Functional analysis of putative restriction-modification system genes in the Helicobacter pylori J99 genome - PubMed (original) (raw)
Functional analysis of putative restriction-modification system genes in the Helicobacter pylori J99 genome
H Kong et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000.
Abstract
Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative bacterium, which colonizes the gastric mucosa of humans and is implicated in a wide range of gastroduodenal diseases. The genomic sequences of two H.pylori strains, 26695 and J99, have been published recently. About two dozen potential restriction-modification (R-M) systems have been annotated in both genomes, which is far above the average number of R-M systems in other sequenced genomes. Here we describe a functional analysis of the 16 putative Type II R-M systems in the H. pylori J99 genome. To express potentially toxic endonuclease genes, a unique vector was constructed, which features repression and antisense transcription as dual control elements. To determine the methylation activities of putative DNA methyltransferases, we developed polyclonal antibodies able to detect DNA containing N6-methyladenine or N4-methylcytosine. We found that <30% of the potential Type II R-M systems in H.pylori J99 strain were fully functional, displaying both endonuclease and methyltransferase activities. Helicobacter pylori may maintain a variety of functional R-M systems, which are believed to be a primitive bacterial 'immune' system, by alternatively turning on/off a subset of numerous R-M systems.
Figures
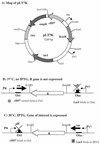
Figure 1
Map of plasmid pLT7K. Ori, origin of replication (colE1 derived from pBR322); ampR, β-lactamase gene (ampicillin resistance gene); KanR, kanamycin resistance gene which is flanked by multiple restriction sites suitable for cloning; cI857, the gene for a mutant form of the λ repressor; _lac_I, the gene for the lactose repressor protein, LacI; PR, bacteriophage λ major rightward promoter; PT7, bacteriophage T7 promoter; OcI, λ operator bound by λ CI repressor; Olac, lac operator bound by _Lac_I.
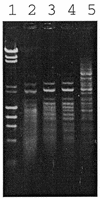
Figure 2
Agarose gel (1%) showing the electrophoresis patterns of bacteriophage λ DNA digested by different amounts of restriction endonuclease, _Hpy_99II, encoded by JHP46. Lane 1, bacteriophage λ DNA + _Hin_dIII, φX174 + _Hae_III, size standard; lane 2, λ DNA digested with 9 µl _Hpy_99I; lane 3, λ DNA digested with 3 µl _Hpy_99I; lane 4, λ DNA digested with 1 µl _Hpy_99I; lane 5, λ DNA digested with 0.3 µl _Hpy_99I.
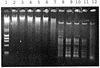
Figure 3
Agarose gel (1%) showing the electrophoresis patterns of λ DNA digested by restriction endonuclease _Hpy_99III, encoded by JHP1049, from consecutive fractions of a heparin column. Lane 1, λ DNA + _Hin_dIII, φX174 + _Hae_III, size standard; lanes 2–12, λ DNA digested with 5 µl of _Hpy_99III eluted from a heparin column.
Figure 4
Dot blot assay to measure methylase activities using rabbit primary antibodies that react specifically with DNA containing m6A or m4C modifications. The dot blot assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods. The ORF from which each DNA sample was derived is marked above each set of dots. (A) Methylase dot blot assay using m6A antibody with dilution of 1:750 000. (B) Methylase dot blot assay using m4C antibody with dilutions of 1:150 000. Three dilutions of DNA samples were spotted: 0.45, 0.15 and 0.05 µg of DNA (top to bottom on each panel).
Similar articles
- Genomic methylation: a tool for typing Helicobacter pylori isolates.
Vale FF, Vítor JM. Vale FF, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Jul;73(13):4243-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00199-07. Epub 2007 May 4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17483255 Free PMC article. - Comparative genomics of the restriction-modification systems in Helicobacter pylori.
Lin LF, Posfai J, Roberts RJ, Kong H. Lin LF, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb 27;98(5):2740-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.051612298. Epub 2001 Feb 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11226310 Free PMC article. - The complex methylome of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori.
Krebes J, Morgan RD, Bunk B, Spröer C, Luong K, Parusel R, Anton BP, König C, Josenhans C, Overmann J, Roberts RJ, Korlach J, Suerbaum S. Krebes J, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Feb;42(4):2415-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1201. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24302578 Free PMC article. - Restriction-modification systems may be associated with Helicobacter pylori virulence.
Ando T, Ishiguro K, Watanabe O, Miyake N, Kato T, Hibi S, Mimura S, Nakamura M, Miyahara R, Ohmiya N, Niwa Y, Goto H. Ando T, et al. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 May;25 Suppl 1:S95-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06211.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20586875 Review. - Contributions of genome sequencing to understanding the biology of Helicobacter pylori.
Ge Z, Taylor DE. Ge Z, et al. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1999;53:353-87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.53.1.353. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10547695 Review.
Cited by
- Modeling kinetic rate variation in third generation DNA sequencing data to detect putative modifications to DNA bases.
Schadt EE, Banerjee O, Fang G, Feng Z, Wong WH, Zhang X, Kislyuk A, Clark TA, Luong K, Keren-Paz A, Chess A, Kumar V, Chen-Plotkin A, Sondheimer N, Korlach J, Kasarskis A. Schadt EE, et al. Genome Res. 2013 Jan;23(1):129-41. doi: 10.1101/gr.136739.111. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23093720 Free PMC article. - Bacterial N4-methylcytosine as an epigenetic mark in eukaryotic DNA.
Rodriguez F, Yushenova IA, DiCorpo D, Arkhipova IR. Rodriguez F, et al. Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 28;13(1):1072. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28471-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35228526 Free PMC article. - Plasmid pEC156, a Naturally Occurring Escherichia coli Genetic Element That Carries Genes of the EcoVIII Restriction-Modification System, Is Mobilizable among Enterobacteria.
Werbowy O, Kaczorowski T. Werbowy O, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Feb 5;11(2):e0148355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148355. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26848973 Free PMC article. - Association between Helicobacter pylori cagA-related genes and clinical outcomes in Colombia and Japan.
Watada M, Shiota S, Matsunari O, Suzuki R, Murakami K, Fujioka T, Yamaoka Y. Watada M, et al. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011 Dec 22;11:141. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-11-141. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 22189161 Free PMC article. - One recognition sequence, seven restriction enzymes, five reaction mechanisms.
Gowers DM, Bellamy SR, Halford SE. Gowers DM, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jun 29;32(11):3469-79. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh685. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15226412 Free PMC article.
References
- Wilson G.G. and Murray,N.E. (1991) Restriction and modification systems. Annu. Rev. Genet., 25, 585–627. - PubMed
- Smith H.O. and Wilcox,K.W. (1970) A restriction enzyme from Haemophilus influenzae. I. Purification and general properties. J. Mol. Biol., 51, 379–391. - PubMed
- Roberts R.J., Breitmeyer,J.B., Tabachnik,N.F. and Myers,P.A. (1975) A second specific endonuclease from Haemophilus aegyptius. J. Mol. Biol., 91, 121–123. - PubMed
- Schildkraut I.S. (1984) Screening for and characterizing restriction endonucleases. In Setlow,J.K. and Hollaender,A. (eds), Genetic Engineering, Principles and Methods, Vol. 6. Plenum Press, New York, NY, pp. 117–140.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases