Megaplasmid pRme2011a of Sinorhizobium meliloti is not required for viability - PubMed (original) (raw)
Megaplasmid pRme2011a of Sinorhizobium meliloti is not required for viability
I J Oresnik et al. J Bacteriol. 2000 Jun.
Abstract
We report the curing of the 1,360-kb megaplasmid pRme2011a from Sinorhizobium meliloti strain Rm2011. With a positive selection strategy that utilized Tn5B12-S containing the sacB gene, we were able to cure this replicon by successive rounds of selecting for deletion formation in vivo. Subsequent Southern blot, Eckhardt gel, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analyses were consistent with the hypothesis that the resultant strain was indeed missing pRme2011a. The cured derivative grew as well as the wild-type strain in both complex and defined media but was unable to use a number of substrates as a sole source of carbon on defined media.
Figures
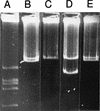
FIG. 1
Eckhardt gel showing plasmid profiles of S. meliloti strains with deletions in pRme2011a. Lanes: A, R. leguminosarum LRS39501 (24) (size standard); B, Rm2011; C, SmA818; D, SmA146; E, Rm2011. All lanes are from the same gel, but some intervening lanes showing derivatives with smaller deletions have been removed for clarity.
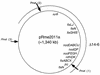
FIG. 2
Schematic representation of pRme2011a showing relative positions of known genetic markers. The approximate position of syrB::Tn_5_ in strain MB101 (5) was determined by conjugal-transfer experiments similar to those which were described for pRmeSU47b (11). The oriT used for these experiments was that of Ω30::Tn_5_-11 from Rm5420 (which is linked to nifH) (18). The direction of transfer was determined to be clockwise, using fixJ2.3::Tn_5_ from strain GMI 5704 as a marker for conjugal transfer (15). The arc shown represents the approximate position of Δ14-6. The end points of this deletion are undefined. The large arrows indicate the positions of _Pme_I restriction sites (23). _Pme_I fragment 5 extends between sites 1 and 2, fragment 6 extends between sites 1 and 3, and fragment 7 extends between sites 2 and 3. All three fragments are missing in strain SmA818.
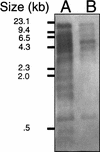
FIG. 3
Southern blot analysis of SmA818. Equal amounts of _Eco_RI-restricted DNA from Rm2011 and SmA818 were electrophoresed, blotted to a nylon membrane, and probed with pRme2011Δ14-6 DNA which was isolated from a preparative Eckhardt gel. Lanes: A, Rm2011; B, SmA818.
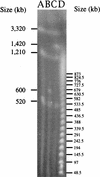
FIG. 4
Pulsed-field gel profiles of _Pac_I-digested S. meliloti strains. Lanes: A, SmA818; B, SmA146; C, Rm2011; D, concatemers, molecular size markers.
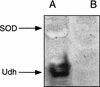
FIG. 5
Unidentified dehydrogenase (Udh) and SOD activities in S. meliloti. Cell extracts of Rm2011 and SmA818 were run on nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels. The gel was stained as previously described (8). Lanes: A, Rm2011; B, SmA818.
Similar articles
- Proteome analysis demonstrates complex replicon and luteolin interactions in pSyma-cured derivatives of Sinorhizobium meliloti strain 2011.
Chen H, Higgins J, Oresnik IJ, Hynes MF, Natera S, Djordjevic MA, Weinman JJ, Rolfe BG. Chen H, et al. Electrophoresis. 2000 Nov;21(17):3833-42. doi: 10.1002/1522-2683(200011)21:17<3833::AID-ELPS3833>3.0.CO;2-I. Electrophoresis. 2000. PMID: 11271501 - Sequence analysis of the 181-kb accessory plasmid pSmeSM11b, isolated from a dominant Sinorhizobium meliloti strain identified during a long-term field release experiment.
Stiens M, Schneiker S, Pühler A, Schlüter A. Stiens M, et al. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 Jun;271(2):297-309. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00731.x. Epub 2007 Apr 27. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17466030 - The tRNAarg gene and engA are essential genes on the 1.7-Mb pSymB megaplasmid of Sinorhizobium meliloti and were translocated together from the chromosome in an ancestral strain.
diCenzo G, Milunovic B, Cheng J, Finan TM. diCenzo G, et al. J Bacteriol. 2013 Jan;195(2):202-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.01758-12. Epub 2012 Nov 2. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23123907 Free PMC article. - High-resolution physical map of the pSymb megaplasmid and comparison of the three replicons of Sinorhizobium meliloti strain 1021.
Barloy-Hubler F, Capela D, Batut J, Galibert F. Barloy-Hubler F, et al. Curr Microbiol. 2000 Aug;41(2):109-13. doi: 10.1007/s002840010103. Curr Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10856376 - High-resolution physical map of the Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 pSyma megaplasmid.
Barloy-Hubler F, Capela D, Barnett MJ, Kalman S, Federspiel NA, Long SR, Galibert F. Barloy-Hubler F, et al. J Bacteriol. 2000 Feb;182(4):1185-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.4.1185-1189.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10648551 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- A high-efficiency scar-free genome-editing toolkit for Acinetobacter baumannii.
de Dios R, Gadar K, McCarthy RR. de Dios R, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022 Nov 28;77(12):3390-3398. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkac328. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022. PMID: 36216579 Free PMC article. - Examination of prokaryotic multipartite genome evolution through experimental genome reduction.
diCenzo GC, MacLean AM, Milunovic B, Golding GB, Finan TM. diCenzo GC, et al. PLoS Genet. 2014 Oct 23;10(10):e1004742. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004742. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25340565 Free PMC article. - The Divided Bacterial Genome: Structure, Function, and Evolution.
diCenzo GC, Finan TM. diCenzo GC, et al. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2017 Aug 9;81(3):e00019-17. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00019-17. Print 2017 Sep. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28794225 Free PMC article. Review. - Scent of a Symbiont: The Personalized Genetic Relationships of Rhizobium-Plant Interaction.
Cangioli L, Vaccaro F, Fini M, Mengoni A, Fagorzi C. Cangioli L, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 20;23(6):3358. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063358. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328782 Free PMC article. Review. - Novel DNA sequences from natural strains of the nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium Sinorhizobium meliloti.
Guo H, Sun S, Finan TM, Xu J. Guo H, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Nov;71(11):7130-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.11.7130-7138.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16269751 Free PMC article.
References
- Banfalvi Z, Kondorosi E, Kondorosi A. Rhizobium meliloti carries two megaplasmids. Plasmid. 1985;13:129–138. - PubMed
- Banfalvi Z, Sakanyan V, Koncz C, Kiss A, Dusha I, Kondorosi A. Location of nitrogen fixation genes on a high molecular weight plasmid of R. meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184:318–325. - PubMed
- Barnett M J, Long S R. Identification and characterization of a gene on Rhizobium meliloti pSyma, syrB, that negatively affects syrM expression. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 1997;10:550–559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources