Inhibition of sustained hypoxic vasoconstriction by Y-27632 in isolated intrapulmonary arteries and perfused lung of the rat - PubMed (original) (raw)
Inhibition of sustained hypoxic vasoconstriction by Y-27632 in isolated intrapulmonary arteries and perfused lung of the rat
T P Robertson et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Sep.
Abstract
We have examined the effects of Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of Rho-activated kinases (ROCK I and ROCK II) upon sustained hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction (HPV) in both rat isolated small intrapulmonary arteries (IPA) and perfused rat lungs in situ. Y-27632 (100 nM - 3 microM) was found to cause a concentration-dependent inhibition of acute sustained HPV in rat IPA. Application of Y-27632 (10-600 nM) in perfused rat lungs caused no change in basal perfusion pressure, but was found to inhibit HPV in a concentration-dependent manner, resulting in complete ablation of the pressor response to hypoxia at a concentration of 600 nM. Furthermore, addition of Y-27632 at any point during hypoxia caused a reversal of HPV in perfused rat lungs. These results suggest that activation of Rho-associated kinase may be a pivotal step in the generation of sustained HPV.
Figures
Figure 1
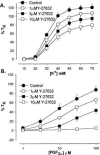
Effect of Y-27632 (1, 3 and 10 μ
M
) pre-incubation upon KPSS (A) and PGF2α (B) induced vasoconstriction in isolated rat IPA. Each point is the mean of 4–6 experiments.
Figure 2
Effect of Y-27632 upon HPV in rat isolated IPA. Each point is the mean of 7–25 experiments.
Figure 3
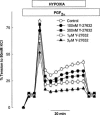
Effect of Y-27632 upon HPV in perfused rat lung in situ. (A) Two hypoxic challenges, 1 h apart. (B) Effect of pre-incubation with 60 n
M
Y-27632. (C) Effect of 600 n
M
Y-27632. (D) Effect of addition of Y-27632 (60 and 600 n
M
) after the establishment of the pressor response to hypoxia. Data are presented as perfusion pressure in mmHg.
Figure 4
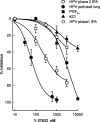
Effect of pre-incubation with Y-27632 upon the maximum responses to hypoxia in the perfused lung in situ, phase 2 and phase 1 of HPV in isolated rat IPA, 100 μ
M
PGF2a and 70 m
M
KPSS in isolated rat IPA. Data are presented as per cent inhibition of the control response, and each point is the mean of 4–9 experiments. Concentration-response curves were fitted using non-linear least-squares regression (SigmaPlot, Jandel Scientific, U.S.A.).
Similar articles
- Inhibition of Rho-kinase attenuates hypoxia-induced angiogenesis in the pulmonary circulation.
Hyvelin JM, Howell K, Nichol A, Costello CM, Preston RJ, McLoughlin P. Hyvelin JM, et al. Circ Res. 2005 Jul 22;97(2):185-91. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000174287.17953.83. Epub 2005 Jun 16. Circ Res. 2005. PMID: 15961717 - Rho/Rho kinase signaling mediates increased basal pulmonary vascular tone in chronically hypoxic rats.
Nagaoka T, Morio Y, Casanova N, Bauer N, Gebb S, McMurtry I, Oka M. Nagaoka T, et al. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004 Oct;287(4):L665-72. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00050.2003. Epub 2003 Sep 5. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004. PMID: 12959926 - Attenuation of acute hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in mice by inhibition of Rho-kinase.
Fagan KA, Oka M, Bauer NR, Gebb SA, Ivy DD, Morris KG, McMurtry IF. Fagan KA, et al. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004 Oct;287(4):L656-64. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00090.2003. Epub 2004 Feb 20. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14977625 - Modulation of the LKB1-AMPK Signalling Pathway Underpins Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction and Pulmonary Hypertension.
Evans AM, Lewis SA, Ogunbayo OA, Moral-Sanz J. Evans AM, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;860:89-99. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-18440-1_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26303471 Review. - Mechanisms of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and their roles in pulmonary hypertension: new findings for an old problem.
Ward JP, McMurtry IF. Ward JP, et al. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;9(3):287-96. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2009.02.006. Epub 2009 Mar 16. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19297247 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction: mechanisms and controversies.
Aaronson PI, Robertson TP, Knock GA, Becker S, Lewis TH, Snetkov V, Ward JP. Aaronson PI, et al. J Physiol. 2006 Jan 1;570(Pt 1):53-8. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.098855. Epub 2005 Oct 27. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16254010 Free PMC article. Review. - The Search for Disease-Modifying Therapies in Pulmonary Hypertension.
Woodcock CC, Chan SY. Woodcock CC, et al. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Jul;24(4):334-354. doi: 10.1177/1074248419829172. Epub 2019 Feb 17. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30773044 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of src-family kinases in hypoxic vasoconstriction of rat pulmonary artery.
Knock GA, Snetkov VA, Shaifta Y, Drndarski S, Ward JP, Aaronson PI. Knock GA, et al. Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Dec 1;80(3):453-62. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn209. Epub 2008 Aug 5. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18682436 Free PMC article. - Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and the soluble epoxide hydrolase are determinants of pulmonary artery pressure and the acute hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstrictor response.
Keserü B, Barbosa-Sicard E, Popp R, Fisslthaler B, Dietrich A, Gudermann T, Hammock BD, Falck JR, Weissmann N, Busse R, Fleming I. Keserü B, et al. FASEB J. 2008 Dec;22(12):4306-15. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-112821. Epub 2008 Aug 25. FASEB J. 2008. PMID: 18725458 Free PMC article. - Role of phosphatase and tensin homolog in hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction.
Krauszman A, Mak TW, Szaszi K, Kuebler WM. Krauszman A, et al. Cardiovasc Res. 2017 Jul 1;113(8):869-878. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx076. Cardiovasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28430879 Free PMC article.
References
- CORNFIELD D.N., STEVENS T., MCMURTRY I.F., ABMAN S.H., RODMAN D.M. Acute hypoxia causes membrane depolarization and calcium influx in fetal pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1994;266:L469–L475. - PubMed
- GONG M.C., FUJIHARA H., SOMLYO A.V., SOMLYO A.P. Translocation of RhoA associated with Ca2+-sensitization of smooth muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:10704–10709. - PubMed
- KIMURA K., ITO M., AMANO M., CHIHARA K., FUKATA Y., NAKAFUKU M., YAMAMORI B., FENG J., NAKANO T., OKAWA K., IWAMATSU A., KAIBUCHI K. Regulation of myosin phosphatase by Rho and Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) [see comments] Science. 1996;273:245–248. - PubMed
- LEACH R.M., ROBERTSON T.P., TWORT C.H.C., WARD J.P.T. Hypoxic vasoconstriction in rat pulmonary and mesenteric arteries. Am. J. Physiol. 1994;266:L223–L231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources