Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of degradation-sensitive DNAs from Clostridium difficile PCR ribotype 1 strains - PubMed (original) (raw)
Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of degradation-sensitive DNAs from Clostridium difficile PCR ribotype 1 strains
J E Corkill et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Jul.
No abstract available
Figures
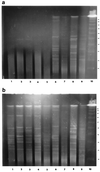
FIG. 1
PFGE patterns obtained with _Sma_I-digested DNA from C. difficile isolates of known PCR ribotype. Electrophoresis was performed in the absence (a) and in the presence (b) of 50 μM thiourea. Lanes 1 to 5, five degradation-sensitive PCR ribotype 1 isolates (from the United States and Newcastle, Wrexham, Tooting, and Truro, United Kingdom, respectively); lane 6, ribotype 2 isolate (Wrexham); lane 7, ribotype 10 isolate (Manchester, United Kingdom); lane 8, ribotype 15 isolate (Carshalton, United Kingdom); lane 9, ribotype 23 isolate (Jersey, United Kingdom); lane 10, λ DNA standard (48.5-kbp concatemer).
Similar articles
- Molecular epidemiology of endemic Clostridium difficile infection and the significance of subtypes of the United Kingdom epidemic strain (PCR ribotype 1).
Fawley WN, Parnell P, Verity P, Freeman J, Wilcox MH. Fawley WN, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Jun;43(6):2685-96. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.6.2685-2696.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15956384 Free PMC article. - Molecular analysis of Clostridium difficile at a university teaching hospital in Japan: a shift in the predominant type over a five-year period.
Sawabe E, Kato H, Osawa K, Chida T, Tojo N, Arakawa Y, Okamura N. Sawabe E, et al. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007 Oct;26(10):695-703. doi: 10.1007/s10096-007-0355-8. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17647032 - Typing of Clostridium difficile.
Brazier JS. Brazier JS. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2001 Aug;7(8):428-31. doi: 10.1046/j.1198-743x.2001.00288.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2001. PMID: 11591206 Review. - How to detect Clostridium difficile variant strains in a routine laboratory.
Rupnik M. Rupnik M. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2001 Aug;7(8):417-20. doi: 10.1046/j.1198-743x.2001.00290.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2001. PMID: 11591204 Review.
Cited by
- Verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in wild birds and rodents in close proximity to farms.
Nielsen EM, Skov MN, Madsen JJ, Lodal J, Jespersen JB, Baggesen DL. Nielsen EM, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Nov;70(11):6944-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.11.6944-6947.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15528570 Free PMC article. - Molecular epidemiology of endemic Clostridium difficile infection and the significance of subtypes of the United Kingdom epidemic strain (PCR ribotype 1).
Fawley WN, Parnell P, Verity P, Freeman J, Wilcox MH. Fawley WN, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Jun;43(6):2685-96. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.6.2685-2696.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15956384 Free PMC article. - Phosphorothioate DNA as an antioxidant in bacteria.
Xie X, Liang J, Pu T, Xu F, Yao F, Yang Y, Zhao YL, You D, Zhou X, Deng Z, Wang Z. Xie X, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Oct;40(18):9115-24. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks650. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22772986 Free PMC article. - Technical improvement to prevent DNA degradation of enteric pathogens in pulsed-field gel electrophoresis.
Koort JM, Lukinmaa S, Rantala M, Unkila E, Siitonen A. Koort JM, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Sep;40(9):3497-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.9.3497-3498.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12202602 Free PMC article. - Molecular subtyping of Vibrio cholerae O1 and O139 by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis in Hong Kong: correlation with epidemiological events from 1994 to 2002.
Kam KM, Luey CK, Tsang YM, Law CP, Chu MY, Cheung TL, Chiu AW. Kam KM, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Oct;41(10):4502-11. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.10.4502-4511.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14532174 Free PMC article.
References
- Brazier J S. The epidemiology and typing of Clostridium difficile. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1998;41(Suppl.):47–57. - PubMed
- George W L, Sutter V L, Finegold S M. Antimicrobial agent-induced diarrhoea—a bacterial disease. J Infect Dis. 1977;136:822–828. - PubMed
- Hyett A P, Brazier J S, O'Neill G L. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis as a method for typing Clostridium difficile in the routine laboratory. Rev Med Microbiol. 1997;8(Suppl. 1):S63–S64.
- Kato H, Kato N, Watanabe K, Ueno K, Sakata Y, Fujita K. Relapses or reinfections: analysis of a case of Clostridium difficile-associated colitis by two typing systems. Curr Microbiol. 1996;33:220–223. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical