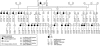Linkage of tuberculosis to chromosome 2q35 loci, including NRAMP1, in a large aboriginal Canadian family - PubMed (original) (raw)
Linkage of tuberculosis to chromosome 2q35 loci, including NRAMP1, in a large aboriginal Canadian family
C M Greenwood et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Aug.
Abstract
An epidemic of tuberculosis occurred in a community of Aboriginal Canadians during the period 1987-89. Genetic and epidemiologic data were collected on an extended family from this community, and the evidence for linkage to NRAMP1, a candidate gene for susceptibility to mycobacterial diseases, was assessed. Individuals were grouped into risk (liability) classes based on vaccination, age, previous disease, and tuberculin skin-test results. Under the assumption of a dominant mode of inheritance and a relative risk of 10, which is associated with the high-risk genotypes, a maximum LOD score of 3.81 was observed for linkage between a tuberculosis-susceptibility locus and D2S424, which is located just distal to NRAMP1, in chromosome region 2q35. Significant linkage was also observed between a tuberculosis-susceptibility locus and a haplotype of 10 NRAMP1 intragenic variants. No linkage to the major histocompatibility-complex region on chromosome 6p was observed, despite distortion of transmission from one member of the oldest couple to their affected offspring. The ability to assign individuals to risk classes was crucial to the success of this study.
Figures
Figure 1
Partial pedigree of the extended kindred. The five culture-negative cases (individuals 10, 13, 15, 21, and 22) had radiological abnormalities consistent with active tuberculosis; individuals 10 and 15 also had symptoms associated with tuberculosis. Not included in the pedigree are nine individuals from whom DNA was not available and among whom there were two infants classified as culture-negative cases (both had radiological abnormalities), three children classified as not having disease (all PPD negative; two were culture negative, and no culture was taken from the third), and four people with unknown disease phenotype. The order of the information below each circle is as follows: mycobacterial test result (c+ = M. tuberculosis culture positive; c− = M. tuberculosis culture negative; nd = no data), liability class, NRAMP1 haplotype, D2S424 alleles, and TNF haplotype. D2S424 alleles 1, 2, and 3 are 185, 181, and 157 bp, respectively. BCG indicates that the individual was vaccinated. For classification of disease phenotype and definition of liability classes, see the Subjects and Methods section; for NRAMP1 and_TNF_ haplotypes, see tables 2 and 3, respectively.
Figure 2
YAC contig of the _NRAMP1_-gene region. The names of loci and chromosome 2–specific IRS probes are indicated at the top of the figure. YAC clones are represented as bars; the YAC address is given to the left of the bar. The blackened area of each bar indicates that the YAC was unambiguously identified by the probe listed directly above the YAC; the unblackened area of each bar indicates that the probe did not hybridize with the YAC; and the gray-shaded area of each bar indicates that the YAC was not tested for the presence of the probe. D2S1471 was not included in STS contig mapping; the order NRAMP1_–_VIL_–_D2S1471 was established by physical mapping in a PAC contig (Abel et al. 1998).
Figure 3
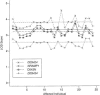
Sensitivity of LOD-score results to the diagnosis of an affected individual, for the NRAMP1 haplotype, two flanking microsatellite markers, and one intragenic polymorphism, D543N. LOD scores in all cases were maximized over the recombination fraction. Horizontal lines show the LOD scores for the original data. The order along the horizontal axis corresponds to the identification numbers of affected individuals in figure 1, with the exception of individuals 23 and 24, who were two culture-negative cases not shown in figure 1.
Comment in
- Genetic predisposition to clinical tuberculosis: bridging the gap between simple and complex inheritance.
Abel L, Casanova JL. Abel L, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Aug;67(2):274-7. doi: 10.1086/303033. Epub 2000 Jul 5. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10882573 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Immunogenetics of leishmanial and mycobacterial infections: the Belem Family Study.
Blackwell JM, Black GF, Peacock CS, Miller EN, Sibthorpe D, Gnananandha D, Shaw JJ, Silveira F, Lins-Lainson Z, Ramos F, Collins A, Shaw MA. Blackwell JM, et al. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1997 Sep 29;352(1359):1331-45. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1997.0118. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1997. PMID: 9355125 Free PMC article. Review. - Genetic predisposition to clinical tuberculosis: bridging the gap between simple and complex inheritance.
Abel L, Casanova JL. Abel L, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Aug;67(2):274-7. doi: 10.1086/303033. Epub 2000 Jul 5. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10882573 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Evidence that genetic susceptibility to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a Brazilian population is under oligogenic control: linkage study of the candidate genes NRAMP1 and TNFA.
Shaw MA, Collins A, Peacock CS, Miller EN, Black GF, Sibthorpe D, Lins-Lainson Z, Shaw JJ, Ramos F, Silveira F, Blackwell JM. Shaw MA, et al. Tuber Lung Dis. 1997;78(1):35-45. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8479(97)90014-9. Tuber Lung Dis. 1997. PMID: 9666961 - Linkage of rheumatoid arthritis to the candidate gene NRAMP1 on 2q35.
Shaw MA, Clayton D, Atkinson SE, Williams H, Miller N, Sibthorpe D, Blackwell JM. Shaw MA, et al. J Med Genet. 1996 Aug;33(8):672-7. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.8.672. J Med Genet. 1996. PMID: 8863160 Free PMC article. - The Nramp1 protein and its role in resistance to infection and macrophage function.
Canonne-Hergaux F, Gruenheid S, Govoni G, Gros P. Canonne-Hergaux F, et al. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1999 Jul-Aug;111(4):283-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1381.1999.99236.x. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1999. PMID: 10417735 Review.
Cited by
- Heritability analysis of cytokines as intermediate phenotypes of tuberculosis.
Stein CM, Guwatudde D, Nakakeeto M, Peters P, Elston RC, Tiwari HK, Mugerwa R, Whalen CC. Stein CM, et al. J Infect Dis. 2003 Jun 1;187(11):1679-85. doi: 10.1086/375249. Epub 2003 May 9. J Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12751024 Free PMC article. - WISARD: workbench for integrated superfast association studies for related datasets.
Lee S, Choi S, Qiao D, Cho M, Silverman EK, Park T, Won S. Lee S, et al. BMC Med Genomics. 2018 Apr 20;11(Suppl 2):39. doi: 10.1186/s12920-018-0345-y. BMC Med Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29697360 Free PMC article. - Mycobacterium tuberculosis, macrophages, and the innate immune response: does common variation matter?
Berrington WR, Hawn TR. Berrington WR, et al. Immunol Rev. 2007 Oct;219:167-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00545.x. Immunol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17850489 Free PMC article. Review. - Host genetics and the dissection of mycobacterial immunity.
Cooke GS, Siddiqui MR. Cooke GS, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004 Jan;135(1):9-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02353.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14678258 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - The role of host genetic factors in respiratory tract infectious diseases: systematic review, meta-analyses and field synopsis.
Patarčić I, Gelemanović A, Kirin M, Kolčić I, Theodoratou E, Baillie KJ, de Jong MD, Rudan I, Campbell H, Polašek O. Patarčić I, et al. Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 3;5:16119. doi: 10.1038/srep16119. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26524966 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Electronic-Database Information
- GenBank Overview, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/GenbankOverview.html (for nucleotide positions [accession numbers D63507, L32185, U57604, and Y14768])
- Genetic Location Database, The, http://cedar.genetics.soton.ac.uk/public_html/ldb.html (for genetic distances and locations)
- Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research/MIT Center for Genome Research, http://www-genome.wi.mit.edu (for sequence and conditions of amplification of WI14333)
References
- Abel L, Sánchez FO, Oberti J, Thuc NV, Hoa LV, Lap VD, Skamene E, et al (1998) Susceptibility to leprosy is linked to the human NRAMP1 gene. J Infect Dis 177:133–145 - PubMed
- Bellamy R, Ruwende C, Corrah T, McAdam KPWJ, Whittle HC, Hill AVS (1998) Variations in the NRAMP1 gene and susceptibility to tuberculosis in West Africans. N Engl J Med 338:640–644 - PubMed
- Boothroyd LJ (1994) Genetic susceptibility to tuberculosis. MSc thesis, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McGill University, Montreal
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases