Interpreting the universal phylogenetic tree - PubMed (original) (raw)
Interpreting the universal phylogenetic tree
C R Woese. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000.
Abstract
The universal phylogenetic tree not only spans all extant life, but its root and earliest branchings represent stages in the evolutionary process before modern cell types had come into being. The evolution of the cell is an interplay between vertically derived and horizontally acquired variation. Primitive cellular entities were necessarily simpler and more modular in design than are modern cells. Consequently, horizontal gene transfer early on was pervasive, dominating the evolutionary dynamic. The root of the universal phylogenetic tree represents the first stage in cellular evolution when the evolving cell became sufficiently integrated and stable to the erosive effects of horizontal gene transfer that true organismal lineages could exist.
Figures
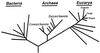
Figure 1
The basal universal phylogenetic tree inferred from comparative analyses of rRNA sequences (4, 5). The root has been determined by using the paralogous gene couple EF-Tu/EFG (6).
Similar articles
- The universal ancestor.
Woese C. Woese C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jun 9;95(12):6854-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.12.6854. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9618502 Free PMC article. - Ribosomal RNA: a key to phylogeny.
Olsen GJ, Woese CR. Olsen GJ, et al. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):113-23. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422957. FASEB J. 1993. PMID: 8422957 Review. - Evolution of genes and organisms: the tree/web of life in light of horizontal gene transfer.
Olendzenski L, Gogarten JP. Olendzenski L, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Oct;1178:137-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04998.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19845634 - The tree of life viewed through the contents of genomes.
House CH. House CH. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;532:141-61. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-853-9_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19271183 Review. - Ancient gene duplications and the root(s) of the tree of life.
Zhaxybayeva O, Lapierre P, Gogarten JP. Zhaxybayeva O, et al. Protoplasma. 2005 Dec;227(1):53-64. doi: 10.1007/s00709-005-0135-1. Epub 2005 Dec 30. Protoplasma. 2005. PMID: 16389494
Cited by
- The N-terminal intrinsically disordered region of Ncb5or docks with the cytochrome b5 core to form a helical motif that is of ancient origin.
Benson DR, Deng B, Kashipathy MM, Lovell S, Battaile KP, Cooper A, Gao P, Fenton AW, Zhu H. Benson DR, et al. Proteins. 2024 Apr;92(4):554-566. doi: 10.1002/prot.26647. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Proteins. 2024. PMID: 38041394 Free PMC article. - Stochastic models for horizontal gene transfer: taking a random walk through tree space.
Suchard MA. Suchard MA. Genetics. 2005 May;170(1):419-31. doi: 10.1534/genetics.103.025692. Epub 2005 Mar 21. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15781714 Free PMC article. - Archaic chaos: intrinsically disordered proteins in Archaea.
Xue B, Williams RW, Oldfield CJ, Dunker AK, Uversky VN. Xue B, et al. BMC Syst Biol. 2010 May 28;4 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S1. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-4-S1-S1. BMC Syst Biol. 2010. PMID: 20522251 Free PMC article. - Are protein domains modules of lateral genetic transfer?
Chan CX, Darling AE, Beiko RG, Ragan MA. Chan CX, et al. PLoS One. 2009;4(2):e4524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004524. Epub 2009 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19229333 Free PMC article. - Ribosomal DNA sequence heterogeneity reflects intraspecies phylogenies and predicts genome structure in two contrasting yeast species.
West C, James SA, Davey RP, Dicks J, Roberts IN. West C, et al. Syst Biol. 2014 Jul;63(4):543-54. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syu019. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 24682414 Free PMC article.
References
- Darwin, C. (1857) (1: p. 456) in a letter to T. H. Huxley (Corresp. 6: p.456) (1887) in The Life and Letters of Charles Darwin, Including an Autobiographical Chapter, ed. Darwin, F. (John Murray, London), Vol. 2, p. 456.
- Zuckerkandl E, Pauling L. J Theor Biol. 1965;8:357–366. - PubMed
- Fox G E, Pechman K R, Woese C R. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1977;27:44–57.
- Fox G E, Stackebrandt E, Hespell R B, Gibson J, Maniloff J, Dyer T A, Wolfe R S, Balch W E, Tanner R S, Magrum L J, et al. Science. 1980;209:457–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources