional groups. Some of the genes identified have been associated with iron transport and metabolism; other genes were previously known to be part of the soxRS regulon. Northern blot analysis of selected genes confirmed the results obtained with the macroarrays. The findings reveal that the mar locus mediates a global stress response involving one of the largest networks of genes described.
Figures
FIG. 1
Expression profiles of E. coli strains with MarA deleted and constitutively expressing MarA. Identical arrays were probed with labeled 33P-cDNA populations prepared from total RNA from _mar_-deleted, AG100Kan[pMAK705] (A), and _mar_-expressing, AG100Kan[pAS10] (B), strains. Columns (1 to 24) and rows (A to P) forming the primary grid in field 1 of the autoradiogram are shown. Fields 2 and 3 are similar in format to field 1 and are not shown. The four spots in the four corners of each field are genomic DNA. Boxes underneath are expanded views of representative areas shown in panels A and B, where changes in expression levels are visible for several genes (seven of the differentially expressed genes are labeled as examples).
FIG. 2
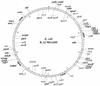
Chromosomal distribution and location of the different genes affected by MarA expression. The internal circle represents the chromosome of E. coli K-12 MG1655 divided in intervals of 1 min, while the external circle is divided in intervals of 100,000 nucleotide residues (adapted from Blattner et al. [8]). Genes induced by constitutive expression of MarA are plotted to face the exterior of the chromosome, and genes repressed by MarA are plotted to face the interior of the chromosome. Boldface genes read in the clockwise direction, while lightface genes are on the opposite strand (8). Genes that are in the immediate vicinity of each other are together over the same designation line.
FIG. 3
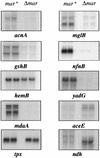
Northern blot analysis of genes affected by constitutive expression of MarA. Eight genes up-regulated by MarA, acnA, gshB, hemB, mdaA, tpx, mglB, nfnB, and yadG, and two genes down-regulated by MarA, aceE and ndh, were selected from those listed in Table 1. Samples were prepared and run in duplicate from _mar_-expressing (mar+) and mar_-deleted (Δ_mar) cells. RNA samples were transferred to nylon membranes and hybridized to 32P-labeled PCR-amplified probes of the genes in the study.
Similar articles
- Autoactivation of the marRAB multiple antibiotic resistance operon by the MarA transcriptional activator in Escherichia coli.
Martin RG, Jair KW, Wolf RE Jr, Rosner JL. Martin RG, et al. J Bacteriol. 1996 Apr;178(8):2216-23. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.8.2216-2223.1996. J Bacteriol. 1996. PMID: 8636021 Free PMC article. - Activation of the Escherichia coli nfnB gene by MarA through a highly divergent marbox in a class II promoter.
Barbosa TM, Levy SB. Barbosa TM, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2002 Jul;45(1):191-202. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03006.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12100559 - Role of the acrAB locus in organic solvent tolerance mediated by expression of marA, soxS, or robA in Escherichia coli.
White DG, Goldman JD, Demple B, Levy SB. White DG, et al. J Bacteriol. 1997 Oct;179(19):6122-6. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.19.6122-6126.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9324261 Free PMC article. - Leucine-responsive regulatory protein: a global regulator of gene expression in E. coli.
Newman EB, Lin R. Newman EB, et al. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995;49:747-75. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.49.100195.003531. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8561478 Review. - Redox signaling and gene control in the Escherichia coli soxRS oxidative stress regulon--a review.
Demple B. Demple B. Gene. 1996 Nov 7;179(1):53-7. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(96)00329-0. Gene. 1996. PMID: 8955629 Review.
Cited by
- Resistance/fitness trade-off is a barrier to the evolution of MarR inactivation mutants in Escherichia coli.
Praski Alzrigat L, Huseby DL, Brandis G, Hughes D. Praski Alzrigat L, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021 Jan 1;76(1):77-83. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa417. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33089314 Free PMC article. - Effect of MarA-like proteins on antibiotic resistance and virulence in Yersinia pestis.
Lister IM, Mecsas J, Levy SB. Lister IM, et al. Infect Immun. 2010 Jan;78(1):364-71. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00904-09. Epub 2009 Oct 19. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 19841071 Free PMC article. - The TetR family of transcriptional repressors.
Ramos JL, Martínez-Bueno M, Molina-Henares AJ, Terán W, Watanabe K, Zhang X, Gallegos MT, Brennan R, Tobes R. Ramos JL, et al. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005 Jun;69(2):326-56. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.69.2.326-356.2005. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15944459 Free PMC article. Review. - Regulation of the nfsA Gene in Escherichia coli by SoxS.
Paterson ES, Boucher SE, Lambert IB. Paterson ES, et al. J Bacteriol. 2002 Jan;184(1):51-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.1.51-58.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 11741843 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases