A new locus for autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia associated with mental retardation and distal motor neuropathy, SPG14, maps to chromosome 3q27-q28 - PubMed (original) (raw)
A new locus for autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia associated with mental retardation and distal motor neuropathy, SPG14, maps to chromosome 3q27-q28
G Vazza et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Aug.
Abstract
Hereditary spastic paraplegias (HSPs), a group of neurodegenerative disorders that cause progressive spasticity of the lower limbs, are characterized by clinical and genetic heterogeneity. To date, three loci for autosomal recessive HSP have been mapped on chromosomes 8p, 16q, and 15q. After exclusion of linkage at these loci, we performed a genomewide search in a consanguineous Italian family with autosomal recessive HSP complicated by mild mental retardation and distal motor neuropathy. Using homozygosity mapping, we obtained positive LOD scores for markers on chromosome region 3q27-q28, with a maximum multipoint LOD score of 3.9 for marker D3S1601. Haplotype analysis allowed us to identify a homozygous region (4.5 cM), flanked by markers D3S1580 and D3S3669, that cosegregates with the disease. These data strongly support the presence, on chromosome 3q27-28, of a new locus for complicated recessive spastic paraplegia, which we have named "SPG14."
Figures
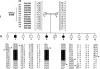
Figure 1
Pedigree of the family with ARHSP. Blackened and unblackened symbols represent affected and unaffected individuals, respectively. Genetic map is according to information from the Genetic Location Database. Haplotype analysis for the 3q27-q28 region showed a homozygous region cosegregating with the disease. Boxes represent the disease-bearing chromosome; blackened portions of the boxes, the regions of homozygosity carried only by affected individuals; arrows, recombination events. Bracketed haplotypes are deduced.
Similar articles
- A novel locus for an autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia (SPG35) maps to 16q21-q23.
Dick KJ, Al-Mjeni R, Baskir W, Koul R, Simpson MA, Patton MA, Raeburn S, Crosby AH. Dick KJ, et al. Neurology. 2008 Jul 22;71(4):248-52. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000319610.29522.8a. Epub 2008 May 7. Neurology. 2008. PMID: 18463364 - Autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia (SPG45) with mental retardation maps to 10q24.3-q25.1.
Dursun U, Koroglu C, Kocasoy Orhan E, Ugur SA, Tolun A. Dursun U, et al. Neurogenetics. 2009 Oct;10(4):325-31. doi: 10.1007/s10048-009-0191-3. Epub 2009 May 5. Neurogenetics. 2009. PMID: 19415352 - Autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia (SPG30) with mild ataxia and sensory neuropathy maps to chromosome 2q37.3.
Klebe S, Azzedine H, Durr A, Bastien P, Bouslam N, Elleuch N, Forlani S, Charon C, Koenig M, Melki J, Brice A, Stevanin G. Klebe S, et al. Brain. 2006 Jun;129(Pt 6):1456-62. doi: 10.1093/brain/awl012. Epub 2006 Jan 24. Brain. 2006. PMID: 16434418 - Hereditary spastic paraplegia: advances in genetic research. Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Working group.
Fink JK, Heiman-Patterson T, Bird T, Cambi F, Dubé MP, Figlewicz DA, Fink JK, Haines JL, Heiman-Patterson T, Hentati A, Pericak-Vance MA, Raskind W, Rouleau GA, Siddique T. Fink JK, et al. Neurology. 1996 Jun;46(6):1507-14. doi: 10.1212/wnl.46.6.1507. Neurology. 1996. PMID: 8649538 Review. - Molecular genetics of familial spastic paraplegia: a multitude of responsible genes.
Kobayashi H, Garcia CA, Alfonso G, Marks HG, Hoffman EP. Kobayashi H, et al. J Neurol Sci. 1996 May;137(2):131-8. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(95)00349-7. J Neurol Sci. 1996. PMID: 8782167 Review.
Cited by
- Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: An Update.
Meyyazhagan A, Orlacchio A. Meyyazhagan A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 1;23(3):1697. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031697. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163618 Free PMC article. Review. - The Silver syndrome variant of hereditary spastic paraplegia maps to chromosome 11q12-q14, with evidence for genetic heterogeneity within this subtype.
Patel H, Hart PE, Warner TT, Houlston RS, Patton MA, Jeffery S, Crosby AH. Patel H, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Jul;69(1):209-15. doi: 10.1086/321267. Epub 2001 May 25. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11389484 Free PMC article. - Insights into Clinical, Genetic, and Pathological Aspects of Hereditary Spastic Paraplegias: A Comprehensive Overview.
Elsayed LEO, Eltazi IZ, Ahmed AE, Stevanin G. Elsayed LEO, et al. Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Nov 26;8:690899. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.690899. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34901147 Free PMC article. Review. - Infantile-onset ascending hereditary spastic paralysis is associated with mutations in the alsin gene.
Eymard-Pierre E, Lesca G, Dollet S, Santorelli FM, di Capua M, Bertini E, Boespflug-Tanguy O. Eymard-Pierre E, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Sep;71(3):518-27. doi: 10.1086/342359. Epub 2002 Jul 26. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 12145748 Free PMC article. - Narrowing of the critical region in autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia linked to the SPG5 locus.
Muglia M, Criscuolo C, Magariello A, De Michele G, Scarano V, D'Adamo P, Ambrosio G, Gabriele AL, Patitucci A, Mazzei R, Conforti FL, Sprovieri T, Morgante L, Epifanio A, La Spina P, Valentino P, Gasparini P, Filla A, Quattrone A. Muglia M, et al. Neurogenetics. 2004 Feb;5(1):49-54. doi: 10.1007/s10048-003-0167-7. Epub 2003 Dec 5. Neurogenetics. 2004. PMID: 14658060
References
Electronic-Database Information
- Genetic Location Database, The, http://cedar.genetics.soton.ac.uk/public_html/ldb.html (for location of SPG14 markers)
- Genome Database, The, http://www.gdb.org/ (for sequences of unlabeled primers)
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for SPG1 [MIM <312900>], SPG2 [MIM312920], SPG3 [MIM <182600>], SPG4 [MIM <182601>], SPG5 [MIM270800], SPG6 [MIM <600363>], SPG7 [MIM <602783>], SPG8 [MIM <603563>], SPG9 [MIM <601162>], SPG10 [MIM <604187>], SPG11 [MIM <604360>], and SPG12 [MIM <604805>])
- Unified Database, Bioinformatics Unit and Genome Center, Weizmann Institute of Science, http://bioinformatics.weizmann.ac.il/udb (for mapping data on candidate genes)
References
- Casari G, De Fusco M, Ciarmatori S, Zeviani M, Mora M, Fernandez P, De Michele G, et al (1998) Spastic paraplegia and OXPHOS impairment caused by mutations in paraplegin, a nuclear-encoded mitochodrial metalloprotease. Cell 93:973–983 - PubMed
- Coutinho P, Barros J, Zemmouri R, Guimaraes J, Alves C, Chorao R, Lourenco E, et al (1999) Clinical heterogeneity of autosomal recessive spastic paraplegias: analysis of 106 patients in 46 families. Arch Neurol 56:943–949 - PubMed
- Dib C, Fauré S, Fizames C, Samson D, Drouot N, Vignal A, Millasseau P, et al (1996) A comprehensive genetic map of the human genome based on 5,264 microsatellites. Nature 380:152–154 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases